Project efficiency is the measure of how well a project uses its resources— including budget, time, and human resources— to complete the agreed work as per the defined quality.
Say, if project efficiency is 100%, it means the project completes the work within the planned resources. It suggests the project plan was accurate and well-crafted.
If it is less than 100%, it means the project requires more resources than planned. Reasons can be anything from poor planning to ineffective execution to unexpected risks.
If it is more than 100%, it means the project utilizes fewer resources than planned. Now, it can either be a good or a bad signal. Maybe the project team performed well and executed the plan better, or your original estimates were inaccurate.
In every scenario, project efficiency is a good measure to evaluate project performance. The concept of project efficiency focuses on making improvements by optimizing project processes, reducing inefficiencies and waste, and maximizing productivity without compromising the quality of deliverables to achieve the project goals within schedule and budget.
In this article, we will discuss what exactly project efficiency is, how it affects projects, factors affecting project efficiency, how to improve it, and how to measure project efficiency.
What is project efficiency?
Project efficiency is the measure of how well a project uses its resources (time, money, people, and tools) to achieve its goals. It involves optimizing processes, reducing waste, and maximizing productivity without compromising the quality of deliverables.
Project efficiency focuses on how well a team can align resources, people, and processes to achieve the desired outcomes with maximum utilization, and not just about finishing on time or staying within budget. In other words, it’s about delivering the planned results with the least possible waste of resources.
This requires a careful balancing act between the three core constraints of any project: scope, time, and cost, often called the project management triangle. Understanding this balance is crucial because without it, projects are much more likely to fail.
Project efficiency doesn’t only mean ‘doing things faster or economically’. It is about maintaining the right balance between speed, cost, and quality. For example, suppose a project can deliver the same quality of results using fewer hours, lower costs, or reduced resources, and manages to produce more or higher quality deliverables with the same level of input. In that case, it is considered to be an ‘efficient’ project.
Unlike ‘effectiveness’, which asks if you are doing the right things to meet goals, ‘efficiency’ focuses on how well resources are managed to achieve those goals. Understanding this difference lays the foundation for enhancing your project’s performance.
A project is said to be efficient if it:
- Achieves outputs with minimal effort, which means the team avoids unnecessary use of time, budget, or resources
- Processes are streamlined, which means workflows are structured to reduce bottlenecks, delays, and redundancies
- Resources are optimally allocated, which means resources are assigned where they can create the most impact
- Value delivered is maximized, which means the project creates outputs that meet or exceed quality standards within planned constraints
Conversely, major causes of inefficiency include poor planning and scope creep, inadequate resource allocation, ineffective communication, failing to manage risks, unrealistic deadlines, limited stakeholder involvement, and weak project management practices.
Also read: Effectiveness vs. Efficiency: Key differences you need to know
Despite best intentions, studies consistently show a high rate of projects that fail to meet their initial objectives, whether that’s delivering on time, staying within budget, or achieving a desired level of quality. Standish Group’s Annual CHAOS 2020 report states that 66% of technology projects (based on the analysis of 50,000 projects globally) end in partial or total failure. Even successful projects often suffer from delays and budget overruns, eroding their profitability and impacting stakeholder satisfaction.
Factors affecting project efficiency
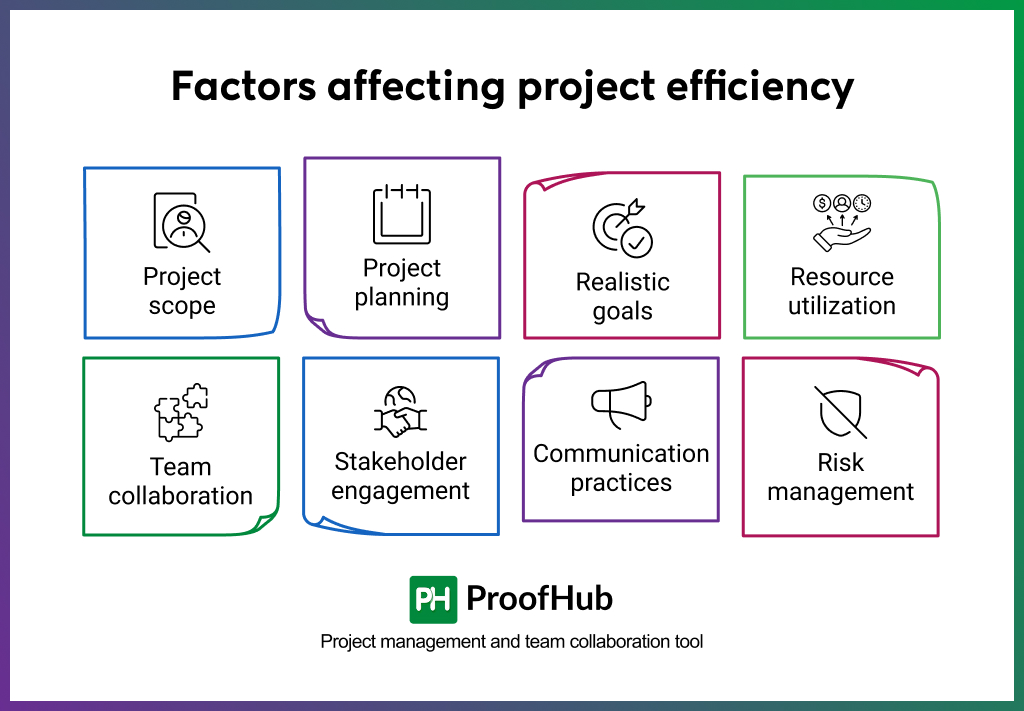
Several factors play a role in shaping how efficiently a project runs, from planning to execution.
