
Asynchronous collaboration is a method of teams working together without needing to communicate or act simultaneously. It allows individuals to contribute, review, and respond at different times through shared digital platforms, enabling flexibility and productivity across time zones.
By eliminating the need for real-time interaction, asynchronous collaboration promotes focused work, better documentation, and improved inclusivity. Team members can work during their most productive hours, avoid constant interruptions, and maintain a healthier work-life balance while staying aligned through transparent workflows.
Effective asynchronous collaboration relies on clear communication guidelines, centralized documentation, and visibility of tasks and progress. It encourages accountability and autonomy while reducing dependency on meetings and synchronous updates.
However, it also presents challenges such as delayed feedback, lack of immediate clarification, and potential communication silos. These can be managed through structured processes, detailed documentation, and regular asynchronous check-ins that maintain context and connection.
In this article, we discuss what asynchronous collaboration is, its benefits, best practices for implementation, challenges and solutions, and examples of how teams successfully collaborate across different locations and schedules.
What is asynchronous collaboration?
Asynchronous collaboration is a method of working where team members contribute, communicate, and complete tasks without needing to be online or respond at the same time. It allows information exchange, project updates, and feedback to occur independently of real-time interaction.
Unlike synchronous collaboration, where communication happens simultaneously (like meetings or calls), asynchronous collaboration depends on written communication, documentation, and digital tools that store and share updates, allowing others to access and respond later.
This approach is structured around flexibility, autonomy, and clear documentation, enabling teams across different time zones to work efficiently without interrupting focus time. It removes the scheduling constraint and promotes a results-focused workflow rather than one dependent on instant responses.
What are the benefits of asynchronous collaboration?
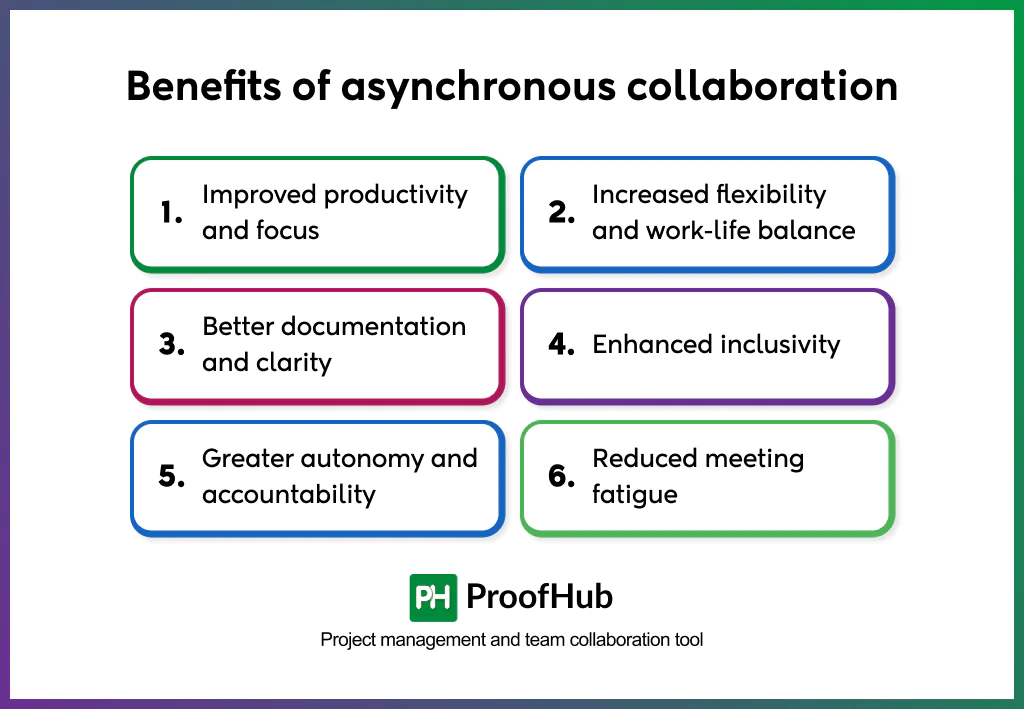
Asynchronous collaboration increases efficiency, flexibility, and clarity by allowing people to work independently of time or place. It shifts the focus from availability to outcomes, improving both team performance and individual satisfaction.
