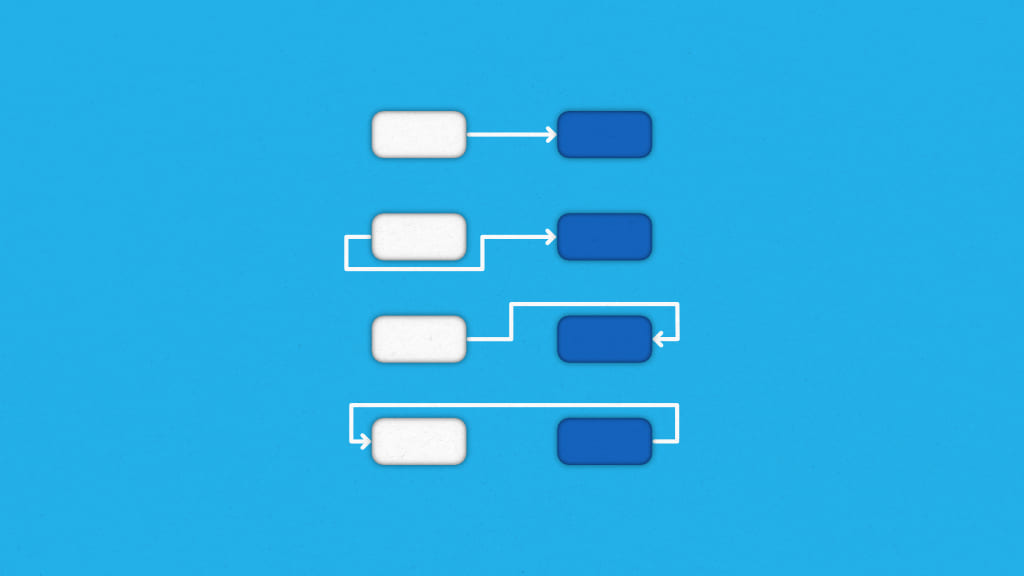
Task dependencies determine the sequence in which project tasks need to be done and they are among the most overlooked reasons why projects get delayed.
For instance, if a task can not begin until another is completed, that’s a dependency. And when those relations are not planned clearly, teams end up waiting around, deadlines are missed, and work gets repeated or blocked.
The main issue? Most managers focus on what needs to be done and tend to overlook when and in what sequence. And that’s when everything starts to fall apart.
Understanding task dependencies allows you to identify bottlenecks before they occur, collaborate effectively across teams, and keep your project on track from day one.
In this article, you will learn what task dependencies are, their types, examples and how to identify them efficiently.
So, without further ado, let us get on with it.
What are task dependencies?
Task dependencies refer to the relationships between tasks in a project where the start or completion of one task depends on the start or completion of another. Together, these dependencies define the logical sequence in which tasks should be performed to ensure timely and efficient delivery.
Task dependencies are central to project scheduling techniques such as Critical Path Method (CPM), Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), and Gantt charts.
For instance, while making tea, it is illogical to pour the tea until the water is boiled. Each step depends on the previous one. Change the order, and the process simply doesn’t work.
Similarly, tasks in a project are rarely isolated. They connect, overlap, and build on each other. Understanding their dependencies can help you:
- Map the logical flow of work.
- Schedule tasks in the right sequence.
- Avoid bottlenecks caused by poor planning.
- Ensure teams don’t interfere with one another’s work.
Whether it’s designing a website, planning an event, or building a product, knowing what depends on what keeps your team aligned and your project timeline realistic.
What are the types of task dependencies?
Not all dependencies are the same. They vary based on how tasks relate to each other in terms of timing, sequencing, and control.
