“Trying to manage a project without project management is like trying to play a football game without a game plan.” – K. Tate
Managing IT projects is like executing a football game, it needs a well-designed plan, organization and good execution. In the world of IT projects, the manager is the coach who is responsible for efficient project execution and timely delivery.
Just like a winning team needs more than talent—it needs coordination, strategy, and adaptability—IT projects require more than just technical know-how. It needs IT project management.
Having spent over 15 years in this industry, I’ve witnessed the challenges newcomers face when building a career in IT project management. The learning curve can be steep, but with the right guidance, you can develop the skills needed to excel.
In this guide, you’ll discover the core concepts of IT project management and learn practical strategies for overseeing projects from start to finish. I recommend starting at the beginning, and reading throughout in order. Each section will help you build your foundations of IT projects, their management, giving you the take on the right tools to make the project better than the last.
What are IT projects?
IT projects are the initiatives related to information technology (IT) infrastructure, systems, and development. It includes projects like software development, hardware installations, network upgrade, infrastructure upgrades, cybersecurity initiatives, cloud migrations, data management and analytics, and implementation of IT services.
Most people think of IT projects as software development projects but there’s a lot more to it. Any information technology driven initiative designed to improve business operations can be considered an IT project.
For example, if a business wants to build a mobile app, upgrade its website, move data to the cloud, or install information technology hardware, all of these come under the realm of IT projects.
What is IT project management?
IT project management refers to the application of project management principles to the IT domain. It is the process of planning, executing, monitoring, and controlling IT projects from their very beginning to the end.
The process ensures that the IT solution aligns with the organization’s while minimizing risks.
IT project management is different from regular project management in the fact that it requires technical expertise and knowledge to perform and manage the project work. IT managers often work with technical teams which include developers, designers, engineers, and other IT experts who work together to plan, build, test, and launch IT solutions. Without the right technical skills and knowledge, it is hard for a manager to execute IT projects.
Just like regular projects, an IT Project Manager is responsible for managing IT projects. An IT project manager has to adapt to shifting user needs, align with product roadmaps, and oversee intricate system integrations that require both speed and precision.
What is the importance of IT project management?
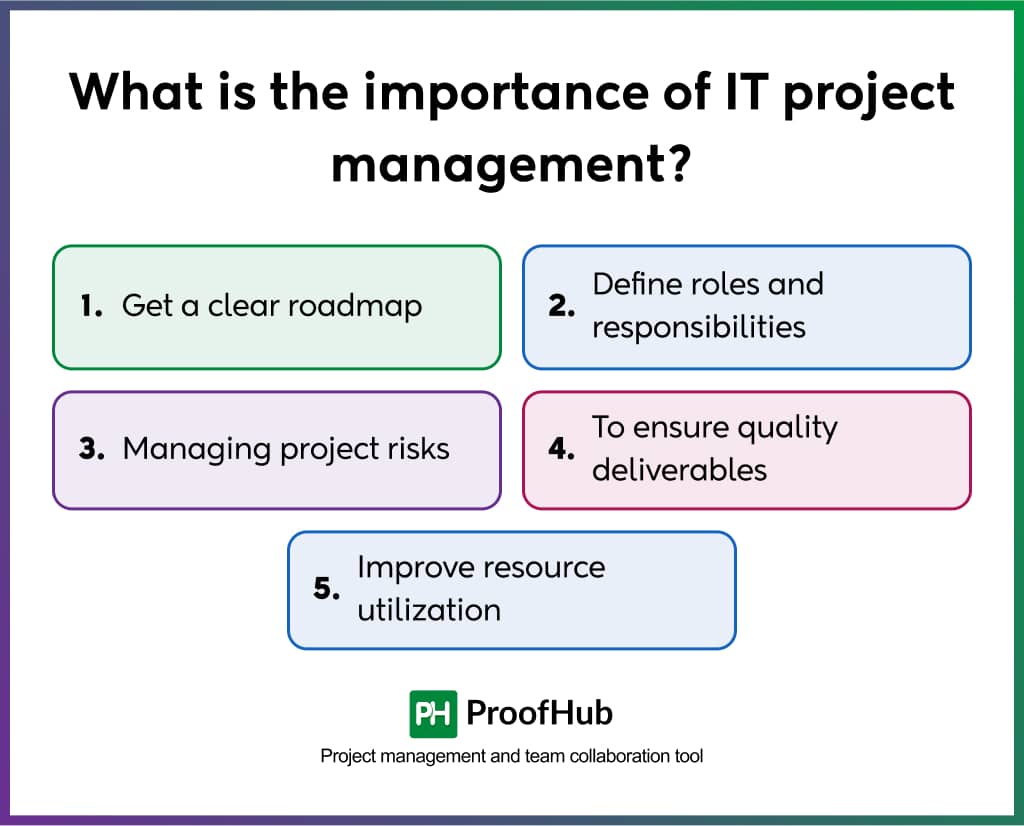
Effective IT project management is the backbone of successful technology implementations. It helps you complete an IT project within budget and time of defined quality. Let’s explore how structured IT project management can help IT initiatives:
1. Get a clear roadmap
A well-executed IT project management begins with defining the requirements of a project and translating them into actionable tasks. This process creates a clear roadmap that guides the entire team through each phase of development, eliminating confusion and providing direction.
