Recently, I was reading an article in the NY Post where it was mentioned that an overwhelming 76% of IT decision-makers said their company’s employees are wasting too much time on menial work. Not just less important work, there are various other causes and ways the problem of poor time management manifests in the workplace. For example, poor task prioritization, inaccurate time estimates, consistent distractions, inefficient workflows, incompetent technology and software systems, and a lack of motivation. Thus, multiple factors are driving the problem of time management in the workplace. As it is getting manifested in multiple ways, it becomes challenging to solve it effectively.
Here are a few statistics highlighting the state of time management in the workplace:
- The average worker spends 51% of their workday on tasks of little to no value.
- On average, employees are interrupted about 60 times a day.
- The average employee is productive for just 2 hours and 53 minutes each day.
That’s why I am of the strong opinion that to understand the cause of poor time management, first identify the time wasters in the workplace, and then implement the right time management strategies to resolve the problem of time management.
This article will go beyond simply mentioning the common time management strategies (time blocking, the Eisenhower matrix, and task batching) and explain how to use each strategy, what its benefits are, and who it is ideal for. This helps you solve the challenge of poor time management based on its cause.
What is time management?
Time management is the skill of managing one’s time effectively to accomplish tasks and achieve goals within the defined timeframe or deadline. It essentially includes dividing or allocating one’s available time between specific activities in order to complete them within the deadlines. To effectively divide and manage time, an individual needs to plan, organize, prioritize, and control the way they use their time. This process might include, but not be limited to, activities like planning your day, prioritizing the most important activities, estimating how long tasks will take, and using time management methods and strategies. This results in effective utilization of one’s time across various activities, leading to maximizing productivity and minimizing wasted hours.
Effective time management allows individuals to make the most of their available time and work with the best possible efficiency and productivity with reduced stress and a better work-life balance, whereas poor time management is essentially the inability to use time effectively, which results in time waste, lower productivity, stress, last-minute rushes, and consistent breaking of deadlines.
What are the causes of poor time management?
Poor time management can be the result of one or multiple factors combined. It includes procrastination, lack of planning, poor prioritization, and distractions. These habits can negatively impact both work and personal life, resulting in consequences like stress, missed deadlines, and low productivity.
Here are some of the biggest causes or indicators of poor time management:
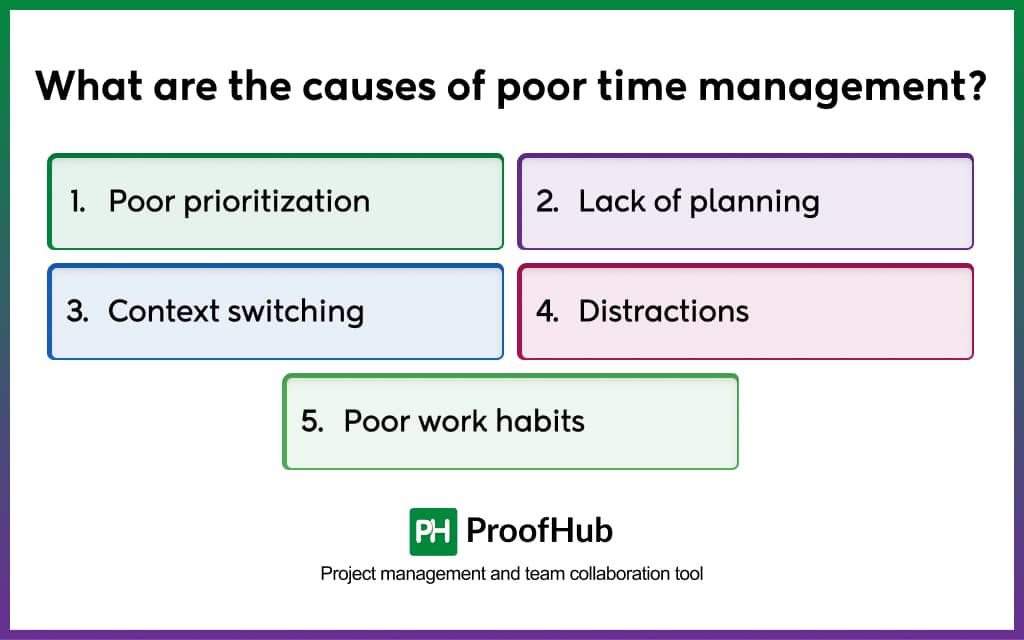
- Poor prioritization: It involves not being able to distinguish between urgent and non-urgent tasks. It happens generally because of a lack of understanding of the workflow or procrastination. Procrastination is a habit where an individual favors less complex tasks than more important ones, despite knowing there will be negative consequences because the task is unpleasant or unenjoyable. This results in an individual wasting time and energy on less important activities.
