A stakeholder engagement plan acts as a strategic manual that offers in-depth insights into your stakeholders’ interests, power, and influence.
As a project manager, you can’t afford to overlook this crucial element while keeping all other factors synchronized. Regardless of stakeholders’ motivations or roles, tailoring your communication style to suit each one is essential for ensuring project success.
Below, we’ll introduce you to the stakeholder engagement plan, its importance, and its key components. We’ll also walk you through the five essential steps to help you draft your plan. In your organization, the general public lacks interest in your success narrative.
What is a stakeholder engagement plan?
A stakeholder engagement plan (SEP) is a formal document that outlines how an organization will communicate and interact with its stakeholders throughout a project’s lifecycle.
Stakeholders can be broadly classified into the following categories:
- Internal Stakeholders: These are individuals within the organization, including employees, functional managers, team leads, department heads, project managers, and board members.
- External stakeholders: These include individuals or organizations outside the organization, including clients, suppliers, customers, company partners, and regulators.
- Financial stakeholders: These are parties that have a financial stake in the organization. They typically include shareholders, creditors, and investors.
Why is a stakeholder engagement plan important?
Here are a few reasons that highlight why drafting a stakeholder engagement action plan is important:
- Keeps stakeholders informed about the project’s course and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Establishes clear communication pathways so all parties stay well-informed and engaged throughout the project.
- Enables early identification and mitigation of risks and conflicts associated with stakeholder groups, minimizing disruptions, one of the key reasons why projects fail.
- Builds trust, confidence, and buy-in for your organization by showing stakeholders that their perspectives are valued.
- Aligns stakeholder expectations with project outputs at each phase to ensure more impactful results.
- Fosters collaboration and trust between team members and stakeholders through consistent communication and engagement.
Major components of the stakeholder engagement plan
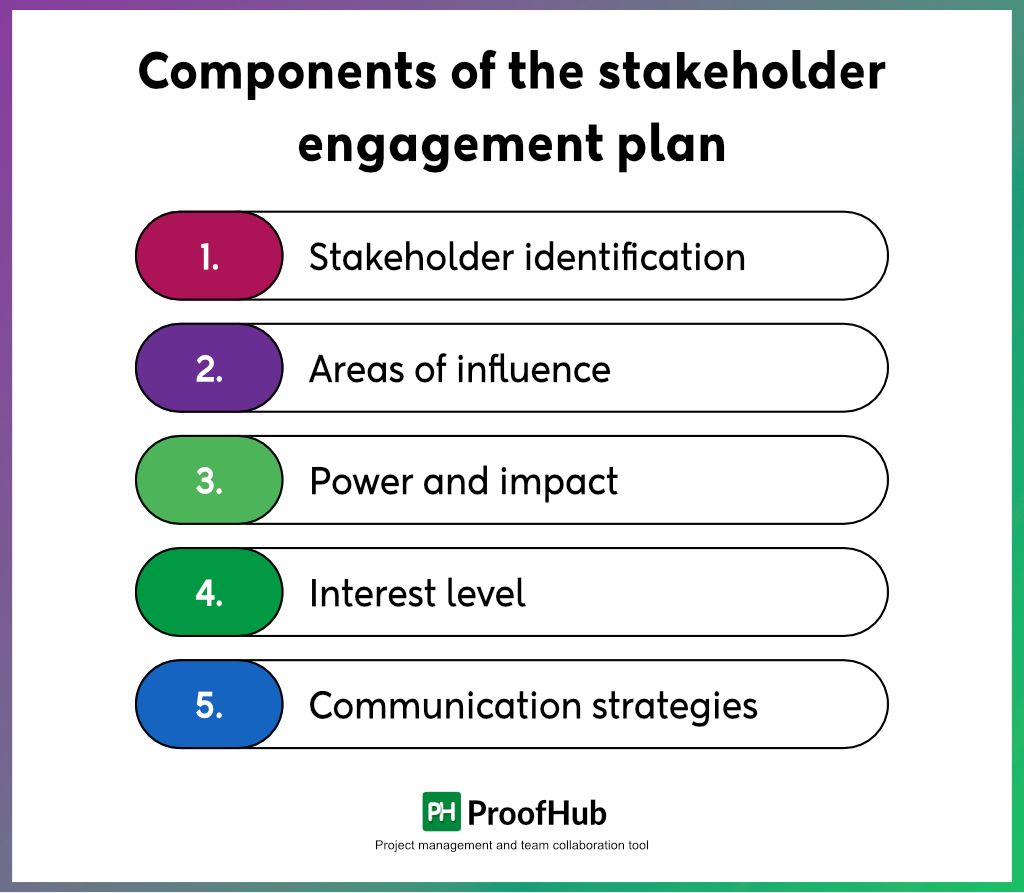
While creating an action plan for stakeholder engagement is subjective, some basic components are universal.