- Improved productivity and focus: By eliminating constant notifications and meetings, async collaboration creates uninterrupted time for deep work. Teams spend less energy on coordination and more on execution, producing higher-quality results in less time.
- Increased flexibility and work-life balance: Team members organize tasks around their most productive hours instead of fixed schedules. This flexibility supports personal well-being, reduces burnout, and improves morale and retention by respecting individual work rhythms.
- Better documentation and clarity: Because async communication is primarily written, every update, comment, and decision is recorded. This creates a single source of truth that minimizes confusion, preserves context, and helps new members get up to speed quickly.
- Enhanced inclusivity: Asynchronous work removes time-zone barriers and gives everyone equal space to contribute. People who prefer to reflect before responding, including quieter team members or non-native speakers, share more thoughtful input, enriching collective decisions.
- Greater autonomy and accountability: Async collaboration encourages individuals to take ownership of their work. With fewer real-time check-ins, employees make decisions independently and feel more trusted, which strengthens accountability and engagement.
- Reduced meeting fatigue: Replacing frequent real-time meetings with async updates limits interruptions and cognitive load. Employees review recordings, notes, or updates at their own pace, resulting in calmer workflows and sustained productivity.
Best practices for effective asynchronous collaboration
The best practices for implementing asynchronous collaboration involve setting clear communication guidelines, prioritizing documentation, using suitable tools, building an async-first culture, and maintaining transparency across teams.
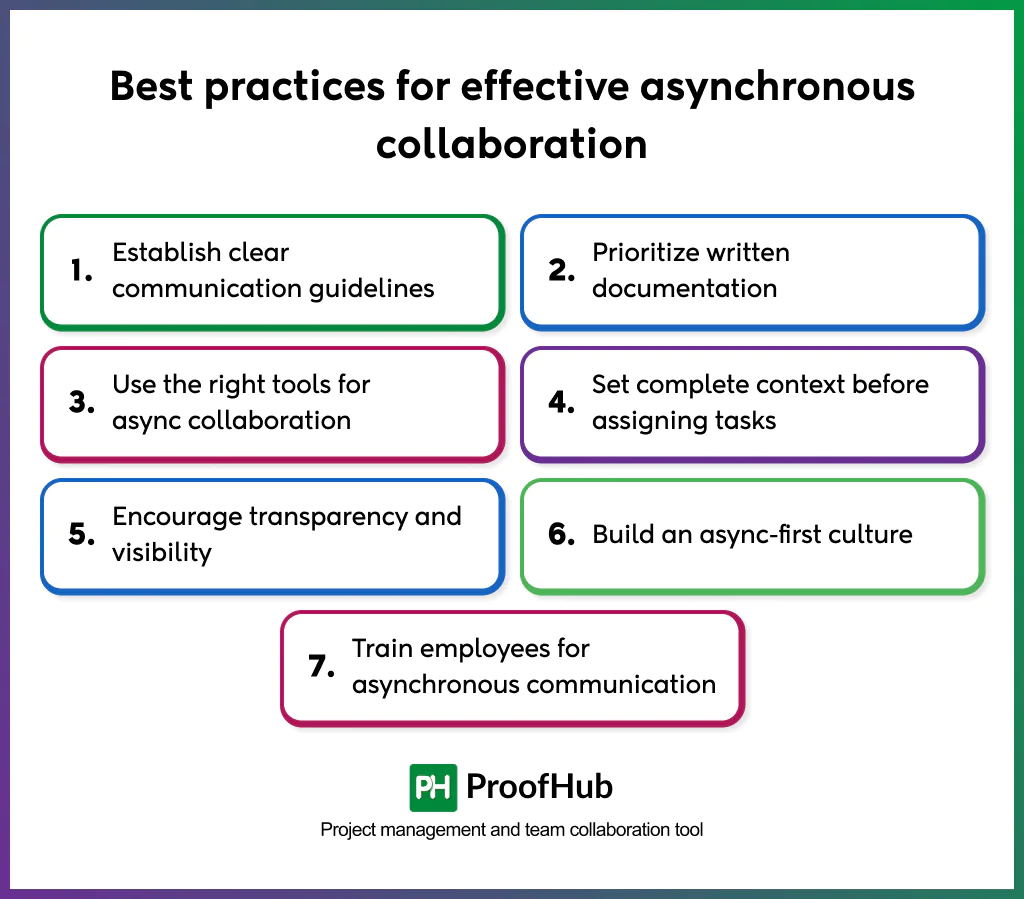
Here are some best practices for effective asynchronous collaboration.