- Lack of planning: It involves failing to create schedules, accurately guessing how long tasks will take, and organizing work. This leads to inaccurate deadlines and poor project time management.
- Context switching: It is another major cause of poor time management, which is related to poor planning for operational processes and tasks. It does not allow individuals to give focused time to complete a task.
- Distractions: It involves the lack of ability of an individual to focus on a task. Distractions include interruptions from social media, emails, or conversations with other people, which disrupt workflow. Its causes can be anything from ADHD to the work environment and low motivation.
- Poor work habits: Poor work habits, such as multitasking, chronic lateness, and procrastination, also result in poor time management, as these affect the individual’s capability to focus and complete a task on time and work with efficiency and quality.
How to fix poor time management?
Irrespective of the cause of the poor time management and strategies you are using to fix poor time management, there are three simple steps you need to follow. Here is my simple three-step framework to fix poor time management:

1. Track and evaluate your time
The first step to make an improvement in time management is to audit your time. Unless you know how you are spending your time, you cannot make improvements.
To do so, you can use a time tracking software or log the details in a spreadsheet. Initially, make four to five categories (Deep work, Shallow work, Admin, Breaks, Distractions, and Life tasks) and track how much time you spend. This will make it easy to analyse data.
2. Create a plan
The insights from the first step will give you a decent idea of how you spend your time and what you need to fix. For example, if you are spending too much time and energy on low-value tasks, it means you need to prioritize your tasks and plan your day well. On the other hand, if distractions are the cause behind the time wastage, you need to create an environment where you can work with complete focus. Similarly, if low motivation is the driving factor behind the poor time utilization, you need to address the questions and choices to be in the right zone to work.
You need to identify the cause of the poor time management, create a plan to address the identified cause, and choose the right strategy to resolve the challenge.
3. Reflect, review, and iterate
Poor time management habits are not something you can fix overnight. It will take time, effort, and consistent motivation to change the habit. Also, it is not guaranteed that you will find success on the first attempt. Therefore, you need to review, iterate, and refine your strategy to fix the issue you are facing. If required, it is appropriate to seek help from mentors, coaches, or healthcare professionals if this problem is affecting your professional and personal life.
What are time management strategies or techniques?
Time management strategies are techniques, methods, and plans used to manage time effectively. The most common time management strategies or methods used to manage time effectively include the Eisenhower Matrix, Time blocking, Task Batching, Pomodoro Technique, and Eat the Frog.
Each strategy is designed to address one or more causes of poor time management. Below is the detailed explanation of how each time management strategy works and who it is ideal for.