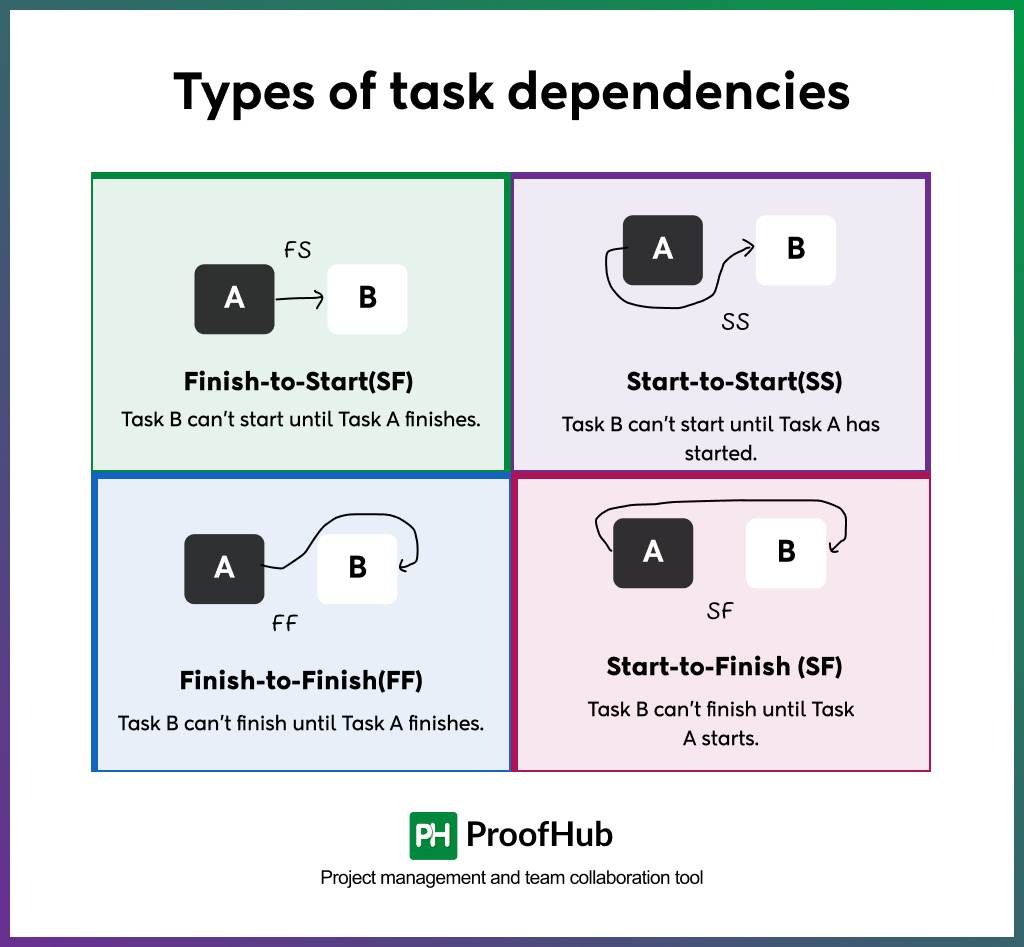
There are four main time-based dependency types you’ll come across in project scheduling:
- Finish-to-Start (FS)
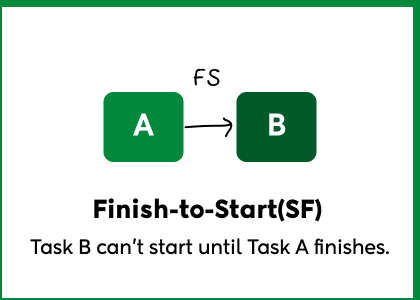
Task B can’t start until Task A finishes.
This is the most common and straightforward dependency. One task must be fully completed before the next can begin.
Example: You can’t publish social media posts (Task B) until the content is written (Task A).
This kind of dependency makes sure that work flows in a logical sequence, especially useful in phases like planning → execution → delivery.
- Start-to-Start (SS)
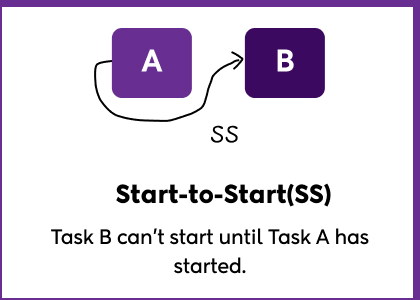
Task B can’t start until Task A has started.
This doesn’t mean both tasks start at exactly the same moment, it just means Task B can only begin once Task A is underway.
Example: Design and content writing for a web page can be done at the same time. Designing can be started (Task B) once content creation begins (Task A).
This type of dependency is useful when tasks can progress in parallel but still need a trigger to begin.
- Finish-to-Finish (FF)
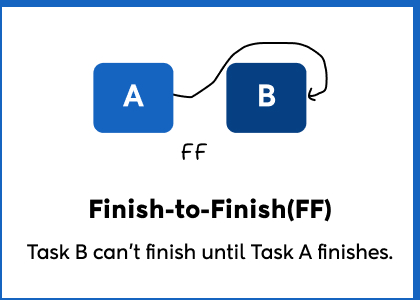
Task B can’t finish until Task A finishes.
This means two tasks may run side-by-side, but one can’t wrap up until the other does too.
Example: Suppose you are recording a product commercial. Recording (Task A) and acting (Task B) happen simultaneously. You can not finish one without the other.
This type of dependency helps you ensure simultaneous wrap-up of certain deliverables that are completed together for a milestone or release.
