You can not improve what you don’t measure.
That saying rings especially true for employees’ productivity, the driving force behind every project, goal, and business outcome.
To quickly put it into words, imagine you have two team members. One logs 10 hours a day, is always responsive, and attends almost every meeting, while the other wraps up in 6 focused hours, regularly meeting deadlines and bringing new ideas to the table.
Who’s more productive?
You might judge by looking at hours logged or online status and choose the first. But in reality, the second might deliver more value with less burnout risk.
That’s the danger of relying on traditional productivity metrics like hours worked, email sent, or online status. These surface-level indicators can be misleading and often fail to capture the whole picture. Being ‘busy’ doesn’t always mean being productive. That’s misleading.
That’s why more and more managers are shifting towards holistic, outcome-based approaches. These methods emphasise the quality and impact of work, not just the effort behind it.
So, how do you do it?
In this article, I will guide you through seven proven ways to measure employee productivity and related metrics that genuinely make a difference.
How can you measure employee productivity?
Measuring employee productivity begins with identifying the right indicators that reflect the output, the effort, and the time used to achieve it. Here are seven key ways to measure employees’ productivity accurately and clearly. These work on both in-office and work-from-home team members.
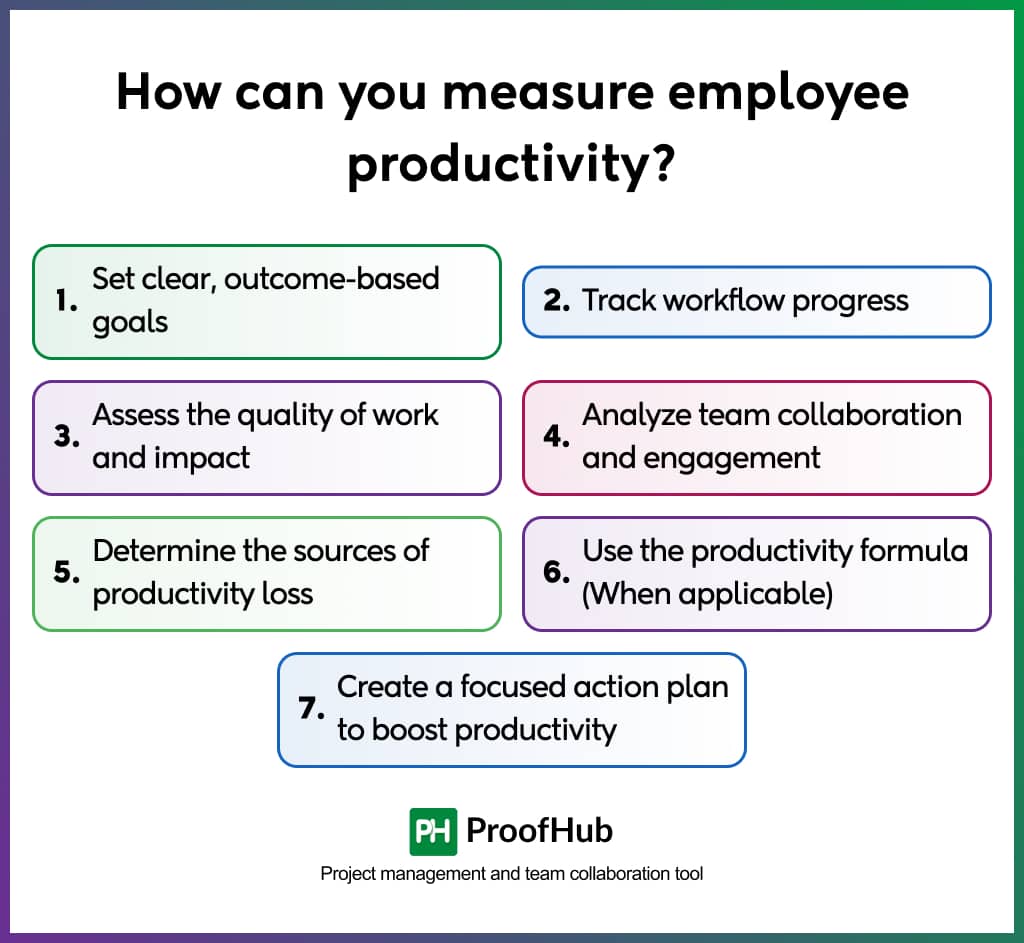
1. Set clear, outcome-based goals
Rather than focusing on how many hours an employee works or how many emails they send, define what success looks like for each role. Use Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound SMART goals to create goals that are specific, measurable, and tied to results.
