Agile leadership is a leadership style that focuses on creating an ability to respond to change quickly and effectively. Inspired by the values and principles of the Manifesto for Agile Software Development, it focuses on empowering people, facilitating collaboration among people, working iteratively, and making continuous improvement, making it completely different from traditional leadership, where power resides in the top brass leadership, decisions move from top-to-bottom, and leaders do not encourage feedback from the people down the hierarchy.
And an agile leader is a leader who has an agile mindset, prioritizes collaboration among individuals, empowers people to make decisions, and encourages continuous improvement.
In this post, we will learn what it means to be an agile leader or have an agile mindset, key characteristics of the agile leader, and frameworks for agile leadership.
Who is an agile leader?
An agile leader is someone who prioritizes people and collaboration, empowers autonomy, and encourages continuous improvement.
To understand what inspires agile leadership, it is essential to first understand what agile means.
Agile is a mindset or approach that focuses on creating an ability to respond to change quickly and effectively. It is based on the four agile values and twelve principles written in the Agile Manifesto.
Four values of Manifesto for Agile Software Development:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
When you read the Agile Manifesto, you will find an agile mindset focused on individuals, collaboration, iterations, feedback, and continuous improvement. The same principles and values inform agile leadership. Thus, the key principles of agile leadership roughly include:
- Respond to change
- Collaboration with people
- People empowerment
- Continuous improvement
In a nutshell, an agile leader prioritizes people, collaboration, autonomy, iterations, and continuous improvement. This agile mindset forms an agile leadership style that focuses on people, giving power to people, facilitating collaboration among people, working iteratively, and sharing feedback to make continuous improvement.
Disclaimer: It is very important not to confuse the agile mindset with agile project management or the frameworks of the agile methodology, such as Scrum and Kanban, but to consider it as a guiding principle for agile leadership.
What are the key characteristics of an agile leader?
An agile leader needs to demonstrate certain characteristics and skills to become truly agile. Here are the key characteristics of an agile leader:
1. Flexibility and adaptability
Flexibility and adaptability are at the core of an agile leader. It simply means the ability of an individual to respond and adapt to changing priorities, projects, clients, and technology in a positive and proactive manner without resistance. An agile leader is willing to adjust, learn new skills, and find new ways of working to respond to the changing circumstances gracefully rather than resisting the change.
There are many leaders who do not embrace change, are rigid in their mindset, and are not comfortable adopting the new technologies and changed ways of working, resisting the change. Whereas, an agile leader showcases true flexibility and adaptability and willingness to experiment, embracing the change.
2. Collaboration
At the heart of Agile is collaboration. An agile leader is someone who collaborates, seeks input, and works together with the people around them to make decisions. Whereas, a traditional leader is someone who works in silos and makes decisions unilaterally with little or no input from team members. This act of collaborating results in providing autonomy to the teams, which is another key characteristic of an agile leader (discussed in the next section).
The same act of collaboration occurs in democratic leadership or democratic ways of working, where the leader involves team members in decision-making, but retains the final authority to make decisions. Whereas in agile leadership, team members have the autonomy to make decisions.
3. Empowering autonomy
People are at the center of Agile. In agile software development, the power of making decisions on how to approach development lies in the hands of the developers, known as a self-organizing team. There is no manager who is making decisions on behalf of the team or managing the day-to-day work of the team. Agile leadership draws a core characteristic of empowering autonomy in people from the Agile Manifesto.
An agile leader empowers others and gives them the power to make decisions. The leader encourages people to make decisions and take accountability and ownership for the decisions. It is completely different from a traditional leader who has complete autonomy over decision making or traditional leadership, which relies on the autocratic leadership style of taking complete control.
4. Open communication and learning
A key characteristic of an agile leader is that they actively listen to the team member, both receive and share feedback, and make consistent efforts to improve. An agile leader prioritizes open and transparent communication and has a mindset of lifelong learning to make continuous improvement.
Agile leadership draws this concept from agile project management, where work is performed in iterations and feedback is received after every iteration to improve.
This fosters a culture of collaboration where everyone has access to the most updated information to work together effectively and creates a culture of continuous improvement where teams are constantly seeking ways to optimize their processes.
To create this culture of collaboration, an agile leader needs a certain set of skills, such as effective communication, empathy, and emotional intelligence.
Read more: 13 Leadership skills you need to lead your team successfully
What are the benefits of agile leadership?
Leaders who adopt agile ways of functioning or agile leadership enjoy a range of benefits. Have a look at some of the key benefits.