- Start-to-Finish (SF)
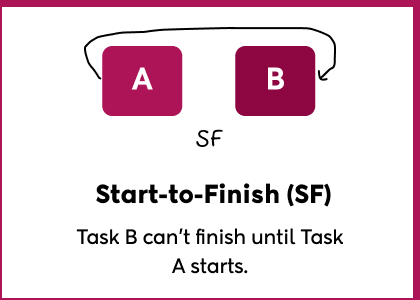
Task B can’t finish until Task A starts.
This is the least common type, but it’s useful in cases like handovers or shift work.
Example: The new website must go live (Task A) before the old one is taken offline (Task B). You can’t shut down the current site until the new one is up and running.
These logical dependencies help you ensure a smooth handover by requiring the next task to begin before the current one can end.
Apart from these time-based ones, there are three other dependencies that influence the scheduling of project tasks and activities.
- Mandatory dependencies: These are non-negotiable based on project constraints such as legal, technical, or physical requirements.
Example: You can’t launch an app without going through testing.
Skipping these dependencies can lead to compliance issues or technical failures. They’re enforced by the nature of the work itself.
- Discretionary dependencies: These are preferential dependencies based on team’s best practices, experience, or internal processes. You could change them, but it’s usually not recommended.
Example: Choosing to write the blog before designing its visuals.
While flexible, discretionary dependencies often reflect the team’s established workflows for quality, consistency, or efficiency.
- External dependencies: These are sometimes refers to as resource dependencies that rely on tasks, resources or events outside the direct control of your team or organisation. These dependencies rely on external parties, such as clients, vendors, or third-party approvals. Since they’re outside your control, they often carry higher risk and variability.
Example: Waiting for a government approval before beginning site construction.
You should factor in potential delays and have risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans at hand for missed approvals, shifting timelines, or unresponsive stakeholders when working with external entities.
Note*: While identifying and managing task dependencies, you also need to factor in lead time, lag time, and buffer. A lead lets a dependent task begin slightly before its predecessor finishes. A lag adds an intentional delay between tasks. A buffer provides extra time to manage risks or uncertainties without impacting the overall timeline. The use of these factors allows you to define the logical sequence of tasks accurately.
Why should you identify task dependencies?
Identifying task dependencies is a foundational practice in task management that ensures work is logically sequenced, efficiently resourced, and realistically scheduled.
Project tasks are usually complex and interconnected. They often rely on one another to start, progress, or finish. When those connections are not clear, projects can quickly go off track. Teams get stuck waiting, timelines slip, and responsibilities blur.
That’s why identifying task dependencies early is necessary for a project manager. It gives you the overview of how your project flows, helping you plan smarter, collaborate better, and reduce risks.
Benefits of identifying dependencies:
- Prevents delays and blockers: When you’re aware of which tasks are dependent on others, you can actively track them and step in before they hinder the workflow.
- Improves task scheduling: Clear dependencies help you schedule work in the correct sequence. Instead of guessing what should happen next, you can build a timeline that reflects how the work should be done.
- Optimizes resource allocation: When you know how tasks connect, you can better manage your team’s time and tools. You avoid conflicts, overloading individuals, or having team members wait around for tasks that weren’t ready to begin.
- Enhances team coordination: Dependencies provide clarity on who’s waiting for what. Teams can stay in sync, communicate proactively, and hand off work more efficiently.
- Reduces risk and uncertainty: Projects rarely go exactly as planned but if you’ve mapped out dependencies, you can respond to changes with confidence. You know what’s affected, what needs adjusting, and how to get things back on track promptly.
How to identify task dependencies?
Before you can manage task dependencies, you need to identify them and that’s not always as simple as it seems. Identifying dependencies means understanding the flow of work and for every task defining:
What needs to happen first, and what follows?
Here is the step-by-step approach to help you identify dependencies efficiently:
Step 1: Review the project scope and deliverables
Before diving into individual tasks, you need to get a clear understanding of the overall project goals and priorities. You can ask yourself questions like:
- What is the outcome your team is working toward?
- What are the major deliverables, phases, or milestones?
- Are there any constraints (e.g., deadlines, resource limits, or client approvals)?
In project management, understanding the project scope can help you see how different tasks contribute to the final goal. You can’t identify logical task sequences if you don’t know where you’re headed.
For instance, if you’re launching a website, your deliverables can include:
- Design assets
- Frontend code
- Backend functionality
- SEO and analytics setup
- Final deployment
All of these are interlinked. Without a clear, defined scope, you risk misalignment, inefficiencies, or incomplete work.
Step 2: Break work into tasks (WBS-level)
Once the project scope is clear, divide the work into deliverables, and then break each deliverable into specific tasks.
The project managers often do this using a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) – a method that helps you organize work into manageable chunks. The goal is to break tasks down until they can be completed by one person within a defined timeframe (e.g., a few hours or days).
