
Business collaboration is the process in which two organizations or individuals work together to achieve common goals by sharing resources, knowledge, and expertise. It integrates diverse skills, knowledge, and resources of businesses to create value that wouldn’t be possible independently.
Business collaboration can occur internally across departments or externally with partners, vendors, and clients. Helping businesses access new markets and customers, gain financially through cost-sharing, drive innovation and creativity from diverse perspectives, enable faster decision-making through real-time collaboration, and improve risk management and resilience through collective problem-solving.
To collaborate with businesses effectively, a well-defined strategy ensures that all partners align on common goals, establish measurable success metrics, and work under a unified vision. Without this clarity, challenges can quickly emerge. Misaligned goals and expectations may cause friction when organizations pursue differing priorities or lack a shared understanding of success.
Additionally, trust deficits—often driven by fears of exploitation or lack of transparency—can hinder open communication and slow progress. Overcoming these barriers requires planning, consistent communication, and a strong foundation of mutual trust and accountability.
This article explains what business collaboration means, why it matters, how it benefits businesses of all sizes, and practical strategies to implement collaboration effectively, including ways to build a collaborative culture, encourage cross-functional teamwork, and establish accountability.
What is business collaboration?
Business collaboration is a strategic process where two or more organizations, teams or individuals come together to achieve a shared business goal. It involves sharing risks, knowledge, resources, and rewards to achieve a common objective that would be difficult, more costly, or unattainable if worked alone.
Organizations can work together internally (within cross-functional teams) or externally (across businesses) with clients, partners, suppliers, and other stakeholders to achieve shared business goals.
Depending on the end goals, business collaboration can take many forms, such as cross-departmental projects, strategic alliances, co-marketing efforts, or joint ventures. When done effectively, it leads to better productivity, stronger relationships, and greater adaptability to market changes. Instead of working in isolation, collaboration helps organizations grow through shared vision and expertise by utilizing collective strength.
Why is business collaboration important?
Business collaboration is important because it enables organizations to leverage diverse skills, combine different perspectives, and share resources to achieve mutual goals.
It enhances innovation by encouraging the exchange of ideas between departments or partners, leading to creative solutions that drive growth. It improves productivity and efficiency, as teams can divide responsibilities based on strengths and avoid duplication of work.
It helps businesses grow, innovate, and remain competitive, as it enhances efficiency and improves problem-solving. Externally, companies can share costs, risks, and access new markets through strategic partnerships.
According to a study, “Collaboration strategies and SME innovation performance”, conducted by David B. Audretsch, Maksim Belitski, Rosa Caiazza, and Phillip Phan (2023), discusses that business collaboration helps in sharing innovation costs, shortening product development, accessing complementary external knowledge, and achieving higher innovation and economic returns.
What are the benefits of business collaboration?
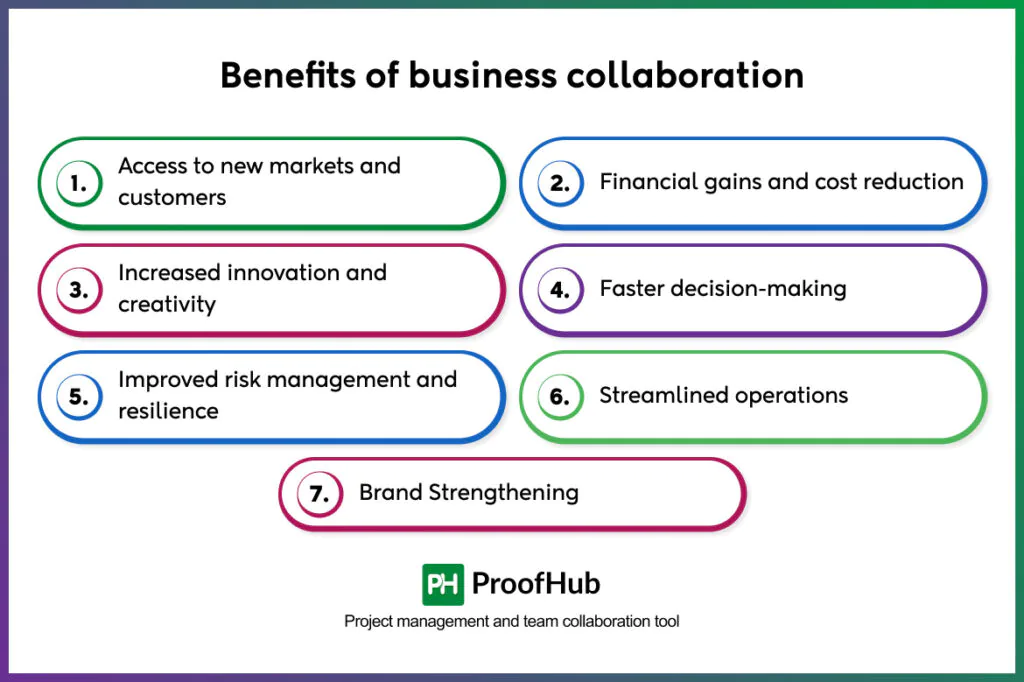
Business collaboration opens access to new markets, reduces costs, improves innovation and creativity, makes decision-making faster, reduces risks, and strengthens brand positioning. It offers organizations significant strategic advantages that extend beyond what they can achieve in isolation. Here are the primary benefits:
1. Access to new markets and customers
When businesses collaborate, they gain entry into markets and customer segments that may have otherwise been inaccessible. Whether it’s through joint ventures, co-branding, or leveraging each other’s networks, collaboration opens doors to new geographic territories, niche markets, and distribution channels. Partners can tap into these opportunities much faster and more efficiently than they could individually, accelerating business growth.