7 Best time management strategies or techniques
There are various time strategies that you can use. Here is the list of the top seven time management strategies and methods commonly used:
1. Eisenhower Matrix
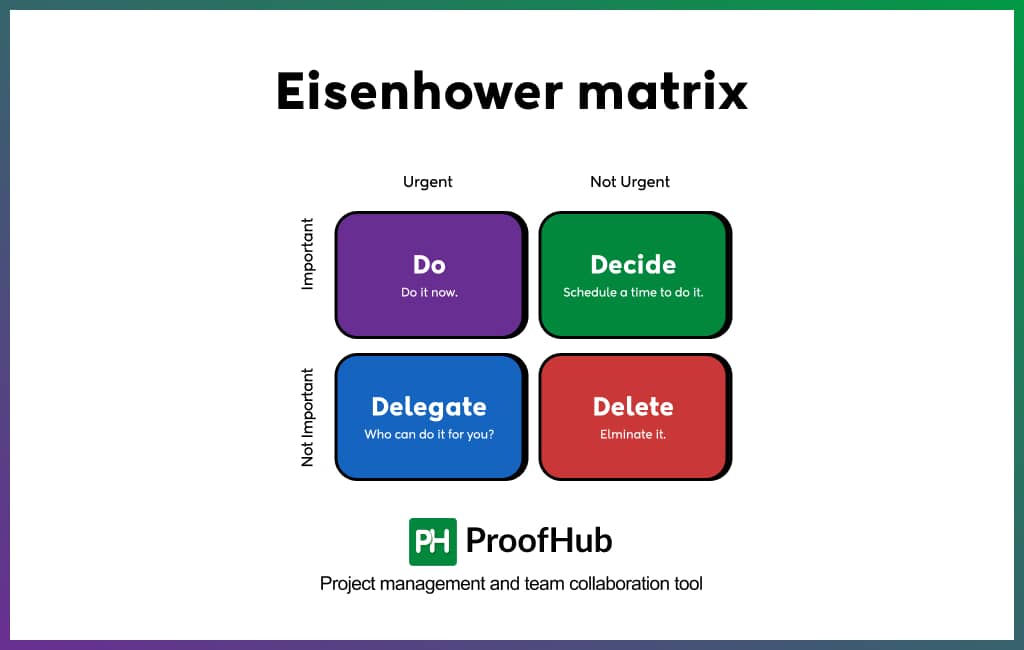
The Eisenhower Matrix is a prioritization technique that involves categorizing all the tasks an individual needs to do into four quadrants based on urgency and importance of the tasks. For each quadrant, it suggests an action for tasks.
- Quadrant 1 (Urgent and Important): Do immediately.
- Quadrant 2 (Important but Not Urgent): Schedule for later.
- Quadrant 3 (Urgent but Not Important): Delegate.
- Quadrant 4 (Not Urgent and Not Important): Eliminate.
It creates a 2×2 grid where the horizontal axis represents urgency (urgent vs. not urgent) and the vertical axis represents importance (important vs. not important).
Who is it for: Those who are unable to use time effectively due to a lack of skills to distinguish between urgent and non-urgent tasks.
How to use it?
- Start by listing all tasks, then plot them on the matrix by assessing urgency and importance.
- Assign actions per quadrant— do, schedule, delegate, or delete.
- Review and update the matrix regularly, such as daily or weekly, as required to adapt to changes.
2. Time blocking
Time blocking is a productivity technique that involves dividing a day into dedicated blocks of time, with each being assigned to a specific set of tasks or activities. It involves grouping similar tasks, assigning them a dedicated block of time, and working on these tasks in the assigned block of time to avoid and save time on context switching. This minimizes distractions, combats procrastination, and promotes deep work by grouping similar tasks and setting boundaries against interruptions.
Who is it for: Those who have to perform multiple activities and are easily distracted by interruptions or frequent requests.
How to use it?
- List tasks with estimated durations. To make accurate estimates, you can use three-point estimation.