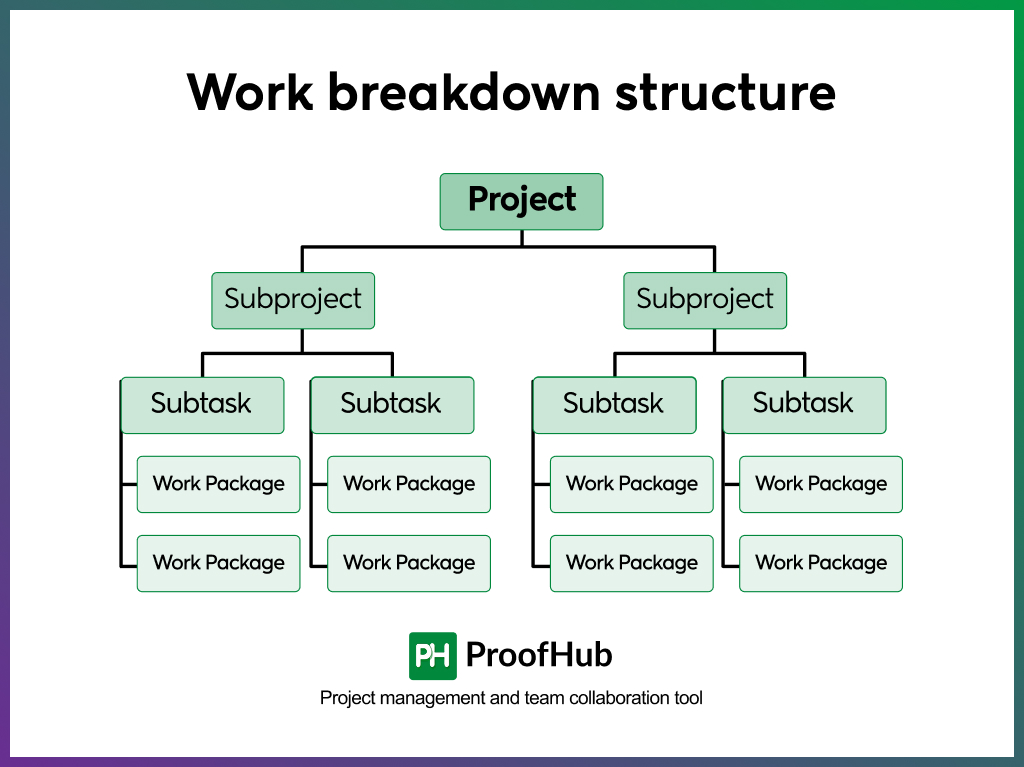
While doing so, avoid vague labels like “work on design” or “do QA.” Be specific about the tasks, such as “Create homepage wireframe,” “Test contact form on mobile.”
The more clearly you define the tasks, the easier it is to identify what depends on what. Overly broad or vague tasks make it hard to find dependencies.
Step 3: Ask: What needs to happen before this and what follows?
This is the most crucial step to identify the dependencies. Once tasks are listed, go through each one and ask:
- What needs to happen before this task can begin?
- Does this task need to finish before something else can start?
- Can this task happen independently? Or does it rely on another?
- What would happen if this task were delayed? Who would be impacted?
- Does this task need input, data, or approval from someone else?
These questions can help you find both obvious and hidden task relationships. Some are sequential (Task A → Task B), while others are conditional (Task A needs to be approved before B).
A project manager can document these relationships using a dependency matrix that allows you to cross-reference tasks and see which ones rely on others. Additionally, it helps you identify patterns and avoid missing critical connections. (explained in detail later in the article)
Don’t look for technical dependencies (like code before testing) only. You need to consider the process, people, access, reviews, and content as well.
Step 4: Collaborate with your team for cross-functional insight
You won’t always have the full context on your own. That’s why team collaboration is necessary to identify accurate dependencies.
So, walk through the task list with each team involved (design, dev, marketing, QA, etc.). Ask team members what they need to start their work and what they’re waiting on. Identify bottlenecks, handoffs, and task overlaps.
Cross-functional dependencies are often missed without alignment. Your designer may be waiting for branding, your developer may need approved copy, and your content team may need wireframes. You won’t know unless you ask.
Step 5: Estimate task durations
Once dependencies are mapped out, you need to estimate how long each task will take. This will help you set a realistic project schedule and identify where potential overlaps or delays may occur.
You can use Three-Point Estimates to factor in uncertainty and risks:
- Optimistic estimate (to): How long will the task take if everything goes better than planned; there are no bottlenecks, no delays – ideal conditions.
