Every organization has a set of objectives to achieve. To achieve those objectives, organizations plan to undertake a set of initiatives. However, due to the limited resources, only a few initiatives can be executed at a time. Project portfolio management is a structured process of selecting, organizing, prioritizing, executing, and managing the project initiatives to achieve the organizational strategic objectives while maximizing the business value by investing resources in high-value projects.
Project portfolio management includes the following key activities:
- Defining the project selection criteria
- Identifying, selecting, prioritizing, and authorizing the projects to be included in a portfolio based on the established criteria
- Allocating resources for the projects
- Monitoring & controlling the projects in the portfolio
- Reporting the progress to the stakeholders
PMI categorizes project portfolio management activities into three portfolio management process groups: the defining process group, the aligning process group, and the authorizing and controlling process group. However, to make it easy to understand, we have explained the process of project portfolio management in easy steps beyond a standard framework.
Read this guide to understand the importance and benefits of project portfolio management, the process of project portfolio management, tools for project portfolio management, and various other things a portfolio manager should be aware of.
What is project portfolio management?
Project portfolio management is the application of appropriate knowledge, processes, skills, tools, and techniques to select, prioritize, execute, and manage the right programs and projects to achieve the strategic objectives of an organization. It focuses on maximizing the business value and return on investments by investing the limited organization’s resources in work aligned with the strategic goals, priorities, and objectives of the organization.
How does project portfolio management differ from program and project management?
Project portfolio management is different from program management and project management. Program management focuses on the management of the projects within the program linked together through a related and common objective, whereas the portfolio components (programs and projects) may not necessarily be interdependent or linked through a common objective but align with shared overarching organizational goals and priorities. Similarly, project management is largely concerned with the management of an individual project and achieving specific deliverables within budget and time that support specific organizational objectives.
What is a project portfolio?
A project portfolio is a collection of projects and programs managed together to achieve strategic objectives. Projects in a portfolio may not necessarily be interdependent or related, but are aligned to achieve shared strategic business objectives.
What is a project program?
A project program is a group of projects that are interrelated or linked through common objectives and managed as a group instead of independently.
What is a project?
A project is an independent temporary endeavor undertaken by a company to achieve a defined outcome objective.
The relationship between portfolio, program, and project management is that portfolio management selects the right projects and programs aligned to organizational objectives, portfolio management groups the interrelated projects and focuses on achieving the success of the program, and project management focuses on achieving specific deliverables of an individual project.
A portfolio is an integral part of organizational planning & strategy. It is a representation of an organization’s intent, direction, priorities, strategies, and progress. If a portfolio is not aligned to its organizational strategy, the organization should reasonably question why the work is being undertaken in the first place.
It is the role of a portfolio manager to manage a company’s project portfolio to achieve the strategic objectives of an organization.
What is the role of a portfolio manager?
Executives, PMOs, program managers, project managers, or anyone interested in managing a portfolio of projects and programs may have to fulfill the following specific responsibilities:
- Establishing and maintaining a framework and methodology for portfolio management within the organization
- Establishing and maintaining relevant portfolio management processes
- Guiding the selection, prioritization, balancing, and termination of portfolio components
- Continuously reviewing, reallocating, reprioritizing, and optimizing the portfolio
- Providing key stakeholders with a timely assessment of portfolio component selection, prioritization, and performance
- Measuring and monitoring the value to the organization through portfolio performance metrics and targets, such as benefit ratios, return on investment (ROI), and net present value (NPV)
- Establishing and maintaining appropriate infrastructure and systems to support portfolio management processes
Why is project portfolio management important?
According to the Project Management Institute’s pulse survey, inefficient project management processes cause nearly 12% wastage of organizational resources.
Project portfolio management helps organizations choose the initiatives aligned with organizational strategic objectives and priorities. This helps organizations maximize the return on investments and make the best use of the organizational resources by utilizing them on the most valuable & high-impact project initiatives.
In addition to that, project portfolio management helps ensure each project has the necessary resources so that projects are not competing for resources.
This act of choosing the right projects, prioritizing projects based on the strategic and business value, and making necessary resources available for each project drives the organization towards strategic goals, increases the likelihood of achieving the goals, and makes a company more profitable and competitive by efficient use of resources.
