The first step of applying project management to projects in the real world for a project manager is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the scope of the project. This is because project scope determines the cost & time of the project and the successful acceptance of the project deliverables.
How?
- Change in scope means change in the cost and time required to finish the new project work
- Disagreements on the project deliverables mean re-work
Thus, a manager needs to pay close attention when it comes to the management of project scope.
Project scope management helps you define and manage project scope to ensure project success. Let’s understand what it includes.
What is the project scope?
Project scope is the description of what is included and what is not included in the project. The purpose of defining project scope is to clearly outline all of the work included within a project upfront so that you can plan and manage a project better. It also defines what is excluded in the project for enhanced clarity.
Project scope is outlined in a formal document known as the ‘project scope management’ which covers a project’s:
- Objectives
- Goals
- Deliverables
- Constraints
Project scope is created based on the requirements gathered from the stakeholders and managed throughout the project using various techniques. The knowledge of this process is covered under project scope management.
What is project scope management?
Project scope management is the process of defining, validating, and controlling the scope of the project. It includes key processes and activities that help you manage the scope of the project.
The purpose of project scope management is to avoid conflicts. It clearly outlines the scope of the project, gets it approved by the stakeholders, and defines the process of scope changes upfront so that there are no conflicts when a project is executed.
It is the most important step of project management that determines the success of the project by defining the cost and time of the project, acceptance criteria of the project deliverables, and risk management of the project.
A project manager uses project scope management knowledge to manage the project scope.
What is scope creep?
Scope creep occurs when your project exceeds your initial project scope. For example, scope creep may occur if a stakeholder adds project deliverables after the project has begun. Unexpected project changes can lead to increased project risks like missed timelines, increased budgets, overwork, or a low-quality end product.
There are various reasons why scope creep can occur. Some reasons include:
- Unclear project scope
- Unrealistic project objectives
- Too many stakeholders
- Poor scope management
- Poor communication with stakeholders
To avoid scope creep, you need to plan against it, which is where a strong scope management plan comes into play.
Project scope management steps
There are certain steps you need to follow for appropriate project scope management. Or, in other words, these steps tell you how to apply project scope management to projects.
Project scope management is a five-step process that includes:
- Collecting requirements
- Defining scope
- Creating WBS
- Verify scope
- Control scope
Each step follows certain activities and produces certain deliverables, which helps you create a comprehensive project scope management plan.
To manage these five steps, there is an additional step followed right upfront, known as plan scope management. This makes the six steps of project scope management.
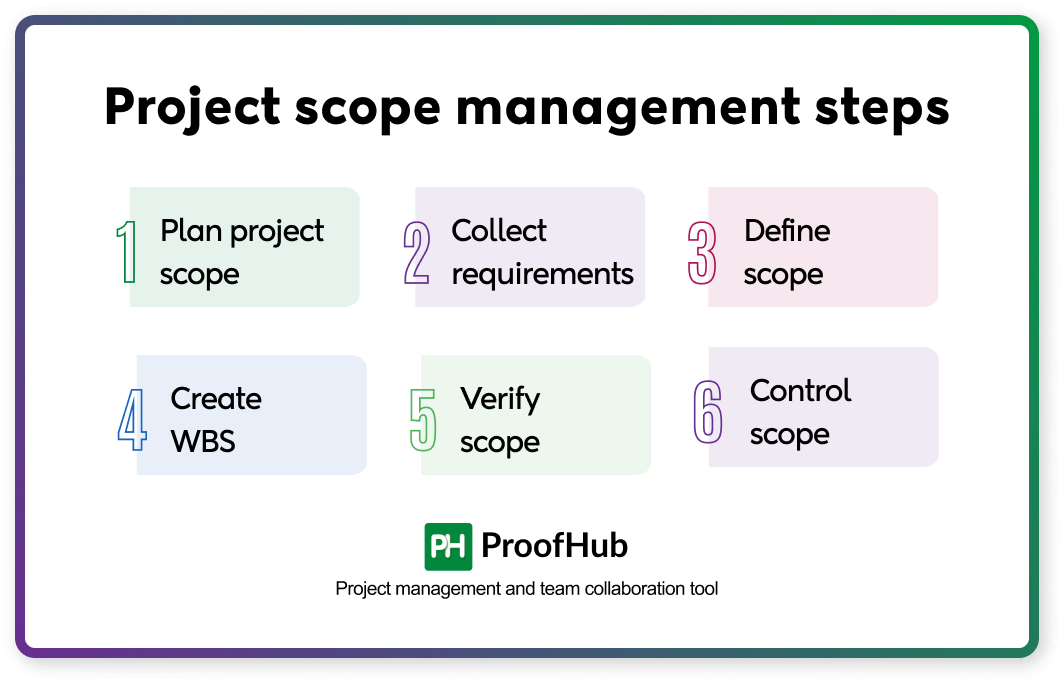
Have a look at the project scope management steps.