- Group similar tasks
- Schedule them into calendar blocks
- Block focused work during high-energy hours
- Add buffer blocks for unplanned tasks, activities, breaks, or overflows
3. Task batching
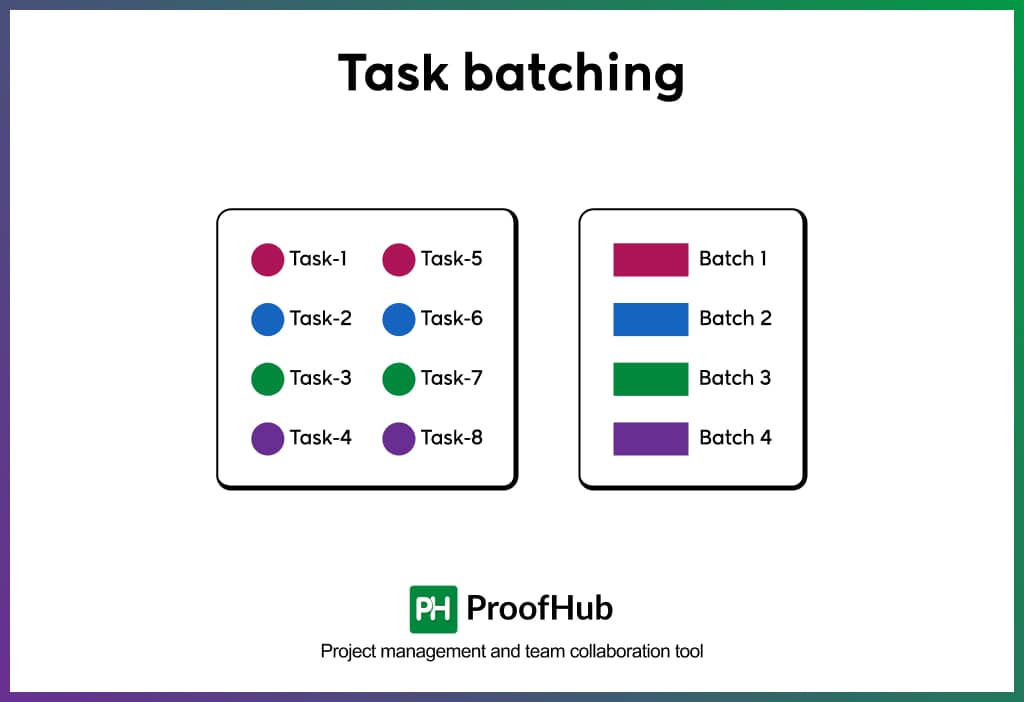
Task batching is a task management technique of grouping similar or related tasks and working on these tasks at once in a dedicated timeframe in order to minimize context switching. It includes categorizing tasks in various categories, such as admin, deep work, and shallow work. By batching similar tasks, it increases work efficiency by reducing context switching.
Who is it for: Those struggling with task organization and planning.
How to use it?
- List all the tasks
- Group similar tasks. For example, answer emails all at once, schedule all meetings in the morning, do content creation in a single block, and do all reviews in a single block
- Assign a timeframe for each set of activities.
4. Pomodoro technique
The Pomodoro technique is a time management method that involves dividing the time into short intervals of work, 25-minute focused intervals called “pomodoros”, and a break, a 5-minute break.
Who is it for: Those who struggle with procrastination, have ADHD, attention challenges, or thrive under structured, short-term bursts.
How to use it?
- Choose a task from your list, set a timer for 25 minutes, and work with full focus until it rings, then mark one pomodoro complete and take a 5-minute break.
- After four pomodoros, take a longer 15-30 minute break to recharge.
- Track pomodoros to refine task estimates and handle interruptions by noting them for later.