2. Define roles and responsibilities
One of the core components of IT project management is to define clear roles and responsibilities for each individual in the project. Team members will be clear about their roles and what is expected of them. This clarity prevents task duplication, reduces confusion, and ensures all project components have designated owners.
3. Managing project risks
To be successful, IT projects involve identifying potential risks before execution. The project management framework will help you track the progress, identify any bottlenecks and technical challenges, and mitigate risks due to increased visibility throughout the IT project lifecycle.
4. To ensure quality deliverables
IT project management follows the process of quality management. It makes sure that the quality outcomes of the project are achieved by involving them in each step of the project and getting approvals from stakeholders before submission.
5. Improve resource utilization
Project management involves breaking a project into small tasks and defining the dependencies between tasks. Thus, you can easily calculate the resources required for a project and predict when tasks will be completed. This leads to better resource allocation and accurate estimates.
What are the phases of IT project management?
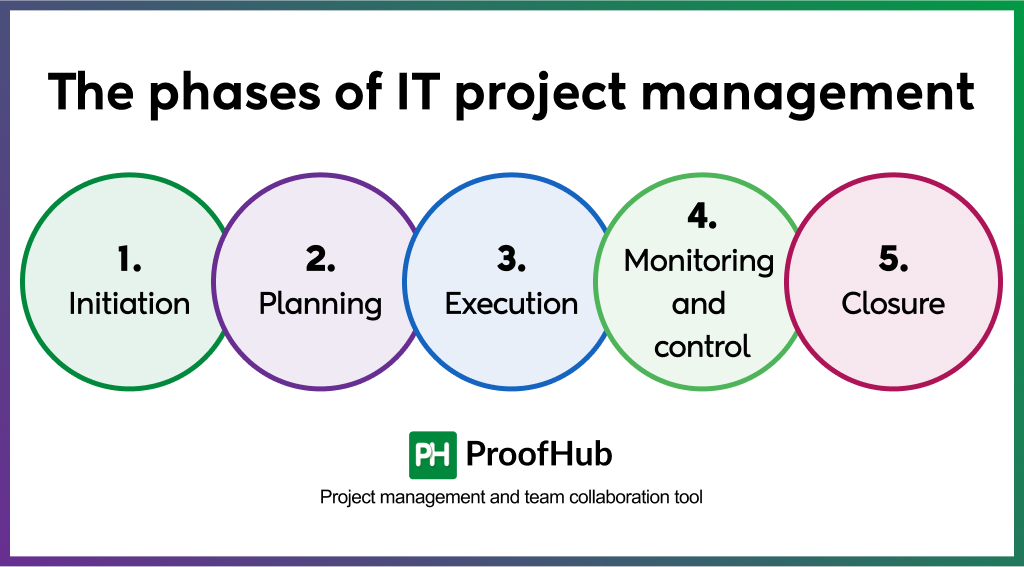
There are five IT project management phases which can be used to manage IT projects to ensure each step is planned, tracked and executed effectively. These phases include:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Execution
- Monitor and control
- Closure
1. Initiation
The initiation phase is the first and foremost step to manage a project. It involves defining the project’s purpose, scope, goals, and feasibility. The main goal of this phase is to identify the project requirements, decide if the project is worth pursuing and gain approval from stakeholders.
A project proposal is formed, feasibility studies are conducted, and a project charter is created to formalize the existence of the project with the approval from the stakeholders. This phase sets the foundation for the entire project.
2. Planning
IT project planning deals with the creation of a project roadmap. It involves breaking a project into smaller parts, determining the resources required for each task, creating detailed schedules, budgets and assigning owners.
Team collaboration is essential between the IT manager and team members to develop a well-organised plan. It is essential to ensure that everyone involved in the project understands their roles and the impact of their work on the project timelines.
3. Execution
In this phase, a project team executes the project plan to create the project deliverables. Taking action on the planned activities is the major aim of execution. It is the most challenging phase for an IT project manager, as unexpected challenges can occur.