- Pessimistic estimate (tP): How long it will take if things don’t go as planned; there are delays, rework, or external dependencies.
- Most likely estimate (tM): How long will the task take if everything goes according to the plan based on typical conditions and past experience.
Then, apply the formula to get the expected estimate (tE):
This gives a weighted average that reflects risk and variability.
To get accurate estimates, you can also use the Bottom-Up approach. Start by breaking large tasks into smaller, more detailed ones. Then, you can estimate time for each individual task while factoring in the resource constraints. This granular approach improves accuracy and gives you a realistic overview of how long the work will actually take.
Estimating durations accurately helps you spot potential delays, allocate resources efficiently, and keep dependencies on track.
Read more: Top-down approach vs bottom-up approach in project management: Key differences.
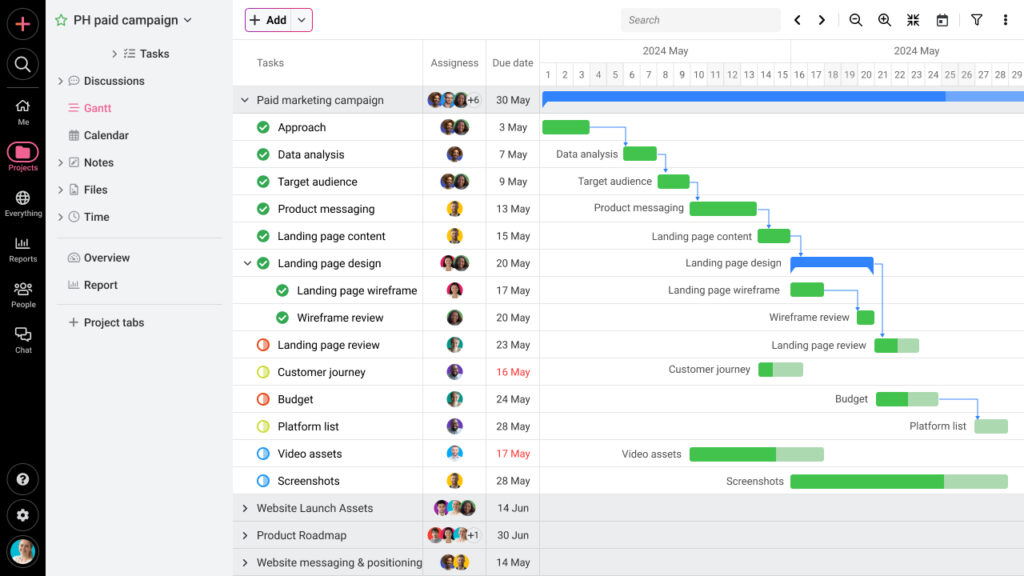
Step 6: Use a Gantt chart to map dependencies visually
Once you’ve identified the relationships, don’t keep them in your head or on a sticky note. Visualize them. You can use a Gantt chart to lay out tasks on a timeline and link them with arrows to show dependencies.
ProofHub – an all-in-one project management software offers multiple task views including a Gantt chart view that allows you to create entire project schedule. You can create tasks, set start and due dates, and link them using simple drag-and-drop. If a task is delayed or rescheduled, the changes reflect immediately, so your team always has an up-to-date view of how everything connects.
When dependencies are visual, your team members can understand the sequence at a glance. No one needs to guess “what’s next”, it’s mapped out and connected.
Set task dependencies, track progress, and adapt to change in real-time – all in ProofHub’s Gantt chart. Sign up now for a 14-day free trial!
Examples of task dependencies
Whether you’re managing a campaign, launching a product, or planning an event, there are always tasks that rely on others to start or finish.
Here are some common examples across different scenarios to understand how task dependencies work:
- Software development
Task A: Create design mockups
Task B: Start frontend coding
Dependency type: Finish-to-Start (FS)
You can’t begin frontend development until the UI/UX designs are ready. The design team needs to finish their mockups before developers can translate them into code.
This dependency makes sure that developers have a clear foundation to work from, reducing the risk of rework or guesswork.
- Event planning
Task A: Book the venue
Task B: Send out event invitations
Dependency type: Finish-to-Start (FS)
You can’t invite guests to an event without confirming the venue first. The venue details such as address, capacity, and availability, need to be finalized so the invitation contains accurate information.
Sending invitations too early could result in confusion or even cancellation.
- Marketing campaign
Task A: Launch the landing page
Task B: Start paid ads and email promotions
Dependency type: Finish-to-Start (FS)
In a digital marketing campaign, it makes no sense to start navigating traffic to a page that doesn’t exist yet.
The landing page needs to be live and functional before you begin promoting it through ads, email, or social media. Otherwise, you risk wasting the budget and disappointing users.