For example, instead of asking a marketing team member to “work on Quora,” a more productive, measurable goal might be:
- “Grow Quora views by 25% this week” or
- “Publish 8 high-quality posts that generate over 500 upvotes each.”
This kind of goal makes performance easy to evaluate. It focuses attention on outcomes that matter and avoids the trap of rewarding busyness over real impact.
2. Track workflow progress
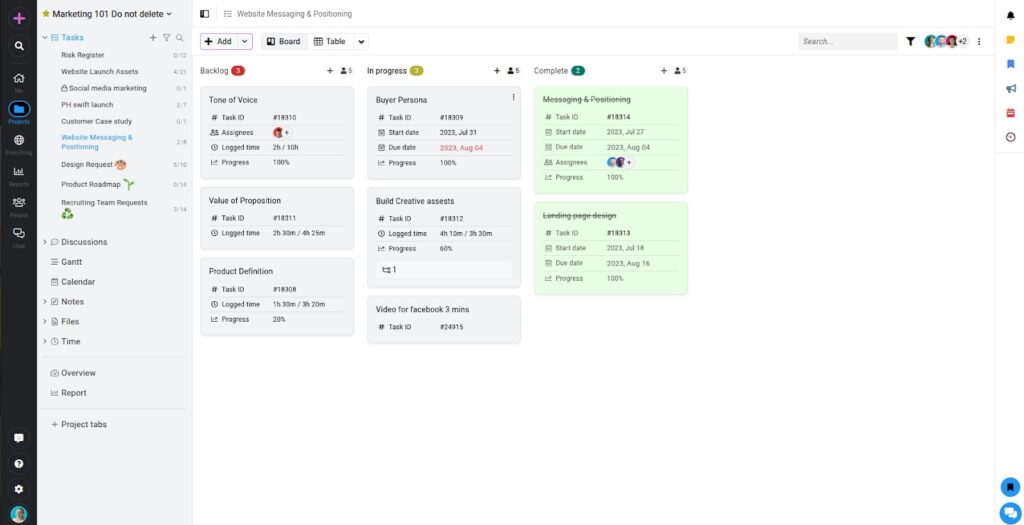
To measure productivity effectively, observe how tasks move through each workflow stage. When tasks frequently get stuck, miss deadlines, or require repeated revisions, it signals deeper productivity challenges.
For example, teams using ProofHub’s Board View can track progress across stages like Backlog, In Progress, and Completed. This real-time visibility helps managers identify bottlenecks, spot those needing support, and ensure work progresses smoothly.
3. Assess the quality of work and impact
True productivity includes quality and impact. To measure this, don’t count outputs. Evaluate how well the task is performed by asking questions like:
- Are deliverables meeting the required standards?
- Are they driving the desired results?
- Are there fewer revisions needed over time?
For example, delivering five blog posts monthly sounds productive in a content marketing role. But if the blogs don’t rank or engage readers, that output is not truly impactful. On the other hand, a team member who writes two blogs but consistently drives traffic and leads is contributing high-impact work.
4. Analyze team collaboration and engagement
Monitor how employees engage during meetings, contribute to team discussions, and take ownership of shared responsibilities. Remember, engaged employees who communicate and support one another are often more productive in speed and quality of work.
Also read: How to motivate disengaged employees’ into passionate performers?
For example, if a project stalls because team members are unclear about responsibilities or wait too long for peer input, it could lead to poor collaboration. Often hidden in communication gaps, these friction points can quietly drag down overall productivity.
To spot these hidden productivity barriers early, ask:
- Are teammates actively contributing to shared goals?
- Do they clarify responsibilities without being prompted?
- Is communication smooth, timely, and transparent?
These collaboration engagements can help you break down barriers before they become full-blown project delays.
5. Determine the sources of productivity loss
Improving productivity starts with pinpointing what’s slowing it down. Don’t rely on assumptions; look at the data from the constructive feedback sessions. Use regular check-ins, team meetings, or feedback sessions to spot patterns that keep coming up.