4. Monitor and control
During the monitoring and controlling phase, the project manager tracks the project’s progress against the plan. This phase is all about ensuring the project stays within budget and scope and is delivered on time. If there are any issues or risks, they are identified and addressed immediately.
5. Closure
This is the last phase of IT project management. It involves finalizing all deliverables, ensuring all the requirements are met, and transferring ownership to the operations department. A thorough review and documentation of lessons learned are also crucial to closing the project effectively.
IT project management methodologies

IT project management methodologies provide you with the best practices, guidelines, and tools for managing an IT project. To manage complex IT projects, managers rely on project management methodologies to adapt to the complexity of different projects. These methodologies provide standard guidelines for everyone to follow and stay on the same page.
Let’s break down the most popular IT project management methodologies!
- Waterfall: It is a linear, sequential, step-by-step approach to project management where each phase must be completed before the next one begins. It’s suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and minimal changes.
- Agile: It is an iterative and flexible approach that breaks a project into small parts and works on smaller parts in iterations. Teams work in short cycles, gather feedback, and adjust as they go.
- Scrum: Scrum is a specific type of Agile methodology where work is done in short, time-boxed periods called sprints (usually 2–4 weeks).
- Kanban: Kanban is also an Agile framework that uses a Kanban board and WIP limits to manage a project.
- Water-Scrum-Fall: It is a hybrid project management methodology which combines the elements of waterfall and scrum methodologies to manage projects which require stability and flexibility.
To have a profound knowledge of the IT project management methodologies, explore our detailed guide on project management.
Tips to manage and deliver IT projects successfully
Managing IT projects is no piece of cake, you must have comprehensive knowledge to get it right. Having a carefully designed strategy plays a crucial role in meeting project deadlines, budgets and desired outcomes.
The following are some steps to manage your IT projects:
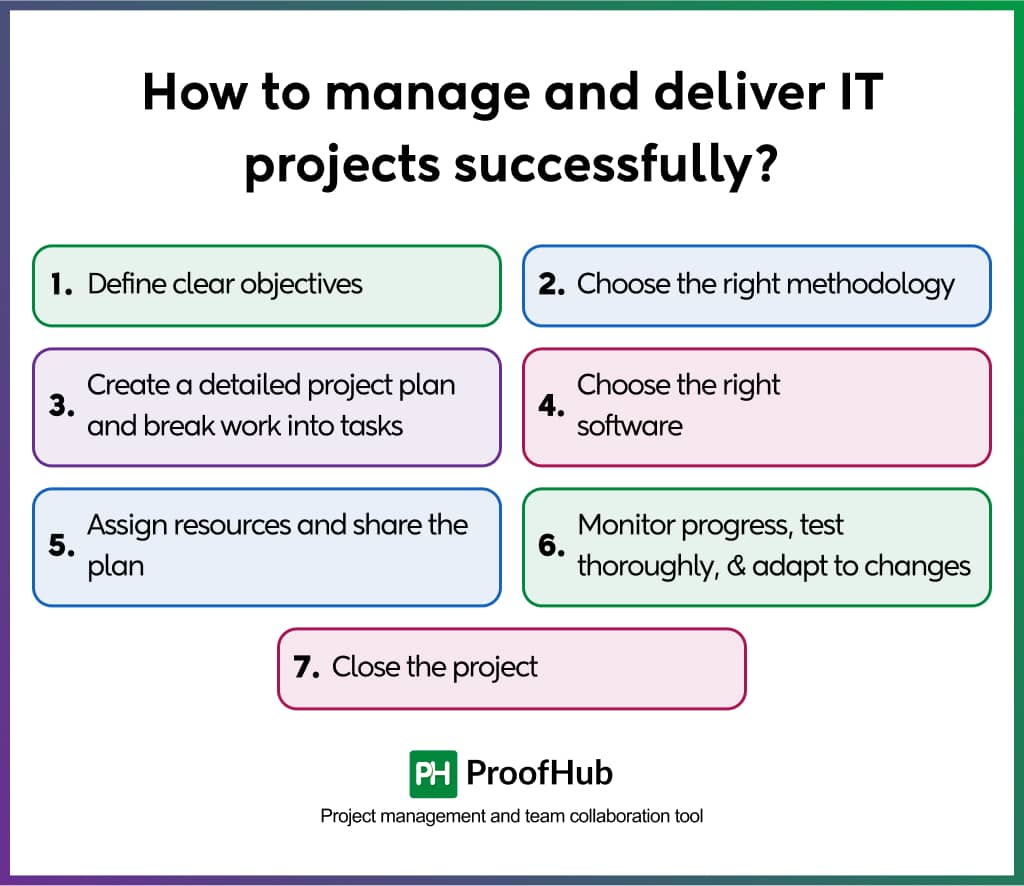
1. Define clear objectives
This is the first step in managing the projects. Define project objectives clearly to have an idea of what success looks like. This involves detailed research of the project, collecting requirements from the stakeholders, identifying problems a project aims to solve, and defining the expectations of the project.