2. Financial gains and cost reduction
By pooling resources, businesses can cut operational costs and share overheads, resulting in improved profitability. Collaborative efforts also lead to an increase in revenue. Through joint projects or large-scale contracts that would be difficult for a single company to handle, business partners can take on bigger challenges and access more lucrative markets. Sharing risks and rewards also mitigates financial exposure while enhancing gains for all involved.
3. Increased innovation and creativity
Collaboration drives innovation and creativity by bringing together diverse perspectives, experiences and skills. Brainstorming together across departments or with external partners sparks creative thinking and helps identify solutions that individuals might overlook. This diversity of thought encourages experimentation and leads to innovative ideas.
4. Faster decision-making
Collaboration accelerates decision-making by enabling real-time communication, shared data access, and diverse input. When teams work closely and share information, decisions become both quicker and more informed. Problems are resolved more efficiently, as team members can directly communicate and support each other, leading to quicker resolutions.
According to a study, “Enhancing Business Performance through Collaboration and Fast Decision Making”, conducted by Frans van den Berg in 2014, collaborative work environments (CWEs) enable faster and better decision making by improved communication and easier sharing of relevant information and data, which aligns with teams making more informed and quicker decisions.
5. Improved risk management and resilience
Collaboration helps businesses better anticipate, share, and manage risks. By partnering with other organizations, companies can pool resources, diversify their supply chains, and share expertise in critical areas such as compliance, technology, and crisis response. This collective approach reduces vulnerability to market fluctuations, disruptions, or operational failures. Collaborative partnerships also enable faster recovery during challenging times, as businesses can rely on each other’s strengths and support systems to maintain stability and continuity.
6. Streamlined operations
Collaboration enables organizations to operate more efficiently by aligning goals, integrating systems, and optimizing workflows across teams and partners. By pooling complementary capabilities, businesses can reduce duplication of efforts, eliminate process bottlenecks, and enhance overall productivity. Joint initiatives often encourage knowledge sharing and process innovation, leading to smarter resource allocation and faster execution.
As a result, collaborating companies can achieve higher operational agility, deliver better outcomes with fewer resources, and build a more cohesive, performance-driven ecosystem.
7. Brand Strengthening
When organizations join forces, they combine their strengths, values, and expertise—creating powerful associations and enhancing brand reputation and market credibility. By aligning with reputable partners, companies can extend their reach, access new audiences, and reinforce trust among existing customers.
Over time, these alliances help position collaborating businesses as thought leaders and innovators who set higher benchmarks for excellence and integrity in their respective domains.