- Establish clear communication guidelines: Defined communication norms eliminate uncertainty about when and how to respond. Every async team should set expectations for:
- Response time frames (for example, within 24 hours for standard updates, faster for urgent issues).
- Preferred channels for each type of message
- Message format that includes clear subjects, background context, and next steps.
This structure reduces friction, ensures consistency across departments, and helps people plan their day without constant message monitoring. Clear rules make asynchronous communication predictable, even in large or global teams.
- Prioritize written documentation
Async work relies on written information as its foundation. Every decision, task, and update should be recorded in a shared system, not just discussed.
Documentation gives asynchronous teams a single source of truth, allowing members to find answers without waiting for replies.
A well-documented workflow preserves knowledge, minimizes repeated questions, and prevents information loss during handovers or transitions.
- Use the right tools for async collaboration: Technology enables asynchronous collaboration by organizing communication, tasks, and files in one accessible environment.
- Project management tools such as ProofHub provide task visibility and progress tracking.
- Knowledge-sharing platforms like Notion or Confluence store documentation and feedback.
- Communication tools such as Twist or Loom support structured updates and video messages.
Selecting tools that complement each other ensures a seamless workflow, where information remains transparent and searchable, rather than buried in chat threads or inboxes.
- Set complete context before assigning tasks: In asynchronous environments, unclear instructions slow down entire projects. Each task or update should include:
- Goal or desired outcome
- Relevant files or examples
- Expected timeline or priority level
- Who is responsible for what
When full context is provided upfront, team members proceed independently without seeking clarification. This autonomy increases execution speed, reduces miscommunication, and strengthens trust within distributed teams.
- Encourage transparency and visibility
Visibility replaces real-time supervision in asynchronous teams. Dashboards, shared calendars, and public progress boards let everyone see what others are working on.
This transparency builds alignment across projects and prevents duplication of work.
It also increases accountability; team members naturally stay more consistent when progress is visible to peers. Regularly updating shared spaces creates a steady communication rhythm without live check-ins.
- Build an async-first culture
An async-first culture means asynchronous communication is the default, not the backup. Instead of scheduling meetings by habit, teams document decisions, share recordings, and use messages that can be read later.
Leaders play a key role by modeling async behavior – writing clearly, responding thoughtfully, and respecting others’ focus time.
This culture supports autonomy, promotes equality among time zones, and helps new employees adapt quickly through existing records.
- Train employees for asynchronous communication: Async collaboration demands a different skill set than real-time work. Employees should be trained to:
- Write concisely and with full context
- Use structured templates for updates and reports
- Manage time independently and prioritize tasks without live oversight
Regular workshops or feedback sessions improve written communication quality and ensure async tools are used effectively. Training eliminates uneven communication styles and keeps collaboration smooth as teams grow.
What are the challenges of asynchronous collaboration?