- Product launch
Task A: Complete final QA testing
Task B: Deploy the product
Dependency type: Finish-to-Finish (FF)
Both QA testing and deployment are the final steps in the release process. Even if they start at different times, they need to finish together.
You can’t push the product live until testing is complete, and you don’t want to delay deployment waiting on last-minute fixes.
- System handoff (IT Ops)
Task A: Set up the backup system
Task B: Decommission the old server
Dependency type: Start-to-Finish (SF)
Before shutting down an old system, the new one should already be running. This ensures continuity and prevents downtime.
It is a common case in IT projects where systems are replaced or upgraded with zero interruption in service.
These examples show how dependencies influence not just task order, but also timing, responsibility, and resource planning. Ignoring them can lead to miscommunication, wasted time, and stalled progress.
Tips for handling task dependencies effectively
After identifying task dependencies, you need to manage them throughout the project. Done right, it keeps your team aligned, prevents delays, and helps you adapt quickly when things change.
Here are some practical tips to manage task dependencies effectively:
- Use visual tools to map relationships
You can manage dependencies easily when you can see them. Tools such as Gantt charts let you visualize how tasks rely on each other, making it clear what needs to happen, when, and in what order.
With ProofHub’s Gantt charts, you can visually map out dependencies between tasks. You can link tasks, drag timelines, and instantly see how changes affect the overall timeline.
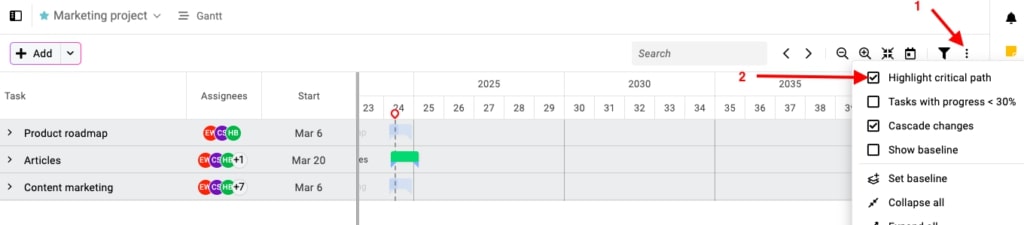
- Prioritize critical path tasks
The critical path is the sequence of tasks that directly impacts your project’s finish date. If one of them is delayed, the whole project’s timeline will be delayed. Identify dependencies on this path and monitor them closely.
With ProofHub’s Gantt chart, you can also identify critical tasks and focus on what’s most time-sensitive. Task linking shows how one delay impacts others, so you can make smart decisions swiftly.
- Set buffer time for risky dependencies
Some dependencies are more uncertain than others, such as ones that rely on client feedback or external vendors. Add a buffer or slack in your timeline to account for unexpected delays without derailing the project.
You can adjust start and due dates easily in ProofHub to add buffer time for high-risk tasks. If anything changes, the connected tasks update automatically, keeping your timeline realistic.
- Communicate changes instantly
Dependencies mean that one change affects many tasks. If a deadline changes, the people responsible for dependent tasks need to know right away. Use notifications, team stand-ups, or shared tools to keep everyone informed.
ProofHub sends real-time notifications when a task is updated, rescheduled, or reassigned. No more email back-and-forth, everyone stays informed without missing anything important.
- Review task dependencies weekly
Project plans change. New risks can appear. That’s why you should review and update project dependencies regularly. A quick weekly check-in helps you spot risks early and adjust before they escalate.
ProofHub makes it easy to track task progress, communicate about issues through task comments or discussions, and update task links directly in the Gantt view, so your team stays aligned and works efficiently.
Common mistakes to avoid when setting dependencies
Here are some common mistakes that can slow down your project, confuse your team, or create bottlenecks during execution.
- Overlooking internal cross-functional dependencies
Sometimes, tasks depend on input from other teams but that relation isn’t always obvious. Ignoring these can result in delays or duplicated efforts, especially in cross-functional projects.
- Making every task dependent on another (micro-management)
Not every task needs to be linked. Overusing dependencies can slow down progress by creating unnecessary waits or forcing a rigid workflow.
- Ignoring external constraints
Dependencies involving clients, vendors, or third-party approvals are easy to miss. But they’re often the most unpredictable and need to be factored into your plan from the start.
- Failing to revisit and revise dependencies
Dependencies aren’t static. As your project progresses, so should the relationships between tasks. Leaving old links in place can mislead the team and disrupt schedules.
- Not tracking progress once dependencies are set
Setting dependencies is only the beginning. Without tracking progress, you won’t know if a delay in “Task A” is quietly holding up “Task B”. That’s how missed deadlines happen.