5. Pareto principle
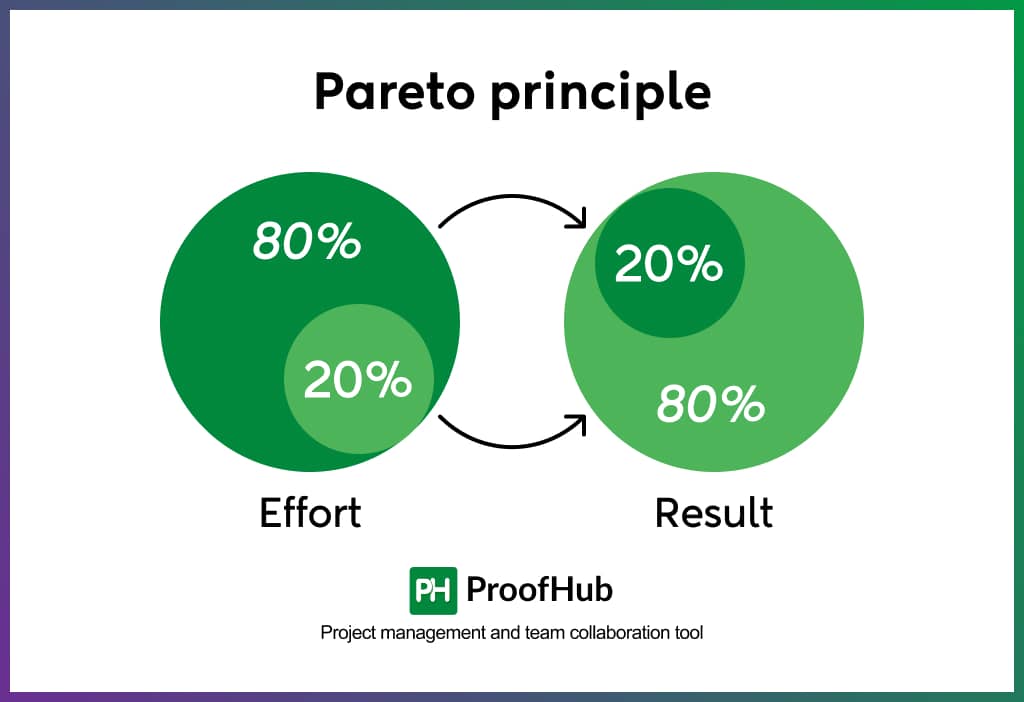
The Pareto Principle states that roughly 80% of outcomes or results come from 20% of causes or efforts. Therefore, it is important to make those 20% of the efforts on the most valuable, high-impact activities at the right moment. It is also known as the 80/20 rule. It helps you make the most of your time and energy and maximize value by focusing on high-impact activities and cutting wasted effort on low-value tasks.
Who is it for: Those struggling with task planning and scheduling
How to use it
- List all the tasks you need to do, ideally daily or weekly, for clarity.
- Analyze your list and identify the most important and high-value vital 20% tasks, which will generate 80% of your desired results
- Start your day with these high-impact tasks, or work on these tasks in prime time when you are your most productive and have the highest energy
- Identify the 80% of tasks that yield minimal results and delegate them if possible.
6. Eat the frog
Eat the Frog is a productivity technique where you identify and complete your most challenging or important task first thing in the day. It is popularized by Brian Tracy and is based on Mark Twain’s famous productivity idea, “If you eat a live frog first thing in the morning, nothing worse will happen to you the rest of the day.”
By tackling the frog early, one can leverage peak morning energy, reduce anxiety from looming big tasks, and create a sense of accomplishment that fuels easier work later. It helps you overcome procrastination and build momentum, but it might not work for everyone.
Who is it for: Those who struggle with poor work habits, like chronic lateness and procrastination.
How to use it
- Review your to-do list and select the frog, the most difficult task
- Start your day by focusing solely on it, and do the rest of the tasks later
- Break it into smaller steps if overwhelming
- Eliminate distractions like notifications during execution.
- Review progress at day’s end and adjust for tomorrow
7. Getting things done
The Getting Things Done (GTD) method is a productivity technique developed by David Allen developed by productivity consultant David Allen and introduced in his 2001 book Getting Things Done: The Art of Stress-Free Productivity. It is a structured approach to task management aimed at enhancing productivity and reducing stress. It includes Capture, Clarify, Organize, Reflect, and Engage.
The core principle of the GTD process is to transfer tasks and ideas from one’s mind into an external system, thereby freeing mental space for focused execution.
Who is it for: Those who are struggling with poor task planning and scheduling.
How to use it?
GTD’s five-step process, Capture, Clarify, Organize, Reflect, and Engage, provides a clear workflow for managing tasks. Implementing GTD can lead to significant benefits.
- Capture: Collect everything on your mind—tasks, emails, ideas—into inboxes like notebooks.
- Clarify: Process each item and convert captured items into concrete next actions. Delete irrelevant ones, delegate if possible, do if under 2 minutes, or define next actions.
- Organize: Organize is about moving clarified items into defined lists: Projects, Next Actions, Calendar, Waiting For, Someday/Maybe.
- Reflect: Review lists daily/weekly to stay current and prioritize.