By talking to the stakeholders, you can paint a clear picture. Having clear communication will help you understand the project objectives deeply, and you won’t miss a single detail about it.
2. Choose the right methodology
Selecting a methodology that matches your project’s needs increases your chances of project success. It is complex to choose the right methodology. While selecting, you must consider factors like the project’s nature, complexity, the size and expertise of the team, the level of customer involvement, organization’s risk tolerance, and the project’s duration.
- Waterfall: For well-defined projects with fixed requirements
- Agile: For projects with unexpected and changing requirements
- Hybrid: For projects with defined project requirements but that require adaptability during execution
Disclaimer: Based on the chosen methodology, the techniques used for managing a project change. However, in general, the below-mentioned steps are followed in every project in some way.
3. Create a detailed project plan and break work into tasks
The next step is to break down the project into small and more manageable tasks. You can use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to break a project into smaller parts.
WBS breaks a project into three levels: deliverables, tasks, and sub-tasks. Sub-tasks are the lowest level where you estimate resources required, estimate durations, and set deadlines for the project activities. This helps you create a detailed project plan.
You need to identify the potential risks that might arise in execution. You can identify and plan the mitigation strategies using a risk assessment matrix.
You can use tools like Gantt chart to visualize the project plan on the timeline, define project activities, and set dependencies between various tasks and subtasks.
4. Choose the right software
It is hard to perform all the project activities manually because it will be ineffective. You need a competent project management software to manage an IT project. These tools can help you collaborate with teams, keep all the project-related documents in a single place, plan tasks, create a project plan, and track the progress. Choosing the right IT project management software is essential for all IT project managers. Without it, you cannot execute the desired plan effectively.
5. Assign resources and share the plan
Once your project goals and tasks are defined, the next crucial step is to assign the right resources and communicate the plan clearly to everyone involved. Assign team members to tasks based on their strengths, availability, and workload to avoid burnout and ensure efficiency.
Make sure sufficient tools, budgets, and timelines are in place to start work on the project. Then, share the complete project plan, including milestones, responsibilities, and deadlines, with your team and stakeholders.
Transparency at this stage sets expectations, aligns efforts, and builds accountability from day one. When everyone knows what they’re doing, when it’s due, and who they’re working with, execution becomes smoother and more predictable.
6. Monitor progress, test thoroughly, and adapt to changes
To ensure successful project delivery, it’s crucial to monitor progress, test thoroughly, and adapt to changes as they come. Use visual tools like Kanban boards or Gantt charts to track real-time progress and conduct regular check-ins to stay aligned.
Integrate continuous testing at every stage to catch issues early and validate that deliverables meet expectations. Be open to change, whether it’s shifting client needs or unexpected roadblocks, by reassessing timelines, adjusting scope, and refining your approach. This combination of visibility, quality control, and flexibility helps teams stay on course, deliver value, and respond smartly to any curveballs along the way.
7. Close the project
This is the last step of a project where a project manager sends the final deliverables for formal acceptance. Depending on the nature of the project, a project is either completed or transferred for ongoing maintenance and support.
A manager conducts a retrospective, defines what went well and what could be improved, and documents insights for future projects.
What challenges do IT project managers face?
IT project managers’ challenges go beyond planning and training the team. There is so much more to their jobs than mere seamless delivery. The projects are not as simple as they sound because technologies keep changing, and adapting to them is difficult. Also, managing different teams may seem like an easy task, but it is quite challenging.
Some of the IT project management challenges faced by the project managers are:
1. Unclear project scope
One of the most common challenges faced by IT project managers is a poorly defined project scope. When there is no clear information about stakeholders’ requirements and agreement on what needs to be delivered, it leads to poor project planning. Thus, stakeholders end up changing requirements mid-project, resulting in scope creep. It leads to delays, budget overruns, frustration, and confusion among team members.
2. Unclear job roles and responsibilities
Poorly defined job roles and responsibilities lead to confusion among team members on what is expected of them.
3. Poor communication
No matter what kind of project it is, different teams spread across various departments complete the project. It adds to the complexity when there are no proper communication channels. Miscommunication between developers, testers, and business teams leads to errors, misaligned expectations, and the project gets delayed.