What are the benefits of project portfolio management?
Project portfolio management leads to a vast range of benefits for an organization when performed correctly. Have a look at the key benefits.
1. Strategic alignment to maximize the business value
Project portfolio management focuses on selecting projects that align with an organization’s strategic objectives and priorities. This ensures the strategic alignment of the company’s work with the organizational goals, resulting in the use of resources in the right direction.
Further, the PPM process involves prioritizing projects based on their contribution to the company’s strategic goals. This helps you eliminate the endeavors with low impact and make the most of the available resources, resulting in maximizing business value and return on investments.
2. Resource optimization to provide the necessary resources for each project
Competing for resources is a common problem in organizations. PPM includes a comprehensive and structured process of identifying, selecting, prioritizing, and authorizing projects. This ensures each project has sufficient resources to be completed on time, and only the projects that can be completed are committed by the organization based on the availability of resources.
3. Better decision-making to increase the chance of project success
PPM involves a comprehensive database of information and cross-functional collaboration with stakeholders to analyse and choose the investments. This helps you make objective and data-driven decisions. In addition to that, with the clear metrics to measure the project performance, PPM makes project governance and performance management easy with well-defined frameworks, helping portfolio managers make better decisions.
4. Effective risk management to reduce the risk of project failure
PPM identifies high-risk projects, low-value projects, and possibilities of projects competing for resources at an early stage with portfolio planning. This helps in better risk mitigation and management with clear risk management strategies to reduce the risk of project failure.
What is the process of project portfolio management?
The process of project portfolio management includes identifying, selecting, prioritizing, governing, allocating resources, monitoring & controlling, and reporting the contributions of the portfolio components.
Disclaimer: These are the general activities performed in project portfolio management. It is hard to explain the process of project portfolio management in the full scope, as the implementation depends on various factors such as organizational project management maturity, the scale of the portfolio management, and the industry.
By organizational project management maturity, we mean: Level 1 – The initial process, Level 2 – Structured process and standards, Level 3 – Organizational standards and institutionalized processes, Level 4 – Managed processes, and Level 5 – Optimizing the process
By scale of portfolio management, we mean enterprise project portfolio management.
By the industry of portfolio management, we mean IT project portfolio management.
Even The Standard of Portfolio Management by PMI notes, the knowledge described in the guide does not mean it should always be applied uniformly to all portfolios; the organization and portfolio manager are responsible for determining what is appropriate for any given portfolio.