Ask yourself:
- Are specific processes consistently causing delays?
- Are certain teams overloaded while others have capacity?
- Are tools or communication gaps creating friction?
For example, if support tickets are piling up or deadlines are frequently missed, it could point to deeper issues like poor workflow design, unclear task ownership, or even team burnout. These signs help managers understand whether the root cause lies in tools, communication gaps, or resource allocation and take targeted action to fix them.
6. Use the productivity formula (When applicable)
In roles where output is quantifiable, a simple productivity formula can offer valuable insight:
Productivity = Output / Input
Output refers to the results or deliverables from managers or stakeholders. This could include the number of resolved support tickets or marketing campaigns that must be launched.
Input refers to the time, effort, and resources required to deliver those outputs. This often means the number of employee hours spent or the software tools used.
Productivity refers to the ratio of output to input. It answers the question: How efficiently is the team turning time and resources into meaningful results?
For example, if a customer support agent resolves 80 tickets in a 40-hour week, their productivity could be measured as 80/40= 2 tickets per hour.
This doesn’t tell the whole story but offers a baseline for comparing performance across similar roles or time periods.
Note: This formula works best in task-driven or repetitive roles where output is easy to define. This formula may oversimplify performance for knowledge-based or creative work, so it should be used alongside qualitative assessments like quality, collaboration, and impact.
7. Create a focused action plan to boost productivity
Once you’ve identified what’s working and what’s not, the final step is to act on it. Use your findings to create a clear plan that addresses the gaps.
That might mean simplifying workflows, productivity tools, or offering coaching.
Involve your team in the process to get buy-in and tap into their insights. When people feel included, they’re more likely to take ownership of the improvements.
Find out: How to be more productive at work? Tips and solutions
5 Key metrics to measure employee productivity
You have learned employee productivity measures above, and now you will find out what to measure. Regularly monitoring these metrics lets you stay informed about your workforce’s performance.
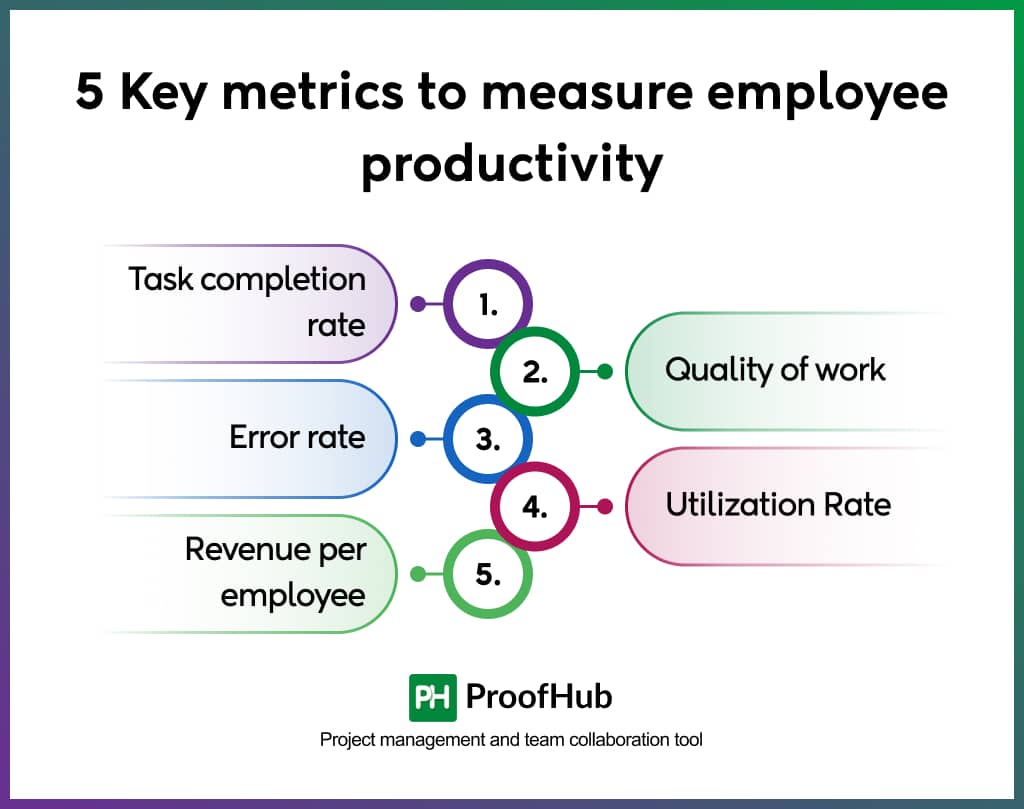
1. Task completion rate
This metric reflects the number of tasks an employee or team completes within a given time frame. It’s one of the simplest and most telling indicators of productivity. You can calculate it through the success calculation formula
For example:
If a marketing team is expected to complete 20 campaigns in a quarter and they finish 18, their productivity can be calculated using the formula:
Success rate = (Number of Completed Tasks / Total Number of Assigned Tasks) × 100
In this case:
Success rate = (18 / 20) × 100 = 90%
This means the team achieved 90% of their targeted output for that period.