1. Plan scope management
This is the first step that defines how project scope management activities will occur. It includes defining the rules, responsibilities, and procedures for handling scope-related activities. You can consider it as a brainstorming session with stakeholders to create a shared understanding of how the scope will be defined, managed, validated, and controlled throughout the project lifecycle. It is like creating a plan for project scope management.
This step results in the creation of the ‘Scope management plan’ and ‘Requirements management plan’.
Key outputs:
- Scope management plan: Defines processes for collecting requirements, defining scope, validating deliverables, and controlling changes.
- Requirements management plan: Describes how requirements will be collected, documented, and tracked.
2. Collect requirements
This is the step where actual project scope management happens. A project manager collects requirements from the stakeholders using various techniques.
The purpose of this step is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the needs of stakeholders or expectations from the project: goals, objectives, purpose, and high-level requirements.
Key techniques used in this step to gather stakeholder requirements are:
- Interviews
- Questionnaires and surveys
- Facilitated workshops
- Focus group discussions
- Group decision-making techniques
- Observation and analysis
This helps you create a document that outlines all the requirements of the stakeholders known as ‘Requirements documentation‘. It categorizes the project requirements into functional requirements (what the project must do) and non-functional requirements (performance, reliability, and standards).
3. Define scope
In this step, a project manager defines the scope of the project based on the understanding of the gathered requirements. A project manager uses techniques like ‘Expert judgment’ to translate the project requirements into project deliverables. The purpose of this step is to create a shared understanding of the scope of the project.
It leads to the creation of the ‘Project scope statement’ that includes a project’s:
- Deliverables: Outcomes of the project.
- Boundaries: What is in-scope and out-of-scope.
- Constraints: Limitations like budget, time, and resources.
- Acceptance criteria: Defines the process and criteria for accepting completed products, services, or results.
- Assumptions: Factors assumed to be true during planning.
4. Create WBS
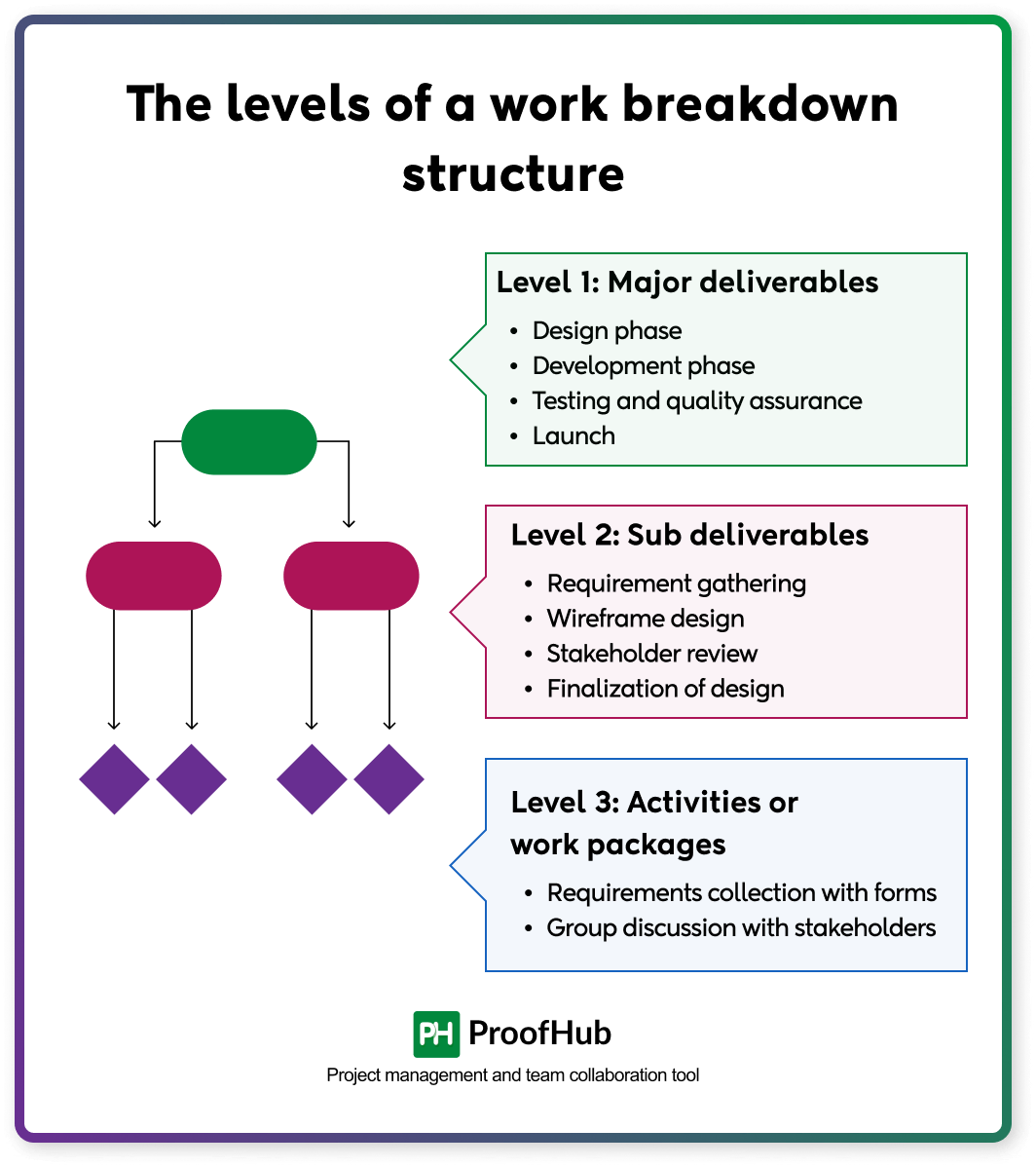
This is the step where high-level deliverables of projects are broken into smaller, manageable tasks. Work breakdown structure (WBS) is used to decompose the project into smaller, manageable tasks, making it easier to plan, assign, and monitor progress. It uses a hierarchical structure, with each descending level of the WBS representing an increasingly detailed definition of the project work:
