A quick question first:
Can any number of skills be enough to master the art of project management?
There is no straight answer to this.
The ever-changing and demanding nature of this job makes it impossible to put a cap on the list.
Most of the time, it’s just about staying on your toes and not falling.
However, there are some must-haves and know-how commonly listed as prerequisites for a project manager’s job. To help you learn more about these, I have curated a list of 28 project management skills.
As a project manager, you must acquire and master these skills to effectively fulfill your roles and responsibilities.
Moreover, managers with these skills are more likely to make it to executive-level roles.
So, let’s get right into it.
What are project management skills?
Project management skills are the attributes and capabilities a project manager must possess to drive a project toward success effectively.
As a project manager, your success is often measured by skillfully balancing the three components of the project management triangle: scope, time, and cost. The truth is, it is not an easy feat.
The intricate dynamics of managing work and teams call for a diverse set of skills, broadly falling into three categories: soft skills, hard skills, and technical skills specific to the industry and role.
While soft skills help you to establish smooth and efficient team dynamics, hard and technical skills help you to manage work like a pro.
28 Project management skills every project manager should have
I will start with some universally applicable soft skills, a must-have for anyone who is going to be in a leadership role.
Following that, I will discuss the hard and technical skills a project manager must possess to successfully delegate, organize, and manage the work.
Project management soft skills
Effective project management is not merely about checking off boxes on a to-do list; it’s about understanding each team member’s unique strengths, weaknesses, and motivations and orchestrating their efforts cohesively.

These requirements hinge vividly on your mastery of the following soft skills:
1. Effective leadership skills
As a project manager, your first and foremost responsibility is assembling a proficient team. To do so, you have to have impeccable leadership qualities. If you know the nitty-gritty of project management, coupling them with leadership skills would strengthen your repertoire as a project manager.
Project leadership comes with a range of different styles. Effective leadership is an active participation and requires more than just the knowledge of theory. You should be able to seamlessly switch between these styles depending on the context and the needs of your team and project.
To get better at it every day, you can start by journaling your leadership experience. Jot down the challenges you faced during the day, and how you handled them, and reflect on what could have done better. Also, seeking opinions from mentors can help you in the long run.
2. Strong communication skills
A project manager needs to know the organization’s vision, mission, and goals, but more critical is clearly and concisely communicating them to team members. You need sound communication and interpersonal skills to articulate your thoughts, requirements, deliverables, and expectations to team members, vendors, and stakeholders.
As 90 percent of a project manager’s time is spent communicating information to others, he must take his communication game to a superior level. You could also seek help from various project management and collaboration tools such as ProofHub to facilitate effective communication at work.
3. Problem-solving
Every project comes with its own set of problems. Some are avoidable while others are unavoidable and uncontrollable such as scope creep, and unforeseen risks, and others happen due to negligence in planning or execution. As an effective project manager, you must have a systematic approach to solving these problems at the need of the hour.
You can use the five problem-solving steps which include defining the problem, determining the causes, generating ideas, selecting the best alternative, and taking action to tackle problems effectively. No matter in what industry you are, you must develop skills to tackle issues and problems arising while working on complex projects.
4. Time management
There are frequent instances where a project gets delayed due to time management or scheduling issues. Thus, time management is the one thing that project managers are overly familiar with. Effective project managers understand that you must be able to manage time well to deliver projects on time.
As a project manager, you have to know how to manage your team well to achieve a common goal with complete harmony and unison. It helps coordinate, delegate, and administer a group of team members in a way that promotes teamwork, resolving conflict, evaluating performance, and the overall progress of both team members and the project.
Ready to master the art of time management? Discover the best time management apps for productive teams – Explore now!
5. Emotional intelligence
“The most effective leaders are those who can manage their own emotions and the emotions of others.” – Daniel Goleman.
Emotional intelligence, often referred to as EQ, is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s emotions and respond accordingly to the feelings of others around them.
EQ is a non-negotiable skill for project managers, perhaps even more essential than technical proficiency. It helps them comprehend team dynamics, empathize with their team members, and tailor their approach to motivate and guide individuals effectively.
Although usually considered an innate characteristic (more on which later), with good understanding, emotional intelligence can very well be acquired through practice. You can cultivate these aspects as a leader through mindfulness, active listening, seeking feedback, and continuous learning. It enhances decision-making, as emotionally intelligent leaders can consider diverse viewpoints and anticipate reactions to different strategies.
6. Negotiation
Although negotiation is a part of the communication skills it does need a special mention as project managers have to negotiate at every step – from vendors to team members. It starts from smartly settling on the best price from the vendor to constantly motivating the morale of team members to keep the project progressing at a good speed.
Oftentimes, project members don’t get along or get into a nasty fight, this is where you need to step in and use your people skills with strong negotiation to avoid letting it come in the way of the overall progress of the work.
7. Adaptability
According to a recent study, adaptability is among the top five skills employers seek in today’s technology-driven world.
Being adaptable while managing projects isn’t just about coping with the change; it’s an inherent part of the job and almost a survival tactic.
As a project manager, you will most likely be surrounded by distinct challenges, all popping up at once, and it’s not just about handling these tasks. Adaptability is seamlessly transitioning between them without letting anything slip through the cracks.
Oftentimes, you will be required to instantly shift your focus from planning the next sprint to brainstorming with a stakeholder.