1. Clarity of project scope: A well-defined scope sets the expectations of the project, what will be done, what won’t, and what outcomes are expected. A vague or shifting scope, commonly known as ‘scope creep’, makes it challenging to manage resources, track progress, and maintain efficiency.
2. Project planning: A well-structured project plan acts like a roadmap, aligning tasks, resources, and timelines. Poor planning, on the other hand, creates confusion, wastes effort, and reduces efficiency.
3. Realistic goals and milestones: Achievable goals keep the team focused, while milestones ensure that tasks become manageable in various steps. Each milestone acts as a checkpoint, giving teams a sense of progress and stakeholders visibility on whether they are moving in the right direction.
4. Effective resource utilization & estimation: Accurate estimation and efficient use of people, budgets, and tools directly impact productivity. Estimating the required resources early helps in setting realistic timelines and budgets, while effective allocation ensures those resources are used optimally. Matching the right skills to the right tasks avoids delays, rework, and wasted effort, whereas poor estimation and allocation cause bottlenecks, cost overruns, and inefficiency.
5. Team collaboration and dynamics: The quality of collaboration within a team directly affects project efficiency. Strong collaboration enables faster problem-solving, adaptability to changes, and sustained momentum, while poor coordination can create friction, slow progress, and lower overall efficiency.
6. Stakeholder engagement: The level and timing of stakeholder involvement affect how efficiently projects progress. Early and active engagement supports alignment and smooth decision-making, whereas delayed or limited engagement can cause misalignment, rework, and last-minute disruptions.
7. Communication practices: Clear and timely communication keeps teams and stakeholders aligned, while miscommunication or information gaps can lead to misunderstandings, duplicated efforts, and delays.
8. Risk awareness and management: How well risks are identified and managed influences a project’s ability to stay on track. Proactive risk management helps prevent setbacks and maintain efficiency, whereas unaddressed risks can derail plans and slow down progress.