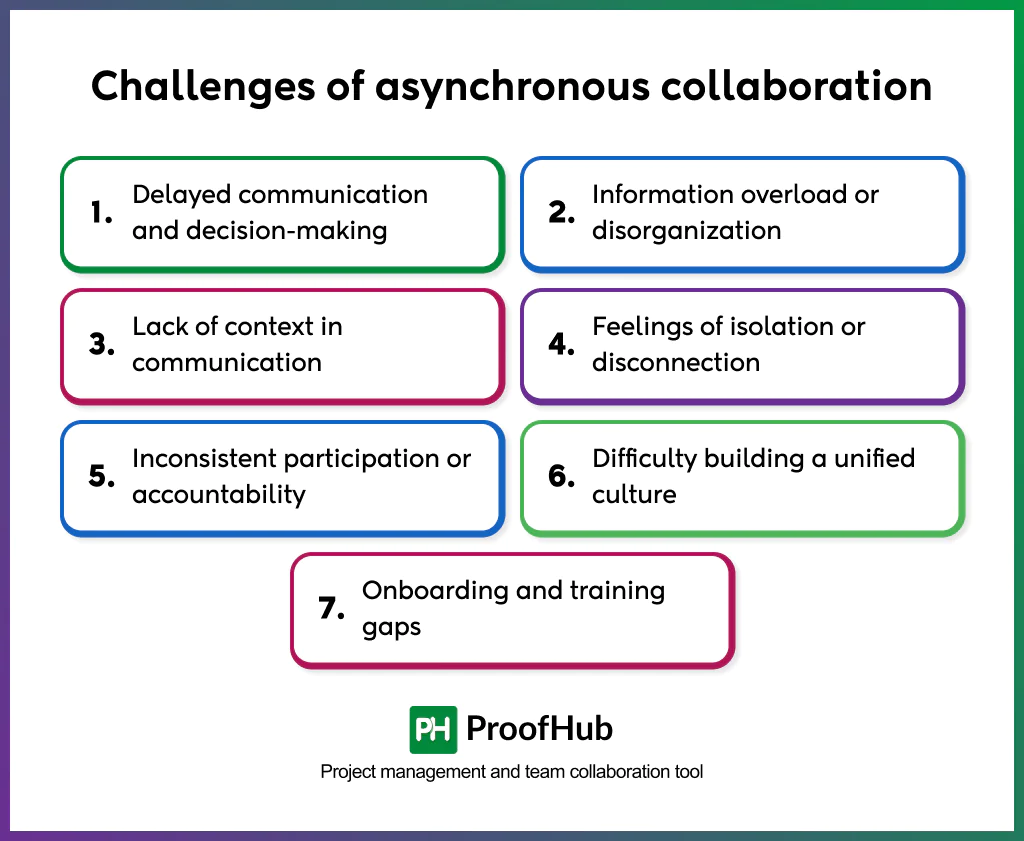
The challenges of asynchronous collaboration are communication delays, lack of visibility, inconsistent documentation, and potential feelings of isolation.
Here are some common challenges of async collaboration and how to address them.
1. Delayed communication and decision-making
Without real-time interaction, discussions and approvals take longer. When updates depend on written replies, projects may stall if someone doesn’t respond promptly.
To address this, set response-time expectations for different message types, use project boards for progress tracking, and assign clear ownership so decisions don’t get stuck in message threads.
2. Information overload or disorganization
Async collaboration generates a large volume of written messages, documents, and comments. Without structure, important details get buried, and teammates waste time searching for information.
Centralize all documentation in organized platforms like ProofHub. Use consistent naming conventions, tags, and summaries to make content easier to search for and navigate.
3. Lack of context in communication
Written messages miss tone or intent, leading to confusion or misinterpretation. When clarification takes hours, productivity declines.
Encourage context-rich messages; include background, goals, and next steps. Use visuals, screen recordings, or examples where possible, and summarize key points after lengthy discussions.
4. Feelings of isolation or disconnection
Working asynchronously makes employees feel detached from the team, especially when interaction is limited to written updates.
Schedule periodic synchronous sessions for team bonding, brainstorming, or celebrations. Use async tools like video messages or voice notes to keep communication more personal and human.
5. Inconsistent participation or accountability
Some team members may respond less actively in async settings, creating uneven workload distribution and reduced trust.
Increase visibility with shared dashboards or progress trackers. Make tasks and ownership public within the system so accountability remains transparent and measurable.
6. Difficulty building a unified culture
When communication happens mainly through text, shared values and team identity weaken over time.