This guide standardizes the process of project portfolio management in three portfolio management process groups and five portfolio management knowledge areas in nearly 200 pages. To make it easy to understand and provide you with a decent overview, I have explained the process here in five basic steps.
Here is a step-by-step guide to project portfolio management:
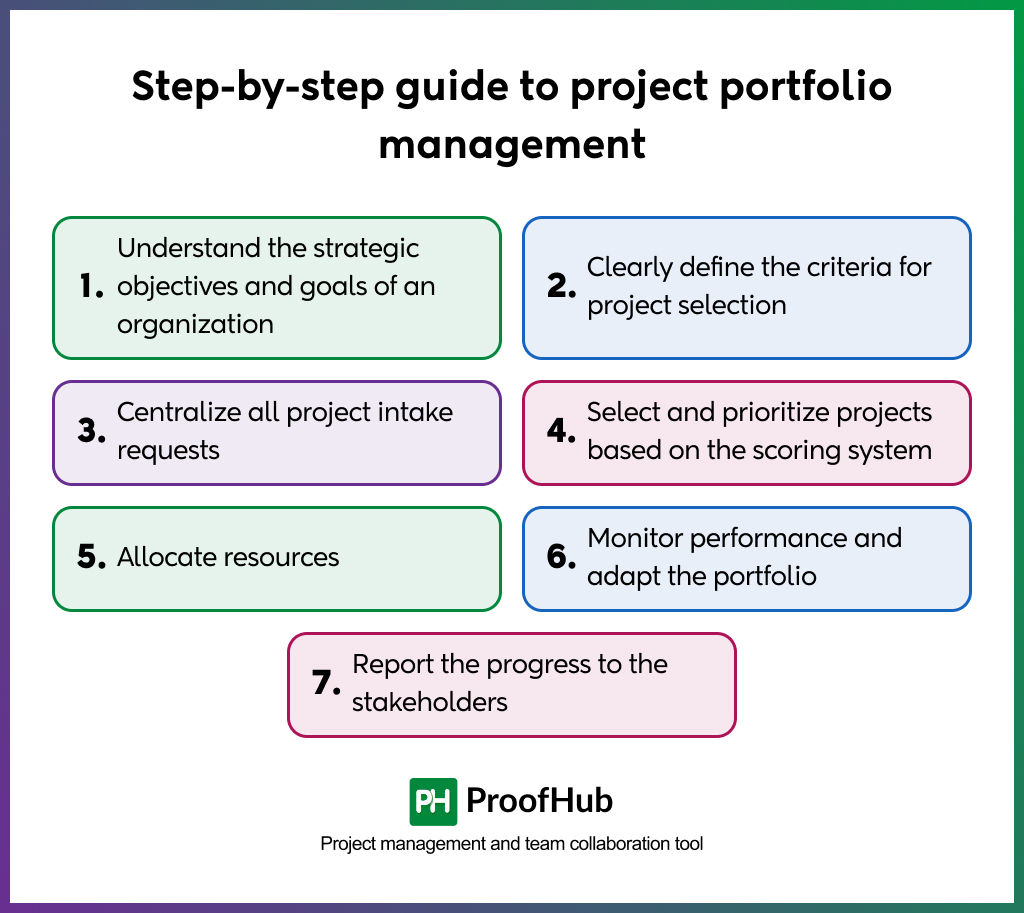
1. Understand the strategic objectives and goals of an organization
The first step of project portfolio management is to understand the strategic goals, objectives, and priorities of the organization. To do so, a portfolio manager needs to work with the leadership, sponsors, board of directors, or C-level executives responsible for defining the organizational strategic objectives and goals.
Project discussions
An organization can have multiple portfolios supporting multiple strategic objectives. But the first step is always the clarity of the organizational priorities, business objectives, and goals, as it will help you establish the selection criteria for the projects and clearly map each project initiative to the parent strategic goal & objective.
Examples of strategic goals and objectives can be increasing sales, improving organizational processes & efficiency, expanding to new markets, new product development, and growth of infrastructure.
2. Clearly define the criteria for project selection
Selecting the right work aligned with the organizational strategic objectives is the primary goal of project portfolio management. To do so, organizations need to build a comprehensive project selection process.
To define the criteria for project selection, the organization requires organizational data, project details, and resource data.
Organizational data includes things like the type of skills people in the organization have, how many people have those skills, and what projects they are assigned to.
Project data includes information on all the projects of the organization and key details and attributes such as Project Name, Project Code, Project Manager, Project Description, Project Milestones, current status, resource assignments, project interdependencies, project cost, project budget, and project business value.
Resource data that includes the information of resources, such as name, primary skill, and rate, and financial information, such as organizational budget and expenditure information.
Based on the list of all the strategic objectives and goals of your organization, available resources & budget, and organizational priorities, organizations create the criteria for project selection.
3. Centralize all project intake requests
The prerequisite of project portfolio management is to have all the database of information in a centralized database. Organizations use project portfolio management software and project management software to centralize all the key project, organizational, financial, and performance data. This software facilitates the open and transparent communication and consistent exchange of information to reach consensus and make decisions related to the project.