Can task dependencies affect project timelines and delivery?
Yes, task dependencies have a direct impact on project timelines and delivery. When dependencies are mismanaged or overlooked, they can derail your timeline.
Here is how task dependencies affect your project timelines:
- Blocked tasks delay others: When a dependent task is waiting on another to finish, any delay in the first task creates a chain reaction. One missed deadline can derail the entire project, resulting in further delays and disruptions.
- Misidentified dependencies cause chaos: If you fail to define which tasks rely on others, your team members may start work too soon or too late. This results in confusion, rework, and wasted effort.
- Overlapping tasks create overload: Trying to run dependent tasks in parallel without proper coordination can overwhelm your team or stretch resources too thin, compromising both quality and speed.
So, how can you fix this? Set clear, realistic connections between tasks based on how work should get done, not only how you hope it will.
You can also use a project management tool like ProofHub to visualize task dependencies, track progress, and adjust timelines as your project progresses.
What is a dependency matrix, and when should you use one?
A dependency matrix is a square matrix-based tool used to map the relationships between tasks within a project. It shows which tasks depend on others, so you can plan better and avoid surprises. It helps you avoid missed handoffs, miscommunication, and duplicated effort, especially in complex, large, or cross-functional projects.
A typical dependency matrix looks like a table. Each task is listed on both the left side (rows) and top (columns). Where two tasks meet, you mark if one depends on the other. Leave blank if there’s no dependency.
Here is an example of a basic dependency matrix:
| Task A | Task B | Task C | |
| Task A | – | FS | |
| Task B | – | SS | |
| Task C | FF | – |
Key: FS = Finish-to-Start, SS = Start-to-Start, FF = Finish-to-Finish
You can use a dependency matrix when:
- Your project is large and complex,
- Many teams are working on shared or dependent tasks,
- You need to spot all dependencies in one place,
- And you want to avoid surprises or missed handoffs.
How to manage task dependencies in ProofHub
ProofHub is a comprehensive project management and team collaboration software that offers Gantt charts to visualize, schedule, and manage task dependencies, so your team doesn’t have to switch between multiple tools, emails, or spreadsheets to figure out what’s next.
So, how can you manage task dependencies within ProofHub?
- Visualize and set dependencies using Gantt Charts
ProofHub’s Gantt chart allows you to see the entire project timeline in one view. You can:
- Create tasks and subtasks with start and due dates.
- Drag and link dependent tasks directly from the timeline.
- Choose from four dependency types (Finish-to-Start, Start-to-Start, Finish-to-Finish, Start-to-Finish).
- Add leads and lags between tasks to control overlap or waiting periods.
- Set buffer time on critical tasks to account for uncertainty and avoid timeline slippage.
This makes it easy to map how tasks connect and identify potential delays before they happen.
- Create and edit task links easily
ProofHub allows you to link tasks with just a few clicks in Gantt chart.
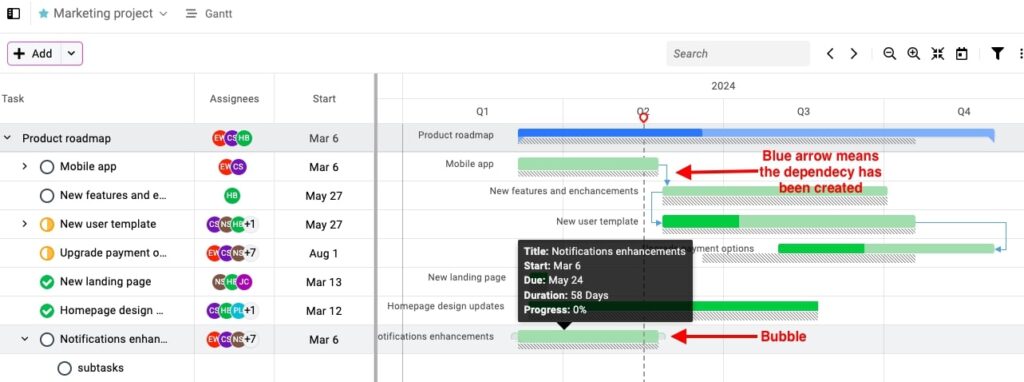
You can:
- Hover over the task bar and use the connector bubbles to link tasks.
- Define what must happen before or after.
- Adjust relationships, including adding lead time (to start early) or lag time (to delay a task’s start).
- Link cross-functional tasks across teams or milestones.