How to improve project efficiency (effective tips)
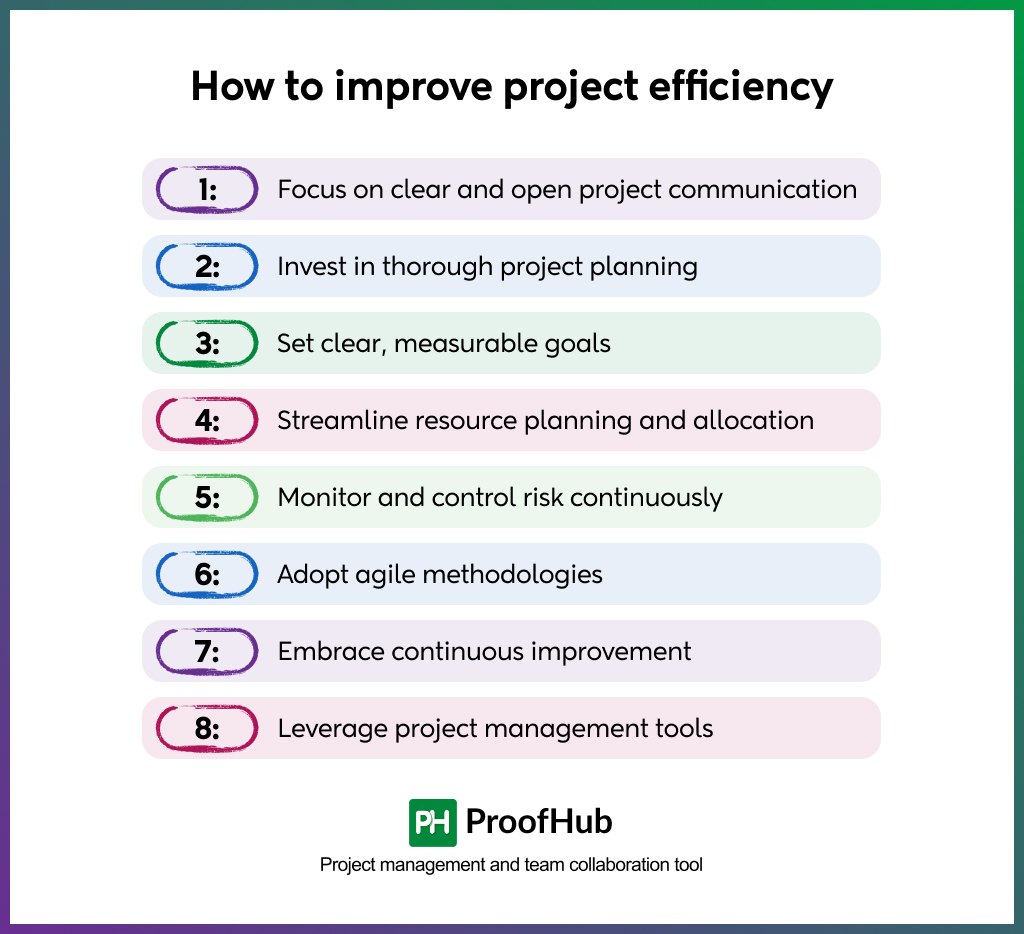
1. Focus on clear and open project communication
Communicating the project status, scope, risks, and upcoming events to stakeholders and others is a crucial aspect of smooth project execution. Without effective communication, those involved will not be able to work together, and no consensus decision can be made. This will have a significant impact on project delays and activities.
Don’t assume everyone automatically knows how to approach a project. Communicate with intent, whether you are sharing information, asking for input, clarifying issues, or resolving a problem. The more precise and transparent the communication, the fewer misunderstandings, delays, and reworks your team will face. By encouraging openness, you also build trust, improve collaboration, and ensure the timely resolution of issues that contribute to project efficiency.
For example, consider what happens when expectations aren’t clear. Stakeholders aren’t sure how they’ll be impacted, team members are unclear on their responsibilities, or the project’s purpose isn’t well understood. These gaps lead to confusion, redundant communication, unnecessary rework, and people chasing answers to questions they shouldn’t have to ask. Instead, clear roles and shared expectations, communicated early and often, keep everyone aligned and focused on outcomes.
2. Invest in thorough project planning
A successful project begins long before the first task is executed. Poor planning leads to significant project delays, resulting in costs that are 20-30% or more above original budgets, which severely impacts profitability and timelines.
When planning is inadequate or missing, projects often suffer from unclear direction, unrealistic timelines, hidden risks, poor coordination, and inefficient use of resources—leading to confusion, rework, delays, budget overruns, and compromised results.
By dedicating time upfront to create a detailed roadmap, you can anticipate challenges, set realistic timelines, and establish benchmarks for success that all ultimately lead to improving project efficiency. This approach enables early identification of risks, optimized resource allocation, and ongoing performance tracking, all of which boost project efficiency.
3. Set clear, measurable goals
Every stakeholder should have a clear understanding of the project’s schedule, goals, and milestones. These milestones are necessary checkpoints that show how work is progressing and how far the project is from completion. While timelines can be refined as more information emerges, the project team knows what needs to be achieved by when and what tasks contribute to each milestone. Having clarity keeps efforts aligned, ensures resources are allocated effectively, and allows teams to measure their progress objectively.
One of the most effective ways to do this is by using the SMART framework, which helps transform vague objectives into actionable targets:
- Specific: Gather stakeholder input, define deliverables, and identify key constraints such as time, budget, and resources. Specific goals provide a roadmap for the team.
- Measurable: Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress. Measurable goals make it easier to evaluate whether the project is on course.
- Achievable: Goals should be realistic and within the team’s capabilities. Overly ambitious targets can lead to burnout and inefficiency.