While there is no surefire way to get better at unexpected context switching, you can practice time blocking. Just focus on the task at hand for a fixed time before the Zeigarnik effect starts to kick in.
8. Conflict resolution
Conflict resolution is a vital skill for any project manager as it involves managing tensions and disagreements within a team from a neutral standpoint.
Not every team member is the same. They come from different backgrounds and experiences and are likely to have disagreements in viewpoints, which can further lead to different types of conflicts. It’s essential to de-escalate the issue as soon as it appears.
The most effective trick is not to mediate the conflict from a position of authority but as someone who equally values the viewpoints of all the parties involved and works in cohesion to find a suitable and mutually acceptable solution.
9. Writing and reading
As a project manager, you are responsible for writing clear project plans, reports, and documentation. Crafting compelling presentations and proposals that effectively convey ideas and project progress is crucial for gaining stakeholder buy-in and securing resources.
Additionally, clear articulation of the facts and figures can help you read between the lines and make better decisions.
As for reading, there is no way out of it. Apart from the project briefs and client requests, project managers often need to go through intense research and analysis. They need to stay updated with industry reports, case studies, and relevant articles that aid in gathering valuable insights and data to make informed decisions and develop strategies.
You can consider subscribing to different newsletters, and magazines, reading blogs, and being a part of project management communities.
Project management hard skills
Project management hard skills refer to specific, teachable abilities or knowledge that are quantifiable and measurable.

These are typically learned through formal education, training programs, or on-the-job experience.
10. Project planning
Project planning is the process of meticulously identifying and prioritizing the scope, cost, and resource requirements of a project. Since planning is one of the initial phases in a project life cycle, it’s all about strategically mapping out the who, what, when, where, and how of a project to ensure it stays on course.
This skill set involves breaking down big goals into manageable tasks, also called creating a work breakdown structure, figuring out what resources are needed (and who’s going to do what), and setting up a roadmap with timelines and milestones.
You can also take advantage of project planning tools to support your planning skills. These tools make it easier to organize tasks, share resources effectively, create clear schedules, and keep track of progress.
11. Risk management
You can easily gauge how good a manager is with his ability to foresee risks in an ongoing project. Risk management is one of the key knowledge areas in which a project manager must be proficient and competent. Risk Management is the process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to risk factors throughout the life of a project and in the best interests of its objectives.
Considering this, the number of project managers embedding risk management is increasing day by day to reap the full benefits of this approach.
12. Scheduling
Did you know that 60% of successful projects attribute their achievements to effective scheduling?
Project scheduling orders, tasks, and milestones while optimizing dependencies and workforces for utmost productivity.
The idea is to optimize allocating resources, time, and effort to complete a project efficiently. As a project manager, you will sequence the tasks to find the most efficient path to project completion, ensuring effective resource utilization and minimizing unnecessary delays.
One thing that is essential to mention here is that the kind of project schedule you are set to create depends on the type of project management approach you are following.
For example, If you follow the Waterfall model, the entire project is planned and scheduled at the beginning. If you follow the Agile framework, plans are broken into smaller iterations (sprints), and scheduling is done for each iteration, allowing for shorter, more flexible timelines.
Also, you should be able to account for any unexpected uncertainties while preparing the project schedule and keep a corresponding buffer within your program.
13. Budgeting and cost control
Understanding budgeting in project management is crucial, especially when managing a large and complex project. You have to have a good grasp of the foundational elements of resource identification, cost estimation, and contingency planning. However, the required proficiency goes beyond multiplying the estimated hours by the respective rates for each resource.
Budgeting is not a one-time task. As a skilled project manager, you should be able to control the cost based on data obtained from continuously monitoring the actual expenses against the budgeted amounts.
Additionally, consider looking into specific courses or materials focused on project budgeting within project management. I would recommend ‘Activity Based Costing: The Key to World Class Performance’ by Peter L. Grieco and Mel Pilachowski. This book gives really helpful tips to help project managers as they plan, control, and make the most out of project budgets.
14. Resource management
Efficient resource management involves assigning tasks and optimizing talent, time, and tools. It’s as much about understanding the individual team member’s strengths and aligning them with project needs as it is about their well-being for better productivity.
Exploring innovative resource allocation methodologies like agile resource planning or resource leveling can ensure smoother project execution and adaptability to changing demands. Resource management software or capacity planning tools can streamline this process, allowing managers to visualize resource allocation and adjust dynamically.
For instance, using a skills matrix to identify specific strengths allows project managers to assign tasks that align with each individual’s expertise, optimizing productivity.
15. Scope management
Scope management, as a skill within project management, revolves around the ability to define, control, and manage the limitations of a project. It’s a dynamic process involving continuous refinement and stakeholder alignment.
A well-managed scope ensures clarity, reducing misunderstandings and conflicts. It minimizes scope creep, which can lead to resource overutilization, missed deadlines, and increased costs. Project managers should be well-versed in project management frameworks to manage their projects’ scope effectively.
For instance, employing agile techniques like backlog grooming can aid in maintaining a flexible scope while ensuring project alignment with customer needs.
16. Quality management
Quality management goes beyond meeting specifications; it’s about delivering value. A skilled quality manager possesses a holistic perspective, viewing quality as a final output and an integrated part of the project lifecycle. They understand that quality starts from initiation and requires continuous monitoring.
Integrating