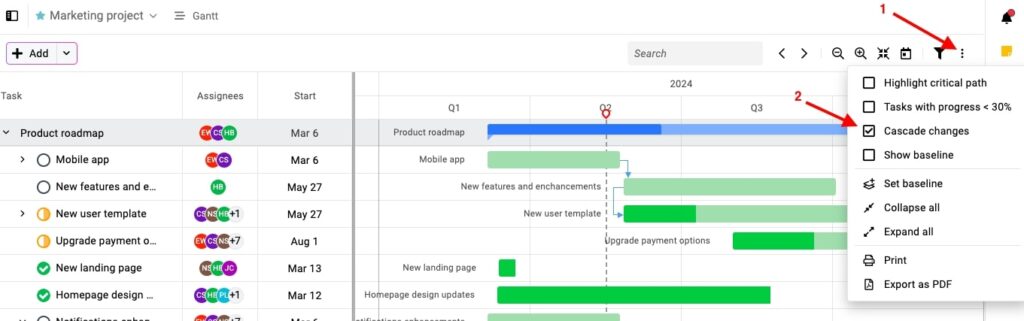
- Cascade changes
When you reschedule a task, ProofHub automatically adjusts all dependent tasks. Just turn on the “Cascade changes” option, and the timeline will update without manual rework, saving time and maintaining the overall project timeline.
- Stay updated with real-time notifications
Once dependencies are in place, you and your team need to stay updated. ProofHub sends instant notifications when:
- A dependent task is marked complete
- Task dates are rescheduled
- Assignments or progress updates happen
This helps everyone stay informed and ready to take action when the previous task is done.
- Facilitate cross-team collaboration
Every task in ProofHub gives your team the space to talk, share, and stay organized, right where the work is happening. You can:
- Add comments or updates directly on tasks
- Attach files, images, and documents
- Set priorities and custom details
- Track time (if needed)
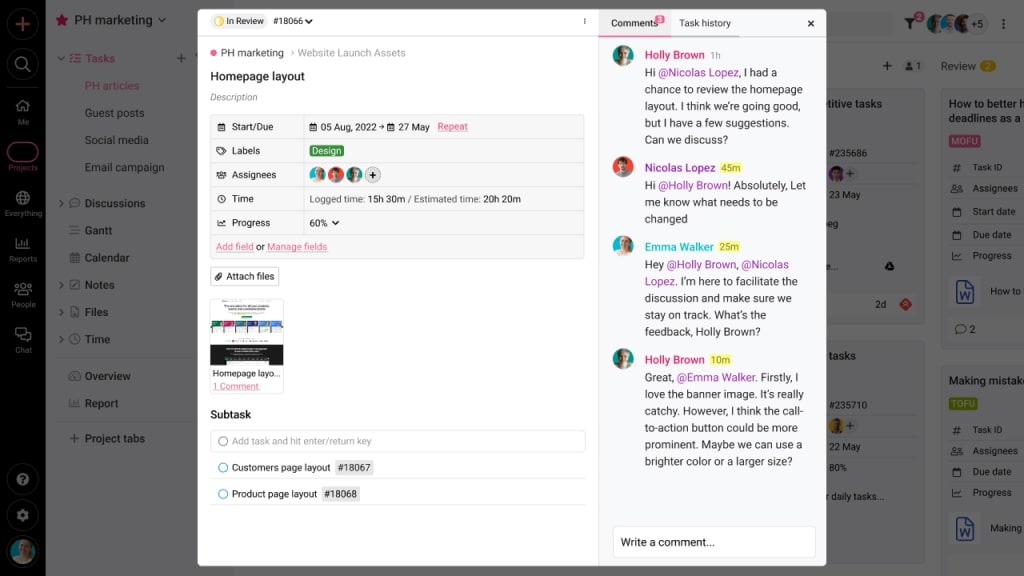
You can also use built-in chat to have real-time conversations without switching apps. This keeps conversations focused, removes the need to switch between tools, and makes sure no one misses important context.
- Keep everything in one place
With ProofHub, you don’t have to switch between multiple tools or lose time tracking down updates. From task lists and dependencies to notes, files, discussions, and deadlines, ProofHub keeps it all together. This centralized workspace helps you reduce confusion, keeps communication focused, and makes it easy to manage projects efficiently.
Conclusion
Projects don’t fail because of bad ideas; they fail because teams aren’t clear on what needs to happen and when.
And task dependencies play a major role in how a project progresses. The entire dependency map serves as input to creating the project baseline. When managers ignore them or don’t plan them properly, deadlines are miscalculated and missed, teams do the same work twice, or someone gets stuck waiting idly because they don’t have what they need to work effectively.
However, it’s not hard to manage them once you understand them. When you track and visualize dependencies, your team gains control, clarity, and confidence.
ProofHub helps you turn confusion into coordination, so projects stay on track, no matter how complex. It allows you to map task dependencies, see how they are related, and keep everyone on the same page.