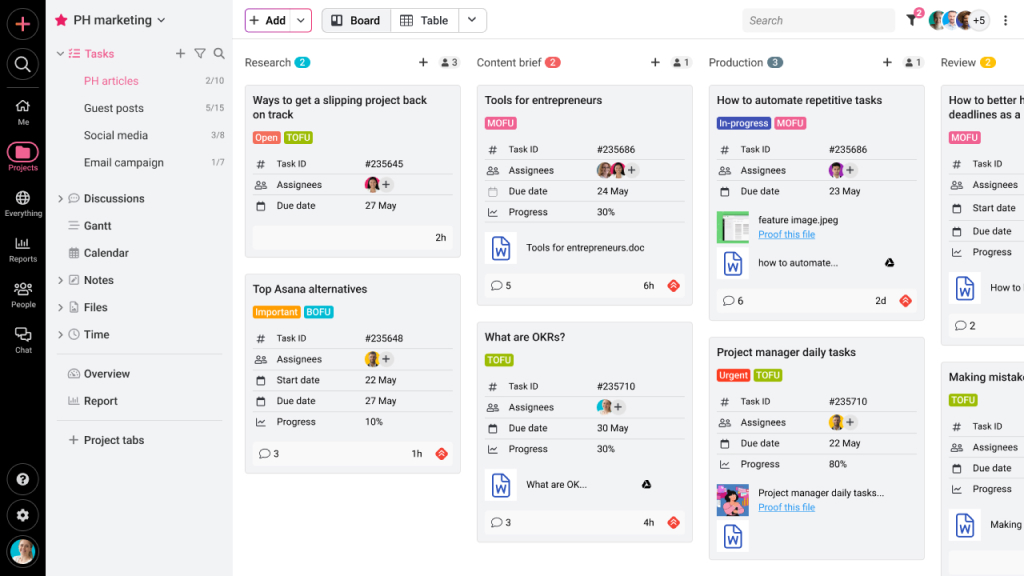
To avoid confusion and miscommunication, it is important to clearly define the role and responsibilities of each individual and the processes for selecting the project. It includes:
- Defining who has the authority to create a project
- Defining how a new project is created, approved, and funded
- Defining the flow of the Project Approval or Gating Process
- Describe the role and the responsibilities of the Management body that authorizes and approves projects and budgets
- Define whether standard Business Cases are used
4. Select and prioritize projects based on the scoring system
To select and prioritize projects, evaluate each project against defined criteria. A PPM team can use various selection methods for ranking projects based on strategic and business value. The most commonly used method is the scoring model. It ranks the project on a five-point scale (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) on various project selection parameters.
Here is an example of a multi-criteria scoring model:
- Strategic fit: (0–5, Weightage (w) 25%)
- Value (0–5, w 25%)
- Time criticality/deadlines (0–5, w 20%)
- Dependencies (0–5, w 10%)
- Risk & complexity (0–5, w 10%)
- Customer impact/NPS (0–5, w 10%)
These ratings are added to yield a quantified Project Attractiveness Score. For a project to be considered, it must clear a minimum score. This Score is a measure of the “value of the project to the company,” but incorporates strategic, leverage, and other considerations beyond just the financial value.
Prioritize each project by its overall business value (High, Medium, or Low) from highest to lowest priority. This will help the PMO make the right decision based on the data and choose the project in alignment with business goals and objectives.
5. Allocate resources
Allocate the available resources to the project. It includes assigning people, funds, time, tools, and other resources required to complete a project. To do so, first of all, you need to assess the availability of the resources by reviewing current resource allocation and workload charts. This helps you avoid projects competing for resources, spreading resources too thin, and overloading team members.
Modern PPM tools allow you to visualize team members’ tasks, balance workloads, and make quick adjustments to avoid bottlenecks
6. Monitor performance and adapt the portfolio
Selecting the right project for a portfolio and allocating resources are part of planning the project portfolio. Monitoring and controlling are a part of alignment and management of the project portfolio.
Alignment simply means tracking the progress of all the projects in the portfolio and making sure projects are aligned with corporate or strategic goals and resource goals. The purpose of this phase is to evaluate performance, identify problems. and make adjustments as necessary to keep projects on track.
If projects are not performing well, the PPM team decides on redistribution of resources and budget, revision of the project & budget schedule, and delaying or canceling projects and modeling alternate project portfolios.‘
There are various techniques, performance metrics, standard governance guidelines, and tools to align and manage the project portfolio.
To do so,
- Set up dashboards and KPIs to constantly monitor status, budget, risks, and outcomes.
- Use performance analytics to detect issues early, resolve resource conflicts, and verify ongoing strategic alignment.
- Regularly reassess active and incoming projects to maximize collective value and minimize risks.
- Employ prioritization models and scenario analysis to adjust resource distribution, add or remove projects, and adapt to changing business or market conditions.
- Use project management and portfolio management software dashboard and reporting tools for data analysis and decision-making.
Book a free demo of ProofHub to understand how it helps organizations with project portfolio management.