Reinforce collaborative culture through clear documentation of principles, async recognition systems (like praise channels), and occasional live sessions where leadership reiterates goals and company values.
7. Onboarding and training gaps
New hires may struggle to adapt to async workflows without proper guidance, slowing productivity.
Create onboarding documentation, recorded tutorials, and structured mentoring processes. A library of past discussions or project templates helps new members learn how the team collaborates asynchronously.
Examples of asynchronous collaboration
Some examples of asynchronous collaboration are:
Example 1: Remote content creation team
A global content team works across multiple time zones. Writers in Asia draft articles during their workday, editors in Europe review them later, and designers in the U.S. finalize visuals before publishing.
By sharing updates through asynchronous collaboration, the team maintains a smooth workflow without waiting for real-time meetings, ensuring 24-hour productivity and faster delivery cycles.
Example 2: Software development sprint
Developers, testers, and product managers contribute at different times using a shared code repository and documentation platform. Pull requests, comments, and issue tracking replace daily stand-ups.
Each member adds updates when available, reducing time lost to scheduling conflicts and improving sprint velocity.
Example 3: Cross-department product launch
Marketing, design, and customer success teams coordinate asynchronously through task boards and recorded video updates. Designers upload campaign assets, marketers schedule promotions, and customer success prepares FAQs for launch.
This approach minimizes dependency on simultaneous meetings and allows teams to focus deeply on deliverables while staying aligned.
Example 4: Distributed HR operations
An HR team supporting offices in multiple countries manages onboarding, policy updates, and employee engagement asynchronously. HR specialists share documents, video orientations, and surveys through a central platform.
By eliminating timezone-bound meetings, HR maintains consistent communication, accelerates onboarding, and keeps employees informed without disrupting local schedules.
Example 5: Client feedback and review process
An agency collaborates with multiple clients for design approvals. Instead of scheduling multiple live meetings, they use proofing tools where clients leave comments directly on design files.
This asynchronous review process saves time, prevents miscommunication, and shortens approval cycles.
What are the best tools for asynchronous collaboration?
Effective asynchronous collaboration relies on digital tools that enable independent work, structured communication, task visibility, and clear documentation without requiring simultaneous participation.
Here are some of the best tools for asynchronous collaboration:
- Communication tools: Platforms such as Twist allow message-based or video-based updates instead of real-time meetings. They help teams share progress, ask questions, and provide feedback without disrupting focused work.
- Project and task management platforms: Tools like ProofHub help teams organize projects, assign tasks, set deadlines, and monitor progress asynchronously. They ensure everyone stays aligned on goals, even when working in different time zones.
- Documentation and knowledge-sharing tools: Systems like Coda create centralized knowledge bases where information, decisions, and updates are recorded for everyone to access anytime. This strengthens transparency and reduces repetitive communication.
- File-sharing and collaboration tools: Solutions such as Google Workspace and Dropbox support secure file storage and version-controlled document collaboration. They make it easy for teams to review, edit, and comment asynchronously.
- Video and screen recording tools: Tools like Loom and Vidyard allow users to record detailed video messages or walkthroughs to replace long meetings. They convey tone and context effectively, improving understanding and engagement.
- Comprehensive async work platforms: All-in-one platforms such as ProofHub integrate communication, task management, file sharing, and reporting into one workspace, reducing context switching and tool fatigue.
When do you need asynchronous collaboration?

Asynchronous collaboration is needed when teams work across time zones, handle tasks that require deep focus, or operate in environments where real-time communication is inefficient. It becomes essential whenever flexibility, uninterrupted work, or documentation accuracy are priorities.
You need asynchronous collaboration when:
- Teams are distributed globally: Async methods allow communication and decision-making to continue smoothly without depending on overlapping working hours.
- Tasks demand concentration and uninterrupted time: Writing, design, research, and development benefit from fewer real-time interruptions, improving the quality of work.
- Projects require detailed documentation: Async tools preserve context, making information accessible for future reference or onboarding.