1. Improved business agility
The biggest advantage of adopting agile leadership is the enhancement of business agility for an organization. Business agility is defined as the ability of an organization to quickly adapt and respond to market changes and emerging opportunities. Agile leadership creates a culture of collaboration where everyone has access to the most updated information to work together effectively and provides autonomy to employees to make decisions. This reduces the time between sensing the opportunity and responding to the opportunity.
Not just that, this consistent collaboration with customers in agile leadership improves customer satisfaction with the business by focusing on customer needs and continuously incorporating feedback, leading to improved business agility.
2. Enhance innovation and resilience
Agile leadership focuses on collaboration, iterative ways of working, and continuous improvement. This collaboration among individuals with diverse backgrounds and skills leads to innovation, the creation of new ideas, and the development of novel solutions. Also, when individuals with diversity work together, it leads to comprehensive and faster problem sensing, effective risk management, faster decision making, and collaborative learning, which may not happen in organizations with a traditional leadership style due to a lack of a culture of open communication and collaboration.
Paired with the iterative ways of working, agile leadership encourages experimentation and learning from failures. This leads to building resilient organizations that are ready to adapt to change.
3. Improve employee experience
Adopting agile leadership improves the employee experience by enhancing employee engagement through empowering autonomy. When employees are given the responsibility and power to make decisions, this increases the employees’ accountability and sense of belonging to the work and workplace. This increased accountability and engagement improves employee experience and engagement. It also makes it easy for managers to manage the employees as they are communicating openly about the concerns and identifying the potential bottlenecks and challenges early on before they become a concern.
Read more: Traditional vs Agile project management method: Which one is right for your project?
Frameworks and tools for agile leaders
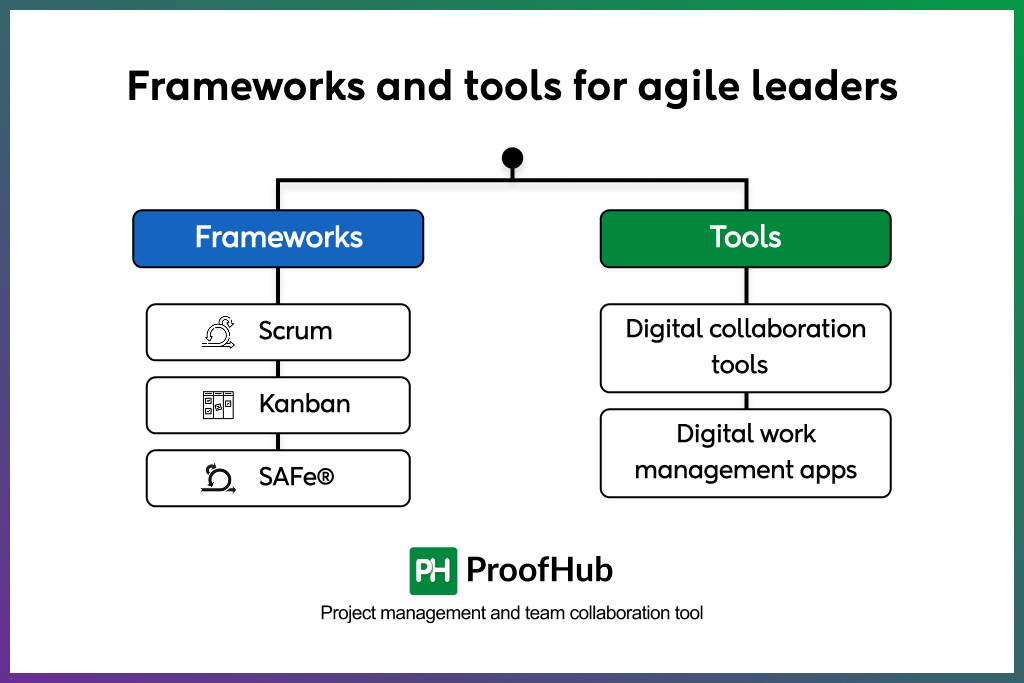
Agile leadership and being an agile leader are more about mindset and behaviour derived from Agile Manifesto values and principles. However, there are certain frameworks and tools that can help you adopt and implement agile leadership. As a competent agile leader, you should be aware of the following frameworks and tools:
Scrum
Scrum is a framework for agile project management that focuses on iterative and incremental approaches to managing project work. It divides the project work into small parts known as user stories, and involves working on these user stories in short and fixed-length iterations or cycles, called sprints, usually of 2-4 weeks. At the end of each sprint, a user story is released for customer and stakeholder feedback. This helps in the continuous improvement of the developed product and ensures customer satisfaction by meeting the demands of end-users who will use the product, thereby ensuring project success.