Here is a quick rundown of the major SEP components that ensure project sustainability:
1. Stakeholder identification
First and foremost, start listing all your stakeholders. After thorough analysis, make a list or a register of all your project stakeholders.
Be it internal or external, smaller or larger, powerful or less, clearly state all stakeholder information. The rationale behind the evaluation is to ensure their concerns and perspectives are respected and addressed.
2. Areas of influence
Once the stakeholder register is ready, rate down stakeholders’ influential levels on the project and organization. Not just that, you also need to identify the areas that their involvement will most impact.
The scale of the stakeholder influence ranges from very high to very low. These are typically categorized as very high, high, medium, low, or very low.
3. Power and impact
The next thing to consider is the power and impact a stakeholder can exert. Both these factors are in correlation with each other. Where power defines the ability to influence a project, the extent to which the project may affect or be affected by each stakeholder is known as impact.
By understanding these two components, organizations can strategize their actions accordingly.
4. Interest level
You should conduct the next segregation based on the interest and engagement levels. You can utilize this information to tailor your approach based on their preferences.
The five levels of stakeholder engagement include Leaders, Contributors, Neutral, Resistant, and Unaware. The first four mentioned stakeholders are generally aware of the project’s impact, but their participation varies. However, Unaware stakeholders show little to no involvement.
5. Communication strategies
The final component is to craft an engagement plan for stakeholders. Remember, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. This document outlines the communication channels the company aims to use, the frequency of those communications, and the information that will be shared.
And all these factors may vary for every stakeholder involved. Putting all these elements together, you can effectively manage their expectations while keeping them engaged.
Read more: Streamline your stakeholders’ communication using the best 15 team communication tools for businesses
Steps to create a stakeholder engagement plan
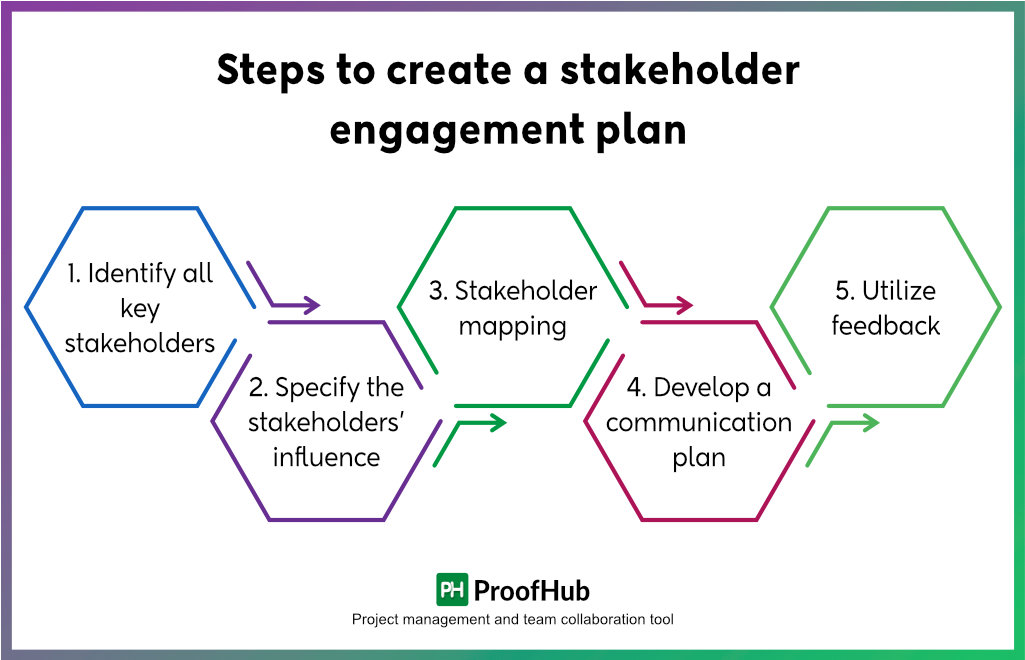
Developing a systematic stakeholder engagement plan ahead of project kickoff is necessary to ensure that they stay informed of all the developments.