7. Report the progress to the stakeholders
Stakeholder management is a key part of portfolio management. A portfolio manager has to report the progress of the portfolio to the key stakeholders and coordinate efforts with project and program managers. Reports help you track and report the progress transparently.
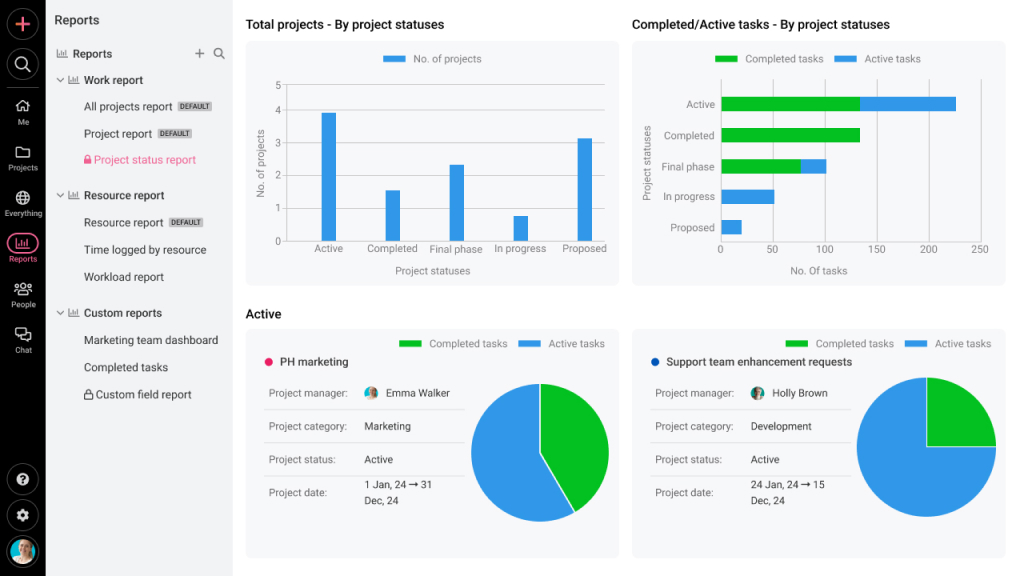
To do so, track the established KPIs such as cost, schedule, risk, quality, resource usage, and monitor strategic KPIs such as benefits realization and OKR progress. This helps you keep all the stakeholders updated, informed, and involved, and secure the buy-in for dynamic decision-making.
What are the best tools/software for project portfolio management?
To manage a project portfolio, a portfolio manager needs a certain set of tools for project intake management, resource management, database management, and reporting & analytics. In the early days, Excel spreadsheets were the way to go, but today, portfolio managers have a vast range of portfolio and project management software.
According to Fortune Business Insights, the global project portfolio management (PPM) market size was valued at USD 4.74 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 5.04 billion in 2024 to USD 9.23 billion by 2032.
Here are some of the most popular tools used for project portfolio management:
1. Oracle Primavera – Best for project portfolio management
Oracle Primavera is an enterprise-grade project portfolio management software that helps organizations plan, schedule, and manage complex projects. It helps you with project scheduling, resource management, and project management.
2. Smartsheet – Best for work management
Smartsheet is a work management software that helps you streamline the project intake process, plan projects, and provide real-time insights into project portfolios with interactive dashboards.
3. ProofHub: Best for project management and collaboration
ProofHub is an all-in-one project management and team collaboration software that helps you plan, execute, and manage project portfolios. It comes with powerful collaboration features to facilitate teamwork.
4. Tableau: Best for data analysis
Tableau is a data analytics platform that helps you connect, visualize, and analyze data from various sources. It transforms data into interactive reports and dashboards to help businesses make data-driven decisions.
5. Google Drive: Best for document management and collaboration
Google Drive is a cloud storage platform that helps you share, store, and access files from anywhere over the internet. It plays a key role in creating a centralized database of information for project portfolio management.