- Level 1: Phases or deliverables
- Level 2: Sub-deliverables
- Level 3: Activities or tasks
Here is an example of what it may look like:
Level 1: Major deliverables
For a website development project, major deliverables could be:
- Design phase
- Development phase
- Testing and quality assurance
- Launch
Level 2: Sub deliverables
For example, the design phase could include the following sub-deliverables:
- Requirement gathering
- Wireframe design
- Stakeholder review
- Finalization of design
Level 3: Activities or work packages
For example, requirements gatherings could include:
- Requirements collection with forms
- Group discussion with stakeholders
This step of project scope management leads to the creation of the ‘Scope baseline’ which acts as a ground to monitor and control the scope of a project.
Scope baseline is a component of the project management plan that includes the project scope statement, WBS, and WBS dictionary.
The lowest level of WBS is where tasks can be scheduled and you can estimate the cost, time, and resources required for each task in a project.
Estimate project cost, resource, and time
To develop a realistic budget and schedule for the project:
Estimate project resources
Identify resources required:
- Human resources: Team members needed such as developers, testers, designers, and a project manager
- Material resource: Equipment, technology & software, office space, and third-party services
Estimate project time
Estimate how long it will take to complete each task in the WBS.
Use techniques like:
- Expert judgment: Consult experienced team members
- Analogous estimation: Compare with similar past projects
- Three-point estimation: Use optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely durations for a weighted average
Develop a project schedule based on dependencies using tools like the Gantt chart, Critical path method (CPM), or PERT (Program evaluation and review technique).
Estimate project costs
Calculate costs for each resource and activity and include contingencies for risks or uncertainties.
Use cost estimation techniques:
- Bottom-up estimation: Calculate costs for individual tasks and roll them up to the project level.
- Parametric estimation: Use data from past projects to estimate costs.
Finalize the project schedule after review, validation, and approval from stakeholders.
These first four steps of project scope management are part of the project initiation and planning. The next two steps involve project execution, monitoring and controlling, and closure.