Strategies for effective business collaboration
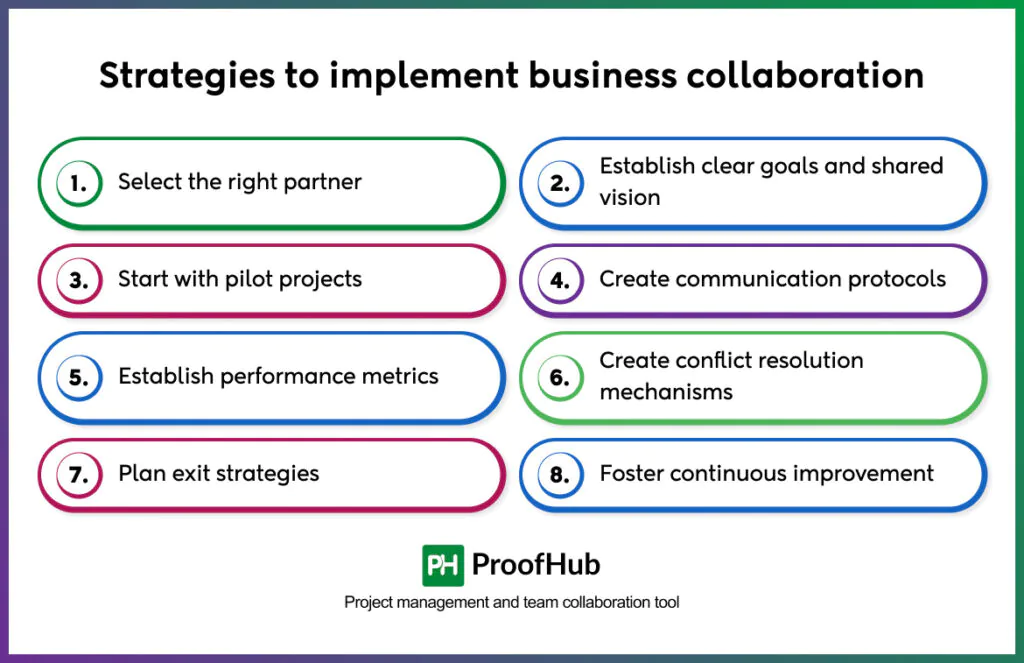
To create effective business collaboration strategies, select the right partners according to your business, establish clear goals and vision, streamline clear communication protocols, set performance tracking metrics, place a strategic resolution mechanism, and create an exit plan. Here are key strategies for implementing effective business partnerships:
1. Select the right partner
Conduct thorough due diligence to identify partners with complementary capabilities, compatible corporate cultures, and aligned values. Evaluate potential partners’ financial stability, market reputation, technical expertise, and track record with previous collaborations. The right partner fit is critical for long-term success.
2. Establish clear goals and a shared vision
Establish specific, measurable goals for the collaboration from the outset. Define what success looks like, the scope of partnership activities, and expected outcomes. Both organizations must align on strategic priorities and ensure the collaboration serves their respective business objectives.
3. Start with pilot projects
Begin with smaller, defined projects to test the partnership dynamics before committing to larger initiatives. Pilot projects allow partners to build working relationships, identify potential issues, and refine collaboration processes with lower risk exposure.
4. Create communication protocols
Implement regular communication channels and meeting schedules to maintain alignment. Establish reporting requirements, information-sharing procedures, and documentation standards. Designate collaboration managers who serve as primary contact points between organizations.
4. Establish performance metrics
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure collaboration success. Track both individual partner contributions and collective outcomes. Implement regular performance reviews to assess progress, identify challenges, and make necessary adjustments. Use data-driven insights to optimize the partnership.
6. Create conflict resolution mechanisms
Establish structured approaches for addressing disagreements before they escalate. Define mediation or arbitration procedures for resolving disputes. Encourage open dialogue and problem-solving rather than adversarial positioning when conflicts arise.
7. Plan exit strategies
Define clear exit provisions and transition procedures from the beginning. Address how assets will be divided, obligations settled, and operations unwound if the collaboration ends. Well-planned exits protect all parties and preserve business relationships.
8. Foster continuous improvement
Regularly evaluate collaboration effectiveness and seek opportunities for enhancement. Encourage partners to share feedback, suggest improvements, and adapt to changing circumstances. Successful collaborations evolve instead of remaining static.
What are the common challenges in business collaboration?

The common challenges of business collaboration include misaligned goals and expectations, trust deficits, unequal contribution and commitment, to name a few. Understanding these challenges is essential for proactive management.
1. Misaligned goals and expectations
Businesses may enter into collaboration with different priorities, timelines, or definitions of success. When strategic objectives diverge or expectations remain unclear, conflicts arise over resource allocation, decision-making, and performance evaluation. Hidden agendas can further complicate alignment efforts.
2. Trust deficits
Building and maintaining trust between organizations requires time and consistent positive interactions. Past negative experiences, competitive concerns, or fear of exploitation can prevent genuine trust development. Without trust, partners withhold information and resist necessary compromises.
3. Unequal contribution and commitment
When one organization contributes significantly more resources, time, or effort than others, an imbalance emerges — leading to frustration, mistrust, and ultimately, a breakdown in collaboration. For instance, if one partner takes the lead on most activities while others remain passive, resentment can build which creates misalignment that slows progress.
4. Complex decision-making processes
Collaboration requires consensus or compromise across multiple organizations, slowing decision-making significantly. Bureaucratic procedures, multiple approval layers, and conflicting organizational hierarchies reduce agility and responsiveness to market opportunities.