- Relevant: Align goals with the project’s overall objectives to ensure resources are directed toward tasks that deliver real value.
- Time-bound: Every goal should have a clear deadline. Deadlines create urgency, keep the team focused, and help prevent costly delays.
By applying SMART principles, project managers can provide clarity, keep teams motivated, and ensure time and resources are used where they matter most.
4. Streamline resource planning and allocation
Aligning resources with project priorities ensures that the right people and tools are used where they create the most value, rather than working on low-impact tasks.
When resource planning is not streamlined, multiple teams or tasks might need the same person, tool, or equipment at the same time without knowing it. This causes conflicts, which slow progress. When planning is streamlined, managers can gain real-time visibility into who is available to redistribute tasks and prevent both overload and underutilization proactively, which is effective for project efficiency.
5. Monitor and control risk continuously
Risks such as budget overruns, scope creep, resource shortages, or technical issues can arise at any stage of a project and can quickly derail progress if not managed proactively. To safeguard efficiency, project teams should identify potential risks early, assess their impact and likelihood, and build clear mitigation and contingency plans.
Incorporating risk reviews into the regular project lifecycle, such as during status meetings or milestone check-ins, helps ensure that risks are continuously tracked and not overlooked.
Engaging key stakeholders in these reviews promotes alignment, transparency, and shared accountability for risk responses. Maintaining a central risk register also helps teams document issues, assign ownership, and monitor resolution progress. By anticipating risks instead of reacting to them after they occur, teams can protect timelines, control costs, minimize disruption, and maintain steady momentum even under pressure.
6. Adopt agile methodologies
Unlike traditional linear approaches, Agile breaks projects into smaller, manageable sprints, allowing teams to deliver value quite early and often. This iterative approach makes it simpler and much easier to work on feedback, adapt to changing requirements, shift to priority tasks, and prevent delays.
Agile practices such as daily stand-ups, sprint planning, reviews, and retrospectives encourage open communication, transparency, and shared ownership of outcomes, keeping the entire team aligned on high-priority tasks.
Involving stakeholders throughout the process ensures continuous feedback, early detection of issues, and alignment with evolving business or customer needs. This reduces the risk of costly rework at later stages and helps maintain steady momentum. By enabling teams to respond rapidly to change, stay focused on delivering value, and collaborate more effectively, Agile creates a dynamic environment that drives both speed and quality in project execution.
7. Embrace continuous improvement
Regularly review project performance to find out what worked well, what didn’t, and where processes can be refined. This involves conducting structured retrospectives, gathering feedback from stakeholders and team members, and analyzing key performance metrics such as delivery timelines, quality benchmarks, and resource utilization. Over time, this mindset builds a culture of continuous learning, where each project becomes faster, more efficient, and more resilient than the last, contributing to consistent long-term success.
8. Leverage project management tools
Project management tools do more than tracking tasks; they streamline communication, enable real-time collaboration, and provide centralized management for projects. By centralizing information, project management platforms reduce duplication, missed updates, and confusion, especially in hybrid or remote teams. Choosing tools that integrate seamlessly with your workflows ensures visibility, accountability, and efficiency across every stage of the project.
Also read: 15 best project management tools in 2026
How to measure project efficiency?
Organizations are increasingly required to manage projects with lower budgets and in shorter time frames. As a result, managers are often forced to make project viability decisions early in the project lifecycle.
One proven way to navigate this challenge is by using Earned Value Management (EVM), a project management technique that helps project managers track progress, identify risks, and make informed decisions.
EVM is based on the concept of earned value, which is a measure of the work that has been completed on a project relative to the work that was planned. By comparing earned value to planned value and actual cost, project managers can identify variances and take corrective action to keep the project on track.
To start applying EVM, it’s important first to understand its core concepts—the three key values that form the foundation for measuring project efficiency.
Step 1: Understand the three core EVM values
EVM is based on the following key concepts:
- Planned value(PV) is the value of the work that was planned to be completed on a project by a specific date. Example: By week 4, you planned to complete tasks worth $50,000. So PV = $50,000.
- Earned value (EV) is the value of the work that has actually been completed on a project by a specific date. Example: By week 4, you completed tasks worth $40,000. So EV = $40,000.
- Actual cost (AC) is the actual cost of the work that has been completed on a project by a specific date. Example: You spent $45,000 to finish that $40,000 worth of work. So AC = $45,000.