2. Quality of work
Productivity is not just about doing more, it’s about doing it well. Measuring quality ensures that deliverables meet expectations and reflect the standards of your organization. You can assess work quality using:
- Rating scales (e.g., 1–10 on accuracy or attention to detail)
- Frequency indicators like “always,” “sometimes,” or “rarely”
These methods provide a fuller picture of performance and help catch potential issues before they escalate.
3. Error rate
Tracking how often mistakes occur can reveal hidden productivity issues. A rising error rate might indicate burnout, lack of training, or unclear processes. To calculate it:
Error Rate = (Number of Errors ÷ Total Number of Tasks Completed) × 100
For example:
If your team completes 50 tasks and 5 of them contain errors, you can calculate the error rate as:
Error Rate = (5 ÷ 50) × 100 = 10%
A lower error rate typically indicates better quality and higher productivity.
4. Utilization Rate
This metric shows how much time an employee spends on productive or high-impact work. It’s beneficial in service-based companies where efficiency drives profitability.
Utilization Rate = (Billable Hours ÷ Total Available Hours) × 100
For example, if an employee has 160 total available hours in a month and 120 of those are billable hours, their utilization rate is:
(120 ÷ 160) × 100 = 75%
A 75% utilization rate indicates a balance between productive work and available capacity for other tasks or breaks.
5. Revenue per employee
This metric shows how much revenue each employee contributes to the business. A higher revenue per employee typically indicates better efficiency and productivity across the team.
Revenue per Employee = Total Revenue / Number of Employees
For example, if your company generates $2 million in annual revenue with a team of 40 people, your revenue per employee is $50,000.
Additional point–
Attendance and punctuality
Consistent attendance is one of the most basic yet telling indicators of productivity, especially in hybrid or on-site teams. When employees regularly miss work or show up late, it disrupts team flow and delays project timelines.
To calculate the absenteeism rate of a team:
Absence Rate = (Total absences / Total scheduled workdays) × 100
For example, if 10 employees work 60 days each in a quarter (600 workdays) and have 30 recorded absences, the absence rate is 5%.
To calculate the absenteeism rate of a single team member
Absence Rate = (Number of days the employee was absent ÷ number of days the employee was scheduled to work) × 100
Example:
One employee was scheduled to work 60 days in a quarter.
That employee was absent for 3 days.
Absence Rate = (3 ÷ 60) × 100 = 5%
What factors affect employee productivity?
On average, employees are productive for only 2 hours and 53 minutes in an 8-hour workday, amounting to approximately 31% of their workday. However, employee productivity is not influenced by just one thing. A mix of internal and external factors shapes it.
Here are some of the key factors that directly impact how productive your team can be:
1. Employee well-being
Mental, emotional, and physical health directly impact how effectively employees can perform their tasks. Healthy, happy employees are more engaged and perform better. Health-oriented programs should be implemented to improve employee well-being, and work-life balance should be encouraged.
Discover 13 Proven work-life balance tips for overworked professionals
2. Manager-employee relationships
A supportive manager can make all the difference. To set a better relationship with your teammates.
- Set a clear vision for your team and help everyone understand what they should do and how their work contributes to the bigger picture.
- Communicate effectively and create an environment where employees feel comfortable asking questions and raising concerns.
3. Work environment
The work environment is pivotal in employee productivity, whether in the office or from home.