What are the challenges in project portfolio management? (+Best practices)
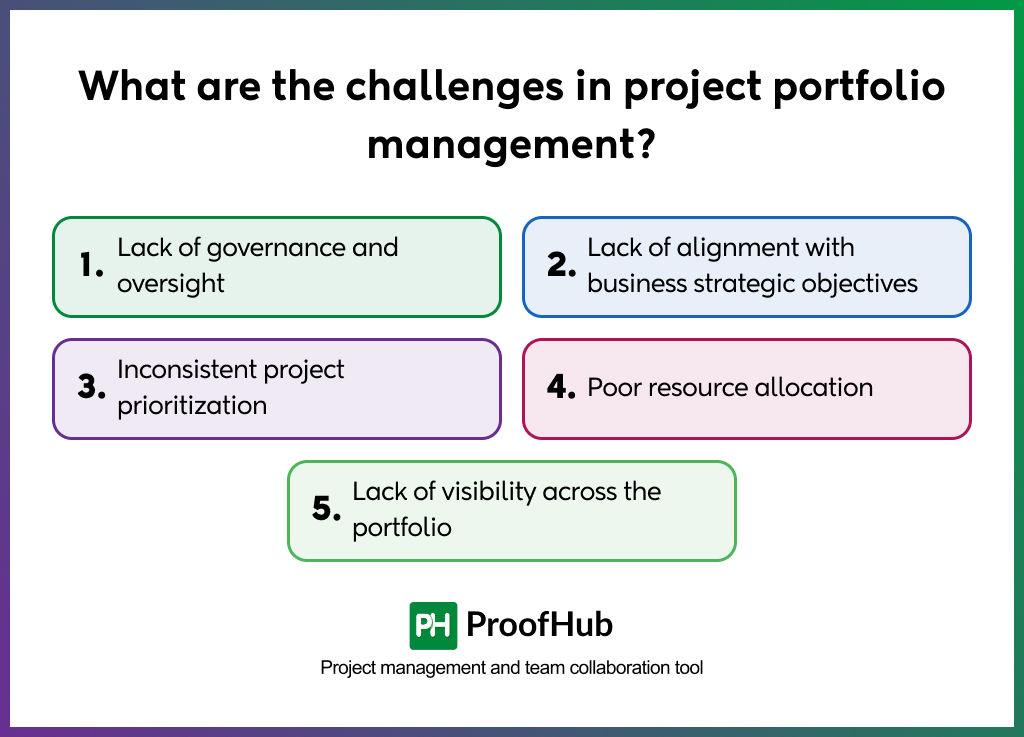
A project portfolio manager is going to face certain challenges in project portfolio management. Have a look at them and the best practices to resolve those challenges.
1. Lack of governance and oversight
Weak governance structures make it difficult to set accountability, maintain transparency, and ensure consistent processes in portfolio management.
- Define clear roles and responsibilities.
- Create standard workflows and clear decision-making frameworks.
- Track commitments and review governance.
2. Lack of alignment with business strategic objectives
Projects are often approved based on short-term goals, individual department goals, executive influence, or ambitions. This leads to misalignment with strategic objectives.
- Establish clear evaluation criteria upfront.
- Make sure every project request links explicitly to strategic goals/OKRs.
3. Inconsistent project prioritization
Conflicting priorities, lack of a standardized and objective framework, potential power biases, and ineffective risk management lead to poor project prioritization. This makes it difficult to maximize business value.
- Make the project prioritization process transparent
- Use the RACI matrix to clearly define the roles and responsibilities
- Involve cross-functional stakeholders to reduce biases and ensure effective risk management
4. Poor resource allocation
Poor estimation of resources or overcommitment creates resource bottlenecks and makes projects fight for resources.
- Use standard methods for capacity planning.
- Consider resource skills, availability, and risks.
5. Lack of visibility across the portfolio
Poor transparency into project status, resource use, and progress across the portfolio results in blind spots for leadership and decision-makers.
- Maintain a centralized portfolio with status, costs, benefits, and owners.
- Use dashboards to track progress.
- Standardize reporting across projects.
What industries and companies benefit from project portfolio management?
The common industries and companies that benefit from project portfolio management are Information Technology (IT) & Software Development, Financial Services, Construction, Engineering & Infrastructure, Manufacturing & Automotive, and Energy, Utilities & Oil & Gas. Top companies include Microsoft, Google, JPMorgan Chase, Bechtel, Toyota, and National Grid.