Here are the five key steps to create a plan in a way that not only engages stakeholders but also increases the likelihood of project success.
1. Identify all key stakeholders
Creating a stakeholder engagement plan is incomplete without identifying the prime stakeholders. No matter how easy it may sound, the task is complex. Why? Because there is a high chance that you can unintentionally compromise the comprehensiveness of the stakeholder list.
So, the first step to increase stakeholder engagement is listing all the stakeholders. And for better clarity and transparency, you should divide them into interest groups.
The 5 different phases of stakeholder engagement or interest are:
- Leaders: These people have a strong influence on project development and are fully aware of the project’s impact.
- Contributors: These people show strong support for project development and are aware of the project’s impact.
- Neutral: These people neither resist nor support the project but are aware of its impact.
- Resistant: These people show resistance to change but are mindful of project outcomes.
- Unaware: These people are clueless about the project’s impact, so participation isn’t even a thing here.
You should also define what specific roles they will play in the project. Along with how the project will impact them.
2. Specify the stakeholders’ influence
Once you are done identifying the stakeholder roles and engagement levels, the next step is to specify their scope of influence.
The basic goal is to identify and understand stakeholders’ motives and expectations from the project. Also, what will be their areas of involvement, and to what extent will they be invested in that zone?
Putting yourself in stakeholders’ shoes is a great practice to grasp their motivation behind the involvement. When you keep track of all this stuff, you lay the foundation for successful project management.
The 5 different parameters of stakeholder influence are:
- Very high: A stakeholder with significant influence and ultimate control over decisions.
- High: A stakeholder with a major influence on project actions and decisions.
- Medium: A stakeholder with moderate influence but a significant part of the decision-making process.
- Low: A stakeholder with limited influence, not substantial enough to take into consideration
- Very low: A stakeholder with minimal engagement but no control over decisions.
3. Stakeholder mapping
The third stage of creating your SEP is to map out your stakeholders. You can visualize the stakeholder analysis process using the Power/Interest matrix by plotting all the involved stakeholders based on the two factors that we have discussed above-
- Interest
- Influence

The goal is to figure out what actions should be performed to prioritize the stakeholders. It presents you with a clear picture of where you need to invest your efforts.
For instance, if you keep feeding in whole-level knowledge and updates to people with low interest and take for granted high-power people, you are just banging your head against a wall. No fruitful results at all.
The four major categories include:
- High power – High interest: These are the most influential stakeholders with the biggest impact. These people usually belong to the “Leaders” and “Contributors” categories. You should ensure keeping them satisfied while managing their expectations.
- High power – Low Interest: These stakeholders are as influential as the above category. You should keep them in the loop about all the major project updates, despite their being uninterested. Why? Because they hold the power. And you need to be cautious and strategic when dealing with them.
- Low power – High interest: Stakeholders of this category belong to the “Neutral” or “resistant” category. Although they do not hold much power, you need to keep them adequately informed and feel involved. Because of being ignored, they can even resist change.