Factors such as lighting, temperature, noise level, and cleanliness directly affect employees” ability to focus and perform tasks efficiently.
To improve the work environment, maintain optimal temperature, and create quiet zones for focused work.
4. Access to the right tools and software
While technology increases an employee’s efficiency, it can also drain their time through the complex learning curve, complicated UI/UX, and constant malfunctions. Here’s how you can mitigate the adverse effects of technology:
- Choose technology that is easy to learn for employees.
- Train your employees to use technology and its advantages.
5. Clarity of roles and goals
When roles and goals are unclear, confusion sets in. Employees may duplicate work, miss deadlines, or waste time on low-impact tasks. To counter this, let team members know exactly what is expected of them, how their work ties into broader objectives, and how success is measured. They can work with focus and purpose.
What are common pitfalls in measuring productivity?
Measuring productivity is crucial, but it’s easy to fall into traps that lead to misleading insights or demotivated teams. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Setting vague goals
Unclear goals may feel flexible, but they leave too much room for confusion. It’s like starting a race without knowing where the finish line is. Teams end up guessing what success means, and that guesswork leads to frustration, misaligned efforts, and unreliable results.
The fix? Set SMART goals. They give everyone a shared direction and make progress easier to track fairly and consistently.
2. Focusing on short-term results
Focusing solely on the short-term results may give you a sense of progress, but without a long-term view, you will overlook opportunities for growth and sustainability. It’s like rearranging chess pieces without understanding the strategy behind the game.
To focus on the bigger picture, measure performance over time, and track trends rather than just isolated outcomes.
3. Focusing only on quantity, not quality
Counting the work done without looking at how well it’s done is like judging a book by its number of pages, not the story it tells. Quantity may look impressive, but it rarely drives real impact without quality.
To truly understand productivity, you must assess whether the outcomes meet standards, solve problems, or deliver value, not just whether tasks were marked as complete.
4. One-size-fits-all metrics
Applying the exact measurement to every role is like expecting a sprinter and a marathon runner to perform identically.
Generic metrics can undervalue unique contributions or pressure teams into the wrong priorities.
Instead, align metrics with the role’s nature and what success genuinely looks like for that specific function.
5. Relying too much on manual tracking
Relying too much on manual tracking can cause problems. It might feel accurate, but it often gives confusing or incomplete information. Using spreadsheets or asking people to report progress can waste time and lead to mistakes or biased results. A more innovative way is to use productivity management tools that automatically track work, show patterns clearly, and save your team time for more critical tasks.
Best tool to measure and improve productivity
ProofHub is an all-in-one project management and team collaboration software designed to help teams plan, organize, and deliver projects efficiently. It offers various solutions to streamline workflows and improve productivity.
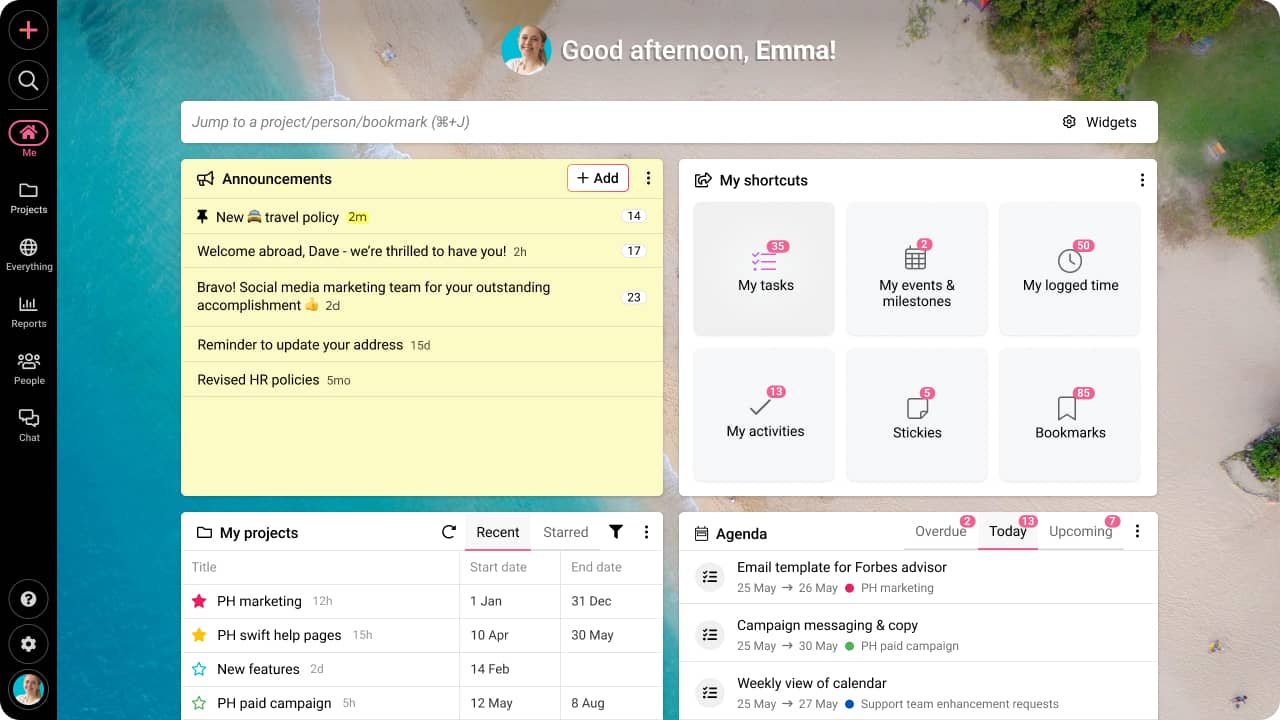