5. Validate or verify scope
This is the step where the focus is on gaining formal acceptance of the completed project deliverables in the scope of the project from stakeholders. A project manager reviews deliverables with stakeholders and gets them verified. This includes comparing the defined project deliverables in the scope with stakeholders’ requirements.
The purpose of this step is to ensure deliverables meet stakeholder expectations before the project progresses further.
If stakeholders agree on the project scope, it results in formal confirmation that the work is satisfactory. This creates formal documents such as ‘Accepted deliverables’ and ‘Formal sign-off documents’.
Otherwise, if issues arise, changes are proposed for review. These changes are raised formally with a ‘Change request document’.
6. Control scope
This is the last step of the project scope management. It monitors the scope and ensures any changes are identified, documented, and approved through a formal change control process. It is where a project manager makes sure the project scope does not go off track, but it happens in most projects. Because you never know when the scope may change, or a customer may add new requirements.
To prevent scope creep, a project manager:
- Compares actual work with the planned scope baseline to manage scope creep by preventing unauthorized work or additions.
- Evaluates change requests by stakeholders and assesses the impact of changes on the budget, timeline, and quality.
This leads to the creation of the ‘Scope change log’ to record approved or rejected changes and the ‘Updated project scope statement or WBS’ (if changes are approved) to manage the updated scope.
This is the six-step standard framework of project scope management to manage every aspect of the project’s scope. Let’s have a look at the benefits of project scope management.
Benefits of project scope management
Project scope management clearly defines the scope of the project, helps create an effective project management plan, gets project deliverables approved by the stakeholders, and creates a formal request to manage changes in scope. This leads to the following list of benefits:
1. Enhanced stakeholder alignment with clear goals and objectives
Project scope management helps you comprehensively gather stakeholders’ requirements and get approval before executing the project. This helps you set clear project goals and objectives and acceptance criteria for project deliverables aligned with stakeholders’ expectations. It also helps you avoid misunderstandings with stakeholders.
2. Keep the project on track with a shared understanding
When a project team understands what is included and what is not in the project, it keeps the team on track by creating a shared understanding of the project’s goals, objectives, deliverables, and what the project aims to achieve. The team is working on what is necessary to complete the project, not wasting time and resources on work that is out of scope.
3. Increase project success with optimal resource allocation
Creating a WBS makes it easy for project managers to allocate resources and make accurate cost and time estimations. This ensures every task has sufficient resources and that resources are utilized optimally. This accurate project planning increases the likelihood of the project’s success, minimizes delays, and prevents budget overruns.
4. Prevent scope creep with a formal change management process
Scope management creates a scope baseline and formal change management process. The project scope baseline helps track progress and ensures the project team is working only on items outlined in the scope. And a formal change management process ensures stakeholders request changes formally, are aware of their impact on the project budget and timeline, and approve the resources. This prevents scope creep, makes it easy to manage ongoing risks, and ensures a project is completed within budget and time.
5. Ensures deliverables meet quality standards
Scope management uses validation to ensure stakeholders review deliverables. This ensures that completed project deliverables meet agreed-upon requirements. It helps you build trust and satisfaction by delivering what was promised without surprises and ensuring quality standards are met from the start.
Tips for effective project scope management
Standard practices mentioned in the project scope management can help you define and manage scope well. However, there are some expert tips and advanced strategies from the experts’ knowledge that can help you enhance scope management.
- Engage stakeholders continuously: First-time managers often involve stakeholders aggressively in planning but take a casual approach during the execution. This can lead to disputes. Keep stakeholders involved throughout the project lifecycle. Use surveys or feedback loops to gather feedback and maintain alignment at every stage of the project.
- Document everything: Any key scope-related decision should be documented. It helps you avoid confusion and disputes. In addition to that, it acts as a reference for the future. You can access the documents anytime and understand why the decision was taken.
- Use project management and collaboration tools: Project scope management cannot happen appropriately and efficiently on the spreadsheets. Use project management and collaboration software like ProofHub, jira and Asana to collaborate with stakeholders, create the project scope management plan, and apply project scope management to real projects.
Simplify project scope management with project management tools
Project management software like ProofHub helps you manage project scope by providing you with tools to define and manage project scope. Let’s understand it by an example of how it happens in ProofHub.