- Schedules are flexible or non-linear: Teams working with freelancers, contractors, or part-time contributors rely on async systems to stay coordinated without rigid timing.
- Meetings become excessive or repetitive: When live sessions add little value or delay execution, async updates replace them efficiently.
- Transparency and accountability are critical: Written records of tasks, decisions, and progress ensure visibility and measurable outcomes.
What is the difference between real-time and asynchronous collaboration?
The main difference between real-time and asynchronous collaboration lies in when participants contribute and how interaction is managed.
- Real-time collaboration happens instantly. Team members interact, discuss, or make decisions together at the same time through tools like video meetings, live chats, or shared editing platforms. It is ideal for brainstorming, quick problem-solving, and immediate feedback. However, it requires everyone to be available simultaneously, which can be challenging for distributed teams.
- Asynchronous collaboration, on the other hand, allows team members to communicate and contribute at different times. Updates, feedback, and deliverables are shared through written messages, recorded videos, or task boards. It supports deep work, flexible schedules, and time zone independence, but demands clear communication and well-documented processes to stay aligned.
How does asynchronous collaboration improve productivity?
Asynchronous collaboration improves productivity by reducing interruptions, promoting deep work, and allowing individuals to work during their most focused hours.
It removes the constant pressure of real-time responses and meetings, giving employees uninterrupted time to complete high-priority tasks. This leads to better concentration and higher-quality output. Since communication is written or recorded, information becomes easily accessible, reducing the need for repetitive explanations and helping new team members catch up faster.
Async workflows also eliminate time zone constraints, enabling continuous progress as team members contribute across different hours. Clear documentation and transparent task ownership ensure accountability, minimizing delays and dependency bottlenecks.
How to train employees for asynchronous collaboration?
To train employees for asynchronous collaboration, build strong communication habits, set documentation standards, and promote an async-first mindset.
Start by educating teams on asynchronous principles; clarify how async differs from real-time work, why it’s important for distributed teams, and how it improves focus and autonomy. Employees should understand that async collaboration doesn’t mean delayed communication; it means intentional, organized workflows.
Provide training on collaboration tools, including project management platforms, shared documentation spaces, and async communication apps. Demonstrate how to document updates, record decisions, and share progress transparently. Encourage teams to use written communication effectively, focusing on clarity, structure, and actionable information.
Establish response-time guidelines and accountability norms to set expectations around availability. Create templates or examples for async updates, feedback, and reporting to help employees adapt easily.
Finally, create an async-first culture by recognizing independent problem-solving, respecting deep work hours, and rewarding outcomes over online presence. This ensures that asynchronous collaboration becomes a sustainable and productive part of the organization’s workflow.
What is the meaning of async-first culture?
An async-first culture is a workplace approach in which communication, decision-making, and collaboration primarily occur asynchronously. It relies on written documentation, recorded updates, and shared tools as the main channels of interaction instead of meetings or live discussions.
It promotes autonomy, transparency, and flexibility by allowing employees to manage their time independently and focus on results rather than availability.
Can asynchronous collaboration work in remote teams?
Yes, it removes the need for overlapping hours and supports work across time zones. Remote employees can contribute, review, and respond when they are most productive instead of coordinating schedules.
Async systems help remote teams maintain progress without constant meetings. It enhances focus and autonomy, allowing individuals to manage their own pace while staying aligned through transparent communication and clear documentation. For distributed organizations, asynchronous collaboration keeps operations efficient, scalable, and equitable.
Can asynchronous collaboration work in hybrid teams?
Yes, asynchronous collaboration creates equal access to information and eliminates location-based communication gaps. It ensures that both in-office and remote employees can contribute, review updates, and stay aligned without relying on real-time interactions.
In hybrid settings, async practices such as documenting meetings, sharing written updates, and storing all project materials in shared tools prevent remote employees from missing critical discussions that happen in offices. This makes collaboration fair, transparent, and consistent across locations.
Async collaboration also strengthens workflow continuity. Team members can progress on tasks independently, regardless of who is online or at the office. It reduces dependency on meeting schedules and supports flexible work habits that fit individual routines.