Kanban
Just like Scrum, Kanban is a framework of agile project management that focuses on iterative development of the product but uses a different set of artifacts, processes, and practices. It uses a Kanban board, cards, and WIP limits to manage work. A project is divided into smaller parts known as user stories. The team picks the user stories to work on based on the team’s capacity and releases the story for feedback as soon as it is completed. There are no time-boxed sprints. Kanban controls and manages the work using WIP limits, which represent the maximum amount of work a team can pull at any given stage in a project.
Apart from Scrum and Kanban, there are other project management methodologies & frameworks, such as eXtreme Programming (XP), Lean, and PRINCE 2, which an agile leader should be aware of.
Scaled Agile Framework®(SAFe®)
Scrum and Kanban frameworks are used at the team level for project management. If you want to implement the same agile practices organization-wide, there is a Scaled Agile Framework®(SAFe®) that provides guidance in the form of a knowledge base of best practices and a set of organizational and workflow patterns to implement agile practices organization-wide. It is based on the three primary bodies of knowledge: agile software development, lean product development, and systems thinking. The purpose of this framework is to provide a knowledge base for leaders to implement Agile organization-wide.
Just like Scaled Agile Framework®(SAFe®), there are other frameworks, such as Large Scale Scrum (LeSS), Scrum@Scale (SaS), Disciplined Agile Delivery (DAD), and Enterprise Kanban.
Note: These frameworks are designed for the management of software development projects and the implementation of agile from the team to the organization level for the agile transformation. These frameworks may or may not apply directly to non-IT organizations, but values, principles, and learning from these frameworks can be adopted by any organization to improve business agility.
For example, according to the State of Agile Marketing Report 2024, 83% of marketers had a positive experience with Agile; 86% of all marketing organizations planned to transition some/all of their marketing teams to Agile.
Digital collaboration tools
To implement the values of agile leadership, agile leaders need certain tools that can help facilitate collaboration, centralized data, and ensure transparency. Digital collaboration tools like ProofHub, Slack, and Teams can help agile leaders by providing a centralized and transparent platform for communication, collaboration, and document sharing.
Digital work management apps
To implement the processes of agile leadership, agile leaders need certain work management tools such as a Kanban board, project reports, and a Gantt chart. Digital work management apps like Jira, ProofHub, and Asana can help you implement the agile leadership values and principles.
Read more: 14 Best agile project management tools for project managers
Who can become an agile leader?
Anyone can become an agile leader. When you truly understand that being an agile leader is about adopting the agile mindset, you start implementing agile values and principles in your behavior. Thus, anyone who can adopt the agile mindset and approach can become an agile leader.
Here is what it means to be an agile leader:
- prioritizes people and collaboration with people rather than making decisions in silos.
- decentralizes the power and empowers people to make decisions rather than holding the decision-making authority and micromanaging people.
- work in iterations and embrace the feedback from stakeholders and customers for continuous improvement rather than following the rigid plan to resist change.
How is an agile leader different from a traditional leader?
An agile leader is different from a traditional leader in mindset, approach, and the ways of leading people. Where a traditional leader tries to control, an agile leader focuses on empowerment. Where a traditional leader makes decisions in silos and functions in the autocratic leadership style, an agile leader collaborates with people to make decisions or even empowers people to make decisions by providing autonomy and functions in a servant leadership style.
Here are the key points reflecting the difference between a traditional leader and an agile leader.
| Aspect | Traditional leader | Agile leader |
| Decision making | Top-down, centralized | Collaborative, decentralized |
| Change response | Resist change, follow rigid plans | Embrace change, iterate when required |
| Team management | Control and micromanage; autocratic leadership | Empower and delegate; servant and democratic leadership |
| Vision | Avoid risks and resist learning new skills | Encourage experimentation and continuous learning |
| Feedback | Open to feedback, inputs, suggestions, and communication | Strong opposition to feedback, defensive, and not easily approachable |
Can traditional managers become agile leaders?
Yes, traditional managers can become agile leaders if they adopt the right mindset. There are certain things a manager needs to adopt to become an agile leader.
- Adopt an Agile Mindset
- Learn about Agile Frameworks
- Develop key agile leadership skills
- Experiment and learn: Work in Agile teams
- Seek feedback
Are there certifications for agile leadership?
Yes, there are various certifications for agile leadership. Top certifications include:
- PMI-ACP® by Project Management Institute
- SAFe® Agilist (SA) by Scaled Agile (SAFe)
- CAgile Agile Coaching (ACC) by ICAgile
- Certified Agile Leader (CAL) by Scrum Alliance