- Low power-low interest: Unaware stakeholders usually fall in this category. You should not waste your time and efforts in contacting and communicating with them. But by sending them occasional updates, you can keep the door open for them to take an interest in the future.
4. Develop a communication plan
After a thorough stakeholder mapping, you should immediately start working on building your communication strategy. Your engagement plan should provide a clear outline of when, how, and how much you will communicate with your stakeholders.
With this strategic approach, you will have ultimate control over how you want to update your stakeholders. So that stakeholders from each quadrant have access to only relevant information.
To do this best, put all your project info in one place, like project management software. A platform like ProofHub can be especially helpful, as it allows you to organize timelines, share updates, and streamline communication across all stakeholder groups from a single dashboard.
Different communication channels that can serve the need are:
- Virtual meetings
- Email communications
- Real-time chats
- In-person visits
- Conferences
Also, how many times will they be expecting planned interactions? It is another trait that should not be compromised at all.
5. Utilize feedback and fine-tune your strategy
Feedback provides insights into what is going right and what areas need modification for better performance. These changes can come to the surface only when you leave a space for feedback intake. You need to actively practice this approach during the entire project lifecycle to prevent your communication strategy from derailing.
Now, these modifications may arise due to numerous reasons, be it unexpected events or stakeholders’ behavior. The key is to act upon their suggestions or concerns for quick resolution. And that can only happen when you stay in sync with the evolving stakeholder needs.
Bonus tips for stakeholder engagement plan
- Promote transparency and consistency: Provide regular updates and promote clear communication across all stakeholder quadrants.
- Prioritize stakeholders strategically: Not all stakeholders require the same level of attention. Use your stakeholder mapping to prioritize engagement efforts and allocate time and resources accordingly.
- Adapt your communication methods: Every stakeholder has a preferred way of receiving information; some prefer detailed reports, others short updates. Tailor your delivery to their preferences.
- Actively listen and respond to feedback: Encourage two-way communication. Don’t just collect feedback, act on it, and close the loop so stakeholders feel heard and valued.
- Document every key interaction: Keep a record of meetings, commitments, concerns, and updates shared with stakeholders. This creates accountability and helps you track alignment over time.
- Use collaboration tools effectively: Centralize stakeholder communication using platforms like ProofHub to avoid email overload, manage updates, and maintain visibility.
ProofHub – your ultimate stakeholder engagement planning solution
A stakeholder engagement plan is an integral component of a project planning strategy. Because setting a stakeholder communication framework yields some invaluable results.
ProofHub gives you the flexibility to customize your stakeholder communication strategy. It allows you to develop a tailored plan and implement it while keeping your stakeholders updated and engaged.
Not just that, the all-in-one platform centralizes all your business operations by bringing all your projects, tasks, and stakeholders together. So, no more scattered efforts, just streamlined communication.
Frequently asked questions
What are the 5 principles of stakeholder engagement?
The 5 key principles of stakeholder engagement are –
- Early & ongoing engagement
- Setting clear goals
- Building relationships
- Ensuring openness and transparency
- Pursuing inclusivity
What are the 5 levels of stakeholder engagement?
The five levels of stakeholder engagement are –
- Leaders: Most significant participants and most influential
- Contributors: Significant participants who support project goals
- Neutral: Neither supports nor opposes the project
- Resistant: Actively oppose the project’s progress
- Unaware: Neither aware of the project nor its impact
What is the key goal of stakeholder engagement?
The major goal of stakeholder engagement is to achieve project success, ensuring all the relevant parties are informed, involved, and aligned.
What are the three pillars of stakeholder engagement?
The three pillars of stakeholder engagement are –
- Stakeholder identification
- Stakeholder engagement
- Stakeholder participation
Can a stakeholder engagement plan change during the project?
Yes. A good stakeholder engagement plan is dynamic. As stakeholders join, leave, or shift in interest or influence, the plan should be reviewed and adjusted accordingly. Regular feedback loops help ensure the plan remains relevant.