- Time tracking and timesheets
Team members can track time spent on tasks and view daily, weekly, or monthly time logs to analyze their spending patterns.
- Task progress and completion rates
Visualize task completion over time and track how much a task is finished.
- Workload and resource management
See who’s over- or under-utilized to balance assignments and ensure accountability by assigning clear ownership.
- Easy proofing and feedback
Upload files (images, PDFs, designs) and annotate directly with comments, markups, and highlights. Your team members get instant notifications when feedback is added or changes are made.
- Team collaboration
Comment on tasks to clarify requirements, share updates or resolve blockers. Quick chats for urgent queries. Use @mentions to grab attention.
Bottomline
Measuring employee productivity is crucial as it can help you identify what’s working, what’s not, and where you can step in to make meaningful improvements. When efficiently tracked, you empower your team to work smarter, stay focused, and consistently deliver better results.
To do this, you can take several steps, like setting achievable goals, assessing task completion rate, comparing quantity over quality, and more, as you will find above. These practices help you provide real insights into team performance, not just surface-level activity.
To make the measuring process even easier, you can use productivity measurement tools software like ProofHub. It brings task tracking, communication, time management, and performance insights into one place, making it easier for managers to measure, analyze, and improve team productivity confidently and clearly.
FAQs
What is productivity?
Productivity measures how efficiently a person, team, or organization turns inputs (like time, effort, or resources) into outputs (like tasks completed, products made, or goals achieved).
In simple terms:
Productivity = Output / Input
For example:
If an employee completes 10 tasks in 5 hours, their productivity is 2 tasks per hour.
What role does employee well-being play in measuring productivity?
Employee well-being directly influences productivity. When employees feel supported, they are more engaged, focused, and consistent in their performance. Ignoring well-being can lead to burnout, higher absenteeism, and reduced work quality, which skews productivity metrics.
What are the four types of productivity measures?
1. Labor productivity
Shows how much each team member contributes to the output. It’s the value of what your team produces divided by the hours they spend making it.
Example: Number of units produced per hour.
2. Capital productivity
Evaluates how effectively capital (like equipment or tech) contributes to output. It’s anything tangible that you use to make your products.
Example: Revenue generated per dollar invested in tools.
3. Material Productivity
Measures how efficiently raw materials or natural resources contribute to output. It’s anything physical you use to deliver your service or product.
Example: Units produced per kilogram of material.
4. Total Factor Productivity (TFP)
It looks at overall efficiency by combining all inputs (labour, capital, materials).
Example: GDP growth not explained by labour or capital increases.
How can we improve employee productivity in the workplace?
Improving employee productivity involves setting clear goals, providing the right tools, offering regular feedback, minimizing distractions, and promoting employee well-being. Empowering employees and removing bottlenecks are key strategies.