Step 2: Calculate EVM performance metrics
The three values are used to calculate the following EVM metrics:
- Cost variance (CV) is the difference between earned value and actual cost. CV measures the amount of money that has been overspent or underspent on a project. A positive CV indicates that the project is under budget, while a negative CV indicates that the project is over budget.
Formula: CV=EV−AC
Example: (CV = 40,000 − 45,000 = −5,000 → Over budget)
- Schedule variance (SV) is the difference between earned value and planned value. SV measures the amount of time that has been saved or lost on a project. A positive SV indicates that the project is ahead of schedule, while a negative SV indicates that the project is behind schedule.
Formula: SV=EV−PV
Example: (SV = 40,000 − 50,000 = −10,000 → Behind schedule)
- Cost performance index (CPI) is the ratio of earned value to actual cost. CPI measures the efficiency of a project’s cost performance. A CPI of 1.0 indicates that the project is on budget, while a CPI of less than 1.0 indicates that the project is over budget.
Formula: CPI=ACEV
Example: (CPI = 40,000 / 45,000 = 0.89 → Over budget)
- Schedule performance index (SPI) is the ratio of earned value to planned value. SPI measures the efficiency of a project’s schedule performance. An SPI of 1.0 indicates that the project is on schedule, while an SPI of less than 1.0 indicates that the project is behind schedule.
Formula: SPI=PVEV
Example: (SPI = 40,000 / 50,000 = 0.8 → Behind schedule)
Step 3: Interpret and use the results
These performance metrics can be used to track project progress and identify areas where the project is at risk. By taking corrective action early on, project managers can help to keep the project on track and achieve its objectives.
Once you have CV, SV, CPI, and SPI, you can:
- Identify early earning signs (CPI or SPI < 1)
- Assess which areas (time, cost, or both) need corrective action.
- Support data-driven decisions such as reallocating resources, adjusting scope, or increasing budget.
Managers can also forecast future performance using advanced EVM formulas:
- Estimate at Completion (EAC): Projects the expected total cost at project completion. Typical formula:
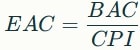
where BAC = Budget at Completion.
- Estimate to Complete (ETC): How much more money is needed to complete the remaining work?
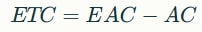
- Time Forecasting: Using SPI, schedule completion estimates can be recalculated to predict whether deadlines will be missed unless corrective action is taken.
Tool for enhancing project efficiency
Project management tools like ProofHub enable better risk management by identifying potential risks and providing solutions to mitigate them. These tools help project managers identify opportunities to reduce costs and improve project efficiency.
For example, by using task management to assign and prioritize work, collaboration tools to centralize communication and file sharing, visual planning features like Kanban boards and Gantt charts to track timelines, reporting and analytics to monitor progress and spot bottlenecks, and resource management to balance workloads and optimize team capacity, managers can streamline workflows, prevent delays, and ensure resources are used effectively.
Can project efficiency improve project success?
Yes, project efficiency plays a critical role in improving project success by ensuring that time, cost, and resources are used wisely to deliver outcomes that meet stakeholder expectations. Efficient project management reduces unnecessary effort, prevents delays, and maintains quality, which creates the right conditions for success.
What is the difference between project efficiency and project effectiveness?
The difference between efficiency and effectiveness lies in their focus: Efficiency is about how well the project is managed using time, cost, and resources to deliver a project.
While effectiveness is about whether the project achieves its intended goals, solves the problem, and satisfies stakeholders. To understand in a much simpler way, efficiency is about doing things right, while effectiveness is about doing the right things. Ideally, a successful project needs to it should be managed efficiently and to deliver outcomes that create real value.
Conclusion
Projects are often complex and full of challenges, which makes managing them effectively a demanding task. Delivering them on time, within budget, and according to scope requires careful coordination of people, processes, and resources.
However, simply meeting deadlines, budgets, or performance targets does not necessarily mean a project is successful. Project success can vary depending on the type of project—some are judged by immediate deliverables, while others are measured by their long-term impact. Success can also be assessed in absolute terms (meeting all agreed objectives) or in relative terms (achieving what was realistically possible given the constraints).
This is where project efficiency becomes crucial. Efficiency focuses on how well time, cost, and resources are used to deliver results. It ensures that every activity, decision, and resource allocation contributes meaningfully to the project’s goals and aligns with broader organizational objectives.
Since managerial decisions shape how resources are planned and used, they play a critical role in driving efficiency. Well-informed, timely decisions enable teams to work smarter, avoid waste, and steer projects toward both short-term milestones and long-term success.