
Collaborative brainstorming is one of the most effective ways teams generate fresh ideas, uncover new solutions, and spark innovative thinking. It is a structured process where teams work together to develop ideas and solve problems. Unlike individual ideation, collaborative brainstorming brings diverse minds together in a creative environment where people build on each other’s ideas and explore possibilities from multiple angles.
Collaborative brainstorming is not just a meeting or a creativity session; it is a dynamic process that combines open communication, collaboration, and a psychologically safe environment to help teams think beyond obvious solutions. When done well, it boosts innovation, increases team engagement, and unlocks quality ideas that are difficult to generate individually.
However, to achieve these outcomes, teams must adopt the right techniques, such as mind mapping, brainwriting, design thinking, storyboarding, or digital whiteboarding, and create an environment where everyone feels encouraged to contribute.
In this article, we will explore the benefits, core techniques, best practices, and essential tools for facilitating successful collaborative brainstorming sessions. Learn how to structure these meetings to foster creativity, capture every idea, and turn collective insights into actionable results.
What is collaborative brainstorming?
Collaborative brainstorming is a group-based ideation process where team members work together to generate ideas, solve problems, and explore creative solutions through open discussion and shared thinking. It is also known as crowdstorming.
It is built on the original concept of “brainstorming” introduced by Alex Osborn, an advertising executive and co-founder of BBDO, in the 1940s. Osborn developed brainstorming as a structured method to improve creative idea generation by encouraging open, judgment-free participation.
Unlike traditional brainstorming methods, which involve thinking in isolation, collaborative thinking builds on the idea that “two heads are better than one.” This strategy enables individuals to resolve problems, find effective solutions, and plan for efficient execution.
What are the benefits of collaborative brainstorming?
One significant benefit of collaborative brainstorming is that it encourages a wide range of ideas and perspectives, leading to more innovative solutions. It promotes team building and improves communication among team members. Furthermore, when more team members are involved in problem-solving, creativity thrives, and multiple ideas can be narrowed down to the best possible solution.

Let’s understand these benefits briefly:
1. Cross-functional innovation
Collaborative brainstorming breaks down silos and allows multiple perspectives from marketing, design, and customer-facing roles to contribute their understanding of the problem. When people with different perspectives come together, their diverse qualities spark fresh ideas that a single team member would have never discovered on their own. Teams from various backgrounds come together to think and find the best-suited solution that aligns with customer needs and business goals.
2. Creativity boost
Collaborative brainstorming sparks creativity as team members share ideas openly. One person’s thought can trigger another’s imagination, leading to creative ideas. It also inspires the quiet team members to participate as the focus shifts from being ‘right’ to exploring possibilities. This results in a space full of new ideas and creativity, boosting the overall quality of ideas and helping individuals think more creatively in future sessions.
3. Improved problem-solving
Collaborative brainstorming helps resolve complex problems through collective intelligence by gathering diverse viewpoints in one place. Different people approach different problems differently; one can see the process flaw, another can see the customer pain point, and another can see cost as an issue. When the team combines these different points of view, they tend to evaluate problems from all sides and reach a conclusion.
4. Better idea capture and prioritization
Collaborative brainstorming sessions help capture every idea in a single shared space using whiteboards, sticky notes, or digital tools. Once all ideas are out in the open, the team can assess them together, identify patterns, and prioritize what truly matters. This process helps prevent great ideas from being drowned out by louder voices or forgotten after meetings. It ensures that brainstorming doesn’t end in chaos but leads to clear, actionable next steps with the most valuable ideas moving forward.
5. Strengthened teamwork and communication
Brainstorming collaboratively strengthens team dynamics and communication through regular sessions. These collaborative experiences build trust among team members as people learn to share half-formed ideas without fear of judgment and see their contributions valued by colleagues.
6. Increase engagement and ownership
Collaborative brainstorming increases engagement as team members transform from passive participants into active contributors. When employees see their suggestions being heard, refined, and even implemented, they naturally feel more invested in the outcome. That sense of ownership drives greater accountability and enthusiasm to bring ideas to life. It’s no longer management’s idea; it’s our idea. And that emotional connection not only boosts morale but also improves follow-through, ensuring ideas don’t die after the meeting but turn into tangible results.
What are the best techniques for collaborative brainstorming?

The best techniques for collaborative brainstorming include Mind Mapping, Starbursting, Brainwriting, Storyboarding, and Round-Robin Brainstorming. Knowing these techniques is essential to generating a wide range of ideas to solve a problem. Moreover, these techniques will help encourage creativity by fostering a judgement-free environment and building on others’ ideas.
1. Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual brainstorming technique that organizes ideas in a tree-like structure, with a central concept at the center, main ideas branching outward, and sub-ideas extending from those branches.
When used collaboratively, it allows teams to build on each other’s thoughts, mirroring natural thinking patterns, using keywords, images, and colors to make connections visible and memorable. This approach helps groups brainstorm more effectively because everyone can see how ideas relate to each other in real-time, participate equally by adding branches, and quickly identify patterns or gaps in their thinking.
2. Brainwriting
Brainwriting is a silent, written brainstorming technique in which participants individually write down ideas on paper or a digital board before sharing them with the group, rather than speaking them aloud as in traditional brainstorming. This method helps overcome common brainstorming challenges like groupthink, dominance by louder voices, and the pressure to respond immediately, helping introverts and thoughtful processors to contribute equally.
A popular version is the ‘6-3-5 method’ where six people each write three ideas in five minutes, then pass their sheets to the next person who builds on those ideas or adds new ones, creating multiple rounds of silent ideation. By separating the generation phase from the discussion phase, brainwriting ensures that all ideas are captured without interruption or premature judgment, often resulting in a higher quantity and diversity of contributions.
The written format also creates an automatic record of all ideas, makes it easier to track who contributed what, and reduces anxiety for those uncomfortable with spontaneous verbal creativity, making it particularly effective for diverse teams or sensitive topics where people might hesitate to speak up immediately.
3. Starbursting
Starbursting is a brainstorming technique that focuses on generating questions rather than answers, using six-pointed star with “Who,” “What,” “Where,” “When,” “Why,” and “How” at each point to encourage a comprehensive and systematic exploration of a concept before moving to solutions.
Create a six-pointed star on a white board or digital canvas. Write the idea, project or problem in the middle of the star. Write one of the W’s on each point of the star. After generating a list of questions, the team can work through them to identify potential issues and unanswered questions before moving forward with solutions.
This technique is particularly valuable in the early stages of project planning, product development, or problem-solving because it helps teams identify potential challenges, uncover assumptions, and reveal gaps in their understanding before committing resources or making decisions.
4. Storyboarding
Storyboarding is a visual brainstorming technique that uses a sequence of drawings, sketches, or images to map out ideas, user experiences, or processes. The method allows groups to collaboratively sketch out key moments, transitions, and interactions in a tangible format that everyone can see, discuss, and refine together, making abstract concepts concrete and identifying potential issues or opportunities that might not emerge through verbal discussion alone.
Storyboarding turns abstract thoughts into a sequential story with images and captions, making complex ideas easier for everyone to understand and discuss. It allows teams to step into the user’s shoes, putting the user’s perspective at the forefront of the brainstorming process. This helps ensure that the final solution meets real needs.
5. Round-Robin brainstorming
Round-robin is a structured idea-generation technique in which each team member takes turns sharing an idea. This ensures equal participation and prevents dominant personalities from monopolizing the discussion.
The group sits in a circle, and the facilitator asks the first person to share an idea. The group then proceeds around the circle, with each person contributing one idea at a time. The facilitator records the ideas as they are shared. No criticism or elaboration on ideas is allowed until everyone has had a turn. Each participant writes down an idea on a card or sheet of paper. They can then pass the card to the person on their left, who reads the idea and adds to it.
This technique encourages equal participation, fosters collaboration, and provides structure to the idea-generating process.