According to a Project Management Institute (PMI) report, more than 50% of respondents in a survey believe communication plays a crucial role in achieving an organization’s objectives.
4. Poor estimation of resources
Underestimating costs, time, and resources required to complete project activities results in unrealistic timelines, budget and time constraints. This leads to project delays, burnout of team members, and constant challenges to finish the project on time while staying on budget.
5. Poor risk management
IT projects face a variety of risks, including errors, technical failures, data breaches, and integration issues. Project managers need to anticipate these risks early, create backup plans, and allocate funds in the budget for unexpected issues. At the same time, they must ensure the end product meets quality standards.
What are the best practices for managing IT projects?

Delivering a successful IT project isn’t just about following a checklist—it’s about adopting the right mindset, methods, and habits throughout the project lifecycle. As technologies evolve and teams become more distributed, applying best practices becomes essential to keep projects aligned, on schedule, and within budget.
1. Involve stakeholders early and often to avoid scope creep
Involving the major stakeholders when you initiate the project is a great practice so that no one is left behind.
You must keep your stakeholders updated. Also, you can ensure a regular check-in, which ensures that feedback is heard, priorities stay aligned, and no surprises are left.
2. Use RACI matrix
You can use the RACI matrix to clearly define the roles and responsibilities. The RACI matrix is a chart that defines who is responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed for a task. It helps clarify roles and responsibilities.
3. Encourage team collaboration
Foster a culture where developers, testers, designers, and other team members collaborate openly. You can either make communication strategies or use a tool to streamline them. Clear ownership and accountability help improve efficiency and reduce misunderstandings.
4. Use estimation techniques
To make realistic estimates, you can use various estimation techniques
Most commonly used techniques include:
- Bottom-up estimation: It breaks work into the smallest tasks and estimates resources for each task
- Three-point estimation: It calculates project resources for three scenarios: Optimistic, Pessimistic, and Most Likely.
- Analogous estimation: It compares the current project with similar past projects for estimates
5. Practice effective risk management and use the right project management tools
Test early and test often. Make sure there are regular quality checks to catch errors, security issues, or gaps in user experience before final delivery. The right tool doesn’t just organize your work, it transforms how your team collaborates and delivers results. Choose a platform like ProofHub that brings everything into one place.
Manage your IT projects with project management software like ProofHub
Managing IT projects requires structure, coordination, and the ability to adapt to constant change. From planning and scheduling to collaboration and risk management, every stage needs a centralized approach to keep things on track. That’s where having the right tool makes all the difference.
ProofHub simplifies the complexity of IT project management by bringing planning, task tracking, team collaboration, time management, and reporting into one unified platform, eliminating the need for multiple disconnected tools.
With features like Gantt charts, Kanban boards, built-in communication, time tracking, and real-time reports, ProofHub helps IT teams stay organized, meet deadlines, and deliver quality results.
Whether you’re managing software development, system upgrades, or tech rollouts, ProofHub empowers you to keep everything under control. It’s scalable, easy to use, and designed to keep your projects moving forward smoothly and successfully.
FAQs
How to become an IT project manager?
To become an IT project manager, gain a solid foundation in IT or computer science, build experience in team coordination or tech projects, and develop strong communication and leadership skills. Earning certifications like Project Management Professional (PMP) or Certified ScrumMaster can boost credibility. Practical experience and adaptability are key to success.
What does an IT project manager do?
The core responsibility of an IT project manager is to take the project through hurdles and changes and take the project to seamless execution. The actual roles and responsibilities of an IT project manager include:
- Deliver the project on time and within budget
- Oversee the full lifecycle of multiple projects
- Estimate costs and allocate resources efficiently
- Identify potential risks early
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Build realistic timelines
- Create a space for collaboration
How to manage project management risks in IT projects?
To manage risks in IT projects, you must start by identifying potential risks early. Use a risk register to track them, build contingency plans, and communicate frequently with stakeholders. Tools with built-in reporting and tracking, like ProofHub, make it easier to spot and mitigate risks before they ruin your project.
How do you ensure effective communication in IT projects?
Ensure effective communication in IT projects by centralizing updates, clarifying roles, and using the right tools. A platform like ProofHub keeps everyone aligned, informed, and on track. Encouraging open feedback and active listening within the team also promotes a culture of transparency and trust. When team members feel heard and informed, collaboration becomes more meaningful and productive.
What are the essential skills for an IT project manager?
An IT project manager should have a mix of technical know-how and soft skills. Key skills include project planning, time management, risk assessment, and budgeting. Equally important are leadership, communication, problem-solving, and the ability to work with cross-functional teams. Familiarity with Agile, Scrum, and project management tools is also essential.