Collaborate with stakeholders
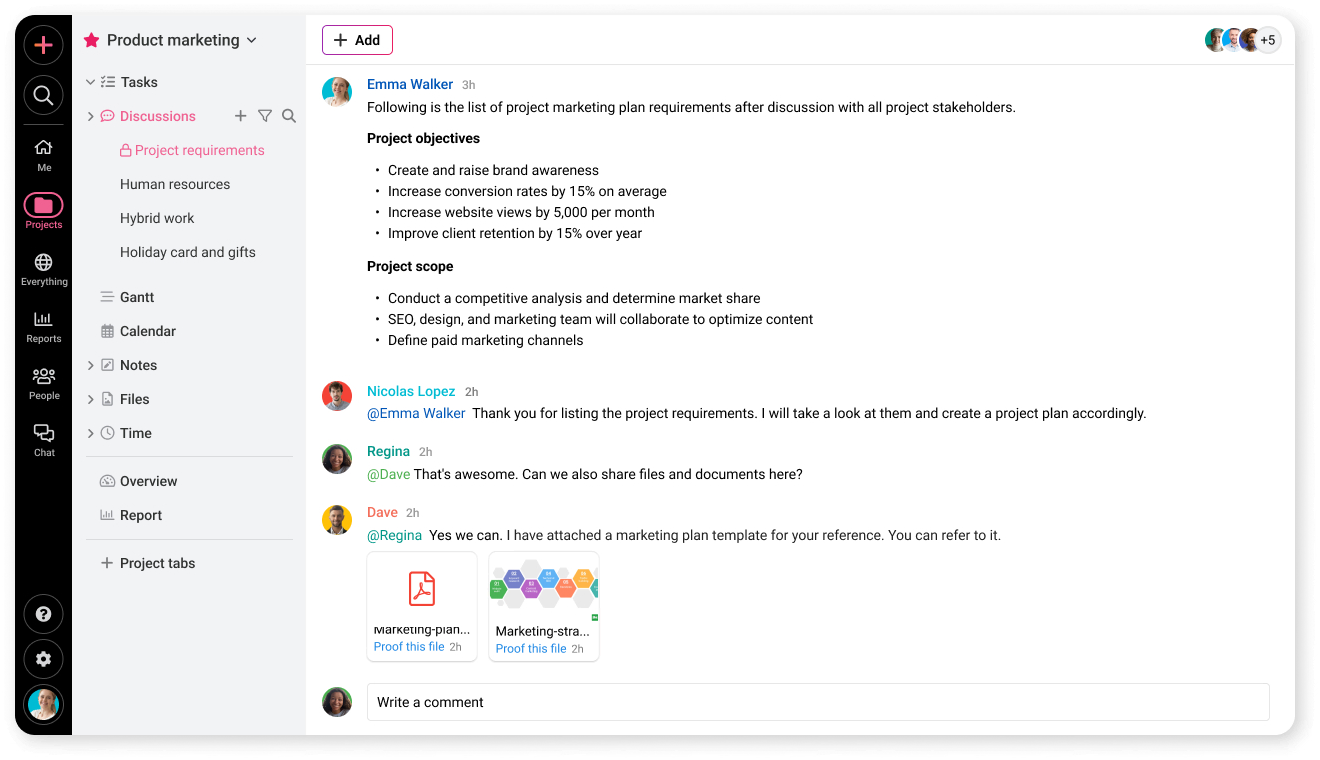
You can use ProofHub discussions to brainstorm with stakeholders. It helps you collect project requirements and document them at the same time.
Using those project requirements, you can write project objectives and deliverables in ProofHub collaborative notes. These notes can be shared later with stakeholders and the project team for collaboration.
Once you document the project deliverables and get agreement from the stakeholders, you can use your project management software to create a work breakdown structure.
Create a work breakdown structure
Every project management software comes with a hierarchical structure and task management capabilities to break a project into small parts. It means software allows you to break a project into key phases, and break each key phase further into tasks and sub-tasks. ProofHub allows you to break a project into smaller parts. You can assign resources and add estimated cost & time at the task level to calculate the project cost, time, and resource requirements.
These task management capabilities help you apply project scope management to the project, delegate tasks, track progress, and manage project work to complete a project within budget and time.
Schedule a free demo of ProofHub to see how project scope management can be applied to projects in the real world.