- Engage: Choose tasks based on context, time, energy, and priority.
How to apply time management strategies and techniques effectively?
There are multiple ways to apply time management strategies and techniques effectively. Here are some of the best practices:
- Begin with a brief time audit to understand how you currently spend your day. Identify the time wasters. Choose the right time management strategy accordingly.
- Manage energy, not just time. Identify your natural energy peaks and align tasks accordingly.
- Adopt one or two strategies at a time, test them for a week, and refine without overcomplicating.
- Consistency matters more than volume. Build daily rituals like morning routines, planning rituals, and shutdown routines to automate your behavior.
- Delegate and automate the tasks that can be delegated and automated. In the end, you only have 24 hours in a day.
Over time, these small operational improvements compound into significantly better control of your day.
Read more: 20 Ultimate time management apps for productivity
What tools support effective time management?
Technology plays a vital role in modern-day time management. Platforms like digital calendars, project management software, and productivity apps support effective time management. Here are some popular tools you can explore:
- Calendar platforms such as Google Calendar or Outlook make time blocking and planning straightforward.
- Project management software like ProofHub, Todoist, Asana, or Trello helps organize priorities and track progress.
- Note-taking apps such as Notion or Obsidian centralize information and support routines and templates.
- Productivity apps include Forest, FocusKeeper, and Freedom, which reduce digital distractions and measure productive intervals.
- Automation and workflow tools like Zapier or IFTTT streamline recurring tasks and reduce manual effort.
Choose one tool per category and keep your system as simple and consistent as possible.
What are the benefits of good time management?
Effective time management increases productivity, reduces stress, and improves decision-making by creating clarity around priorities. It enables more predictable work output, better focus, and less wasted effort from context switching. Individuals experience greater autonomy and confidence because they control their schedules rather than reacting to them. Good time management improves work quality, supports work-life balance, and frees time for long-term initiatives that otherwise get crowded out. Over time, these benefits compound into higher performance, stronger reliability, and sustained well-being.
What are the main challenges in managing time?
Major challenges include unclear priorities, constant interruptions, unrealistic workload expectations, and a lack of structure. Digital distractions and multitasking erode focus and make tasks take longer. Many people underestimate how long work requires, leading to overcommitment and time pressure. Poor energy management also plays a role: performing difficult tasks during low-energy periods reduces effectiveness and increases procrastination. Environmental and organizational factors such as meeting overload, unclear communication, and shifting deadlines further disrupt planning. Without a consistent system, even motivated individuals struggle to maintain control of their schedules.
What are the common time management mistakes to avoid?
Frequent mistakes include multitasking, failing to prioritize, neglecting breaks, and underestimating project durations. People often rely on motivation instead of systems, resulting in inconsistent performance. Overloading daily to-do lists creates pressure and reduces follow-through, while leaving tasks unscheduled leads to reactive work. Checking email or messages constantly breaks focus, and skipping weekly reviews prevents learning from recurring inefficiencies. Another common mistake is using too many tools, which increases friction instead of clarity. Avoiding these pitfalls requires simplicity, structure, and deliberate boundaries.
What are the causes of poor time management?
Common causes include poor prioritization, poor task planning, distractions, poor work habits, low motivation, and outdated technology systems. In addition to that, poor estimation skills lead to unrealistic schedules and chronic overcommitment. Some individuals adopt tools without understanding the underlying principles of time management, resulting in fragmented workflows. Emotional factors such as procrastination, perfectionism, and avoidance also contribute. Organizational issues like excessive meetings, unclear expectations, and shifting priorities further compound personal challenges.
How does poor time management affect performance?
Poor time management reduces productivity, increases stress, and creates inconsistent or low-quality output. Tasks take longer due to distractions and context switching, while important work is often delayed or rushed. Deadlines become difficult to meet, damaging reliability and trust. Chronic overload leads to burnout, reduced creativity, and impaired decision-making. When individuals operate reactively instead of proactively, long-term goals receive little attention, limiting growth and advancement. The overall impact is a cycle of inefficiency, pressure, and diminished performance.