Best practices for successful collaborative brainstorming
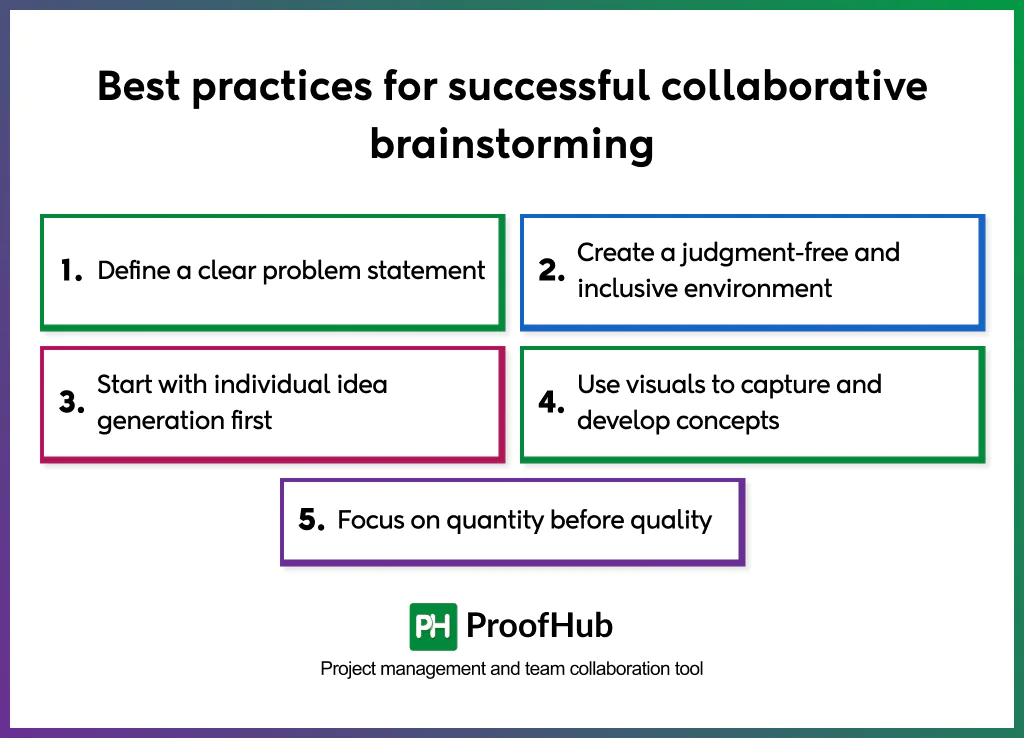
The best practices include setting clear goals and ground rules, creating a judgment-free, inclusive environment, and structuring the session to generate a high volume of ideas before evaluating them. Encourage new ideas, build on other’s suggestions, and use visual tools to help capture and develop concepts, while ensuring there is time for individual preparation and post-session follow-up.
1. Define a clear problem statement
The team should know exactly what challenge they are solving, who it impacts, and what outcome the session aims to achieve. A well-framed problem keeps ideas focused, avoids unnecessary tangents, and ensures everyone is working toward the same goal.
2. Create a judgment-free and inclusive environment
Set simple norms, no idea is a bad idea, don’t interrupt, avoid early criticism, and encourage building on others’ thoughts. This creates a space where people feel free to share openly—especially quieter or less senior members. When the room feels safe, teams generate more authentic, diverse, and original ideas.
3. Start with individual idea generation first
Give 5-10 minutes for everyone to jot down ideas privately. This prevents louder voices or leadership presence from shaping early thinking. It also helps introverted thinkers contribute on equal footing. By the time the group begins sharing, you already have a richer, more varied pool of ideas.
4. Use visuals to capture and develop concepts
Use whiteboards, sticky notes, or digital canvases like Miro or FigJam, or simple charts to map ideas visually. Visuals make it easier to identify patterns, organize thoughts, and strengthen promising concepts effectively.
5. Focus on quantity before quality
Early in the session, encourage teams to generate as many ideas as possible without evaluating them. High volume leads to unexpected connections and combinations. When participants feel free from judgment, they explore bolder and more unconventional ideas, which often become the foundation for breakthrough solutions.
What are the best tools for collaborative brainstorming?
Collaborative brainstorming tools help teams generate, organize, and refine ideas in real time. Whether they’re working in the same room or across different locations, teams can visualize thinking, structure ideation, and use seamless communication features to support both synchronous and asynchronous collaboration.
For mind mapping, Miro is a popular digital tool. Its multi-user interface makes it ideal for distributed teams, offering templates for mind maps, sticky-note sessions, flowcharts, and collaborative workshops. Mural is a similar tool that offers visual collaboration features, including timers, brainstorming & ideation, and design thinking and problem-solving frameworks.
For product, design, and development teams, FigJam, developed by Figma, works exceptionally well. It supports real-time co-editing and integrates with project management platforms, offering visual and functional brainstorming spaces with widgets, diagrams, and interactive elements.
For teams needing a brainstorming and discussion tool connected to project management, ProofHub offers an excellent combination of discussion threads, proofing, notes, and task management. Helping teams move ideas into actionable next steps without switching platforms.
Other useful tools include ClickUp for whiteboard collaboration, Stormboard for structured sticky-note-based ideation, and Notion for collaborative documentation and free-form idea sharing.
Choosing the right tool depends on team size, workflow, and the level of structure needed, but the best tools make idea generation easy, visually engaging, and accessible to everyone involved.
What are the challenges of collaborative brainstorming?
The main challenges of collaborative brainstorming include unequal participation, groupthink, lack of structure, idea overload, insufficient tools, and failing to convert ideas into action.
Unequal participation is one of the biggest challenges. When a few dominant voices take over the discussion, while quieter team members hesitate to contribute, it can lead to idea bias and reduce diversity of thought. Groupthink, commonly occurs when teams agree too quickly on ideas, without challenging or exploring unconventional alternatives. When teams prioritize consensus over exploration, creativity drops.
A lack of structure can disrupt brainstorming; without a clear goal and time limit, sessions often go off track, leading to scattered ideas and no clear direction. Similarly, too many ideas at once without filtering can make it challenging to evaluate and analyze the best ones. Teams may end up spending too much time exploring ideas without implementing any.
Lacking proper tools can create technological barriers, especially in remote teams. Poor tools or unstable connectivity can slow down collaboration and create frustration.
When the teams fail to convert ideas into action, brainstorming becomes just an exercise. Without defined next steps, ownership, prioritization, or end-goal brainstorming, ownership, prioritization, or end-goal brainstorming becomes an isolated activity rather than a meaningful part of the workflow.
Addressing these challenges requires structure, inclusive participation, and effective tools to ensure the brainstorming process leads to valuable outcomes rather than unproductive discussions.
What are the work applications of collaborative brainstorming?
Collaborative brainstorming has several work applications, including:
Product development and innovation: Engineers, designers, product managers, and customer-facing teams can come together to combine technical feasibility with customer needs. This collaborative approach ensures ideas are grounded in market realities while still encouraging out-of-the-box thinking. It speeds up innovation, reduces blind spots, and often leads to breakthrough product concepts.
Marketing and campaign planning: Collaborative brainstorming provides the structure for generating diverse campaign ideas, messaging angles, content themes, and creative directions. Bringing people from different roles—content, design, product, and sales—helps create campaigns that are not only creative but also aligned with customer insights and business goals.
Strategic planning and business visioning: Collaborative brainstorming helps identify growth opportunities, analyze emerging trends, and evaluate scenarios that might otherwise be overlooked. Collaborative strategic sessions promote alignment across leadership teams and build shared ownership of the long-term vision.
What is the difference between collaborative brainstorming and co-creation?
Collaborative brainstorming focuses on generating ideas within a team. It is usually an internal activity where colleagues or cross-functional members come together to explore possibilities and solve problems. The outcome is a pool of ideas, but the team decides which ones to refine or implement later.
Co-creation, on the other hand, involves developing solutions with external stakeholders, such as partners, users, and clients. Co-creating is a longer, iterative process in which participants help shape, test, and improve the final product or solution. Precisely, brainstorming is about idea generation, while co-creation is about active collaboration to create and refine real solutions.
How can you reduce collaboration overload during brainstorming?
To prevent collaboration overload during brainstorming, start with a clear purpose and invite only those who are directly involved. Keep sessions structured, time-bound, and led by a facilitator who ensures equal participation and prevents tangents. Encourage participants to share ideas asynchronously through shared documents or digital tools so collaboration continues without constant meetings. Most importantly, end every session with clarity by summarizing key takeaways, assigning ownership, and setting next steps. This keeps brainstorming productive, focused, and energizing rather than overwhelming.