5. Loss of autonomy and control
Organizations have to surrender some independence when collaborating, which many find uncomfortable. Dependence on partner decisions, inability to act unilaterally, and reduced flexibility often frustrate leaders accustomed to complete control.
6. Financial disagreements
Disputes over cost sharing, profit distribution, investment requirements, and financial reporting create tension. Different accounting practices, financial constraints, or changing economic circumstances can trigger conflicts over monetary arrangements.
7. Operational integration difficulties
Integrating different systems, processes, quality standards, and operational procedures proves technically and logistically challenging. Incompatible technologies, divergent work methods, and inconsistent standards disrupt efficient collaboration.
What are the examples of business collaboration?
Some examples of business collaboration include-
1. BMW and Louis Vuitton business collaboration was a strategic marketing move that intended to reinforce both brand’s luxury images. It turned out to be successful, as it attracted both brands’ customers through joint promotions and exclusive launch events.
2. GoPro and Red Bull have a long-standing, exclusive global partnership that started in 2016. Their business collaboration majorly focuses on co-production, cross-promotion, and innovation using their shared brand identity of adventure and excitement.
3. Nike and Apple’s business collaboration began with the original Nike+iPod, which connected Nike shoes with sensors to an iPod to track runs. It has since expanded to include their successful Apple Watch Nike+ editions with Nike-branded bands and exclusive watch faces.
4. The business collaboration between Taco Bell and Doritos, launched with the popular Doritos Locos Tacos in 2012, was a highly successful partnership that made the best of their similar demographics and brand appeal and reached a broader customer base.
What tools can help in business collaboration?

Business collaboration tools can be categorized by function, including communication, project management, video conferencing, and file sharing and storage. Other important aspects include real-time document collaboration, online whiteboards, and all-in-one platforms.
- Slack: Offers team chat, group messaging, and direct messaging.
- ProofHub: Offers project collaboration and management, team chat, and file sharing.
- Zoom: A popular tool for video meetings, with features like screen sharing and virtual backgrounds.
- Dropbox: A cloud-based platform for file storage and sharing.
- Google Docs: Allows multiple users to edit documents, spreadsheets, and presentations simultaneously.
- Wrike: Helps with managing and tracking projects.
What are the types of business collaboration?
There are two types of business collaboration- internal and external.
Internal business collaboration includes team collaboration, cross-departmental collaboration, and community collaboration. In this kind of collaboration, team members use shared tools and resources to achieve a specific goal, and different departments work together on a project, fostering a sense of community.
External business collaboration takes many forms, like strategic alliances, joint ventures, supply chain partnerships, partner ecosystems, or portfolio collaboration, all aimed at sharing resources, aligning goals, and creating greater value together.
How can business collaboration help in an organization’s growth?
Business collaboration drives organizational growth by combining diverse expertise, resources, and perspectives to create more value than individual efforts can achieve. When teams, departments, or external partners collaborate effectively, they accelerate innovation, reduce inefficiencies, improve productivity, and open new market opportunities.
It also allows organizations to use the collective knowledge and skills to solve problems, develop better solutions, and gain a competitive advantage. Strategic partnerships with clients, suppliers, or industry peers allow businesses to expand capabilities and reach new audiences without heavy investment.
How to measure the success of business collaboration?
Business collaboration success is measured by a mix of quantitative and qualitative indicators that reflect the performance outcomes and the quality of the decisions.
Quantitatively, businesses can track metrics such as project completion rates, revenue growth, cost savings, time-to-market, and customer satisfaction scores to track the tangible impact of collaboration.
Qualitative success is observed in the strength of communication, trust, and alignment among collaborators. Team’s feedback, team satisfaction surveys, and partner relationship assessments help measure how well teams are working together.
Successful collaborations lead to measurable outcomes such as increased revenue, reduced costs, faster decision-making, and access to new markets. Beyond business metrics, assessing improvements in sustainability, ethical practices, and customer satisfaction provides a holistic view of the partnership’s value. Ultimately, a truly successful collaboration delivers tangible results while building lasting strategic and relational advantages for all parties involved.
What is the role of leadership in business collaboration?
Leadership sets a clear vision, aligns goals, and fosters a culture of trust and cooperation among partners. Effective leaders act as facilitators, bridging organizational boundaries, encouraging open communication, and ensuring that every stakeholder’s interests are acknowledged and respected.
Strong leadership also helps navigate challenges—such as cultural differences, conflicting priorities, or resource constraints—by promoting transparency, empathy, and accountability. Ultimately, leaders determine the tone and success of any collaborative initiative; their ability to inspire collective purpose and maintain alignment ensures that partnerships not only achieve their objectives but also create enduring value for all involved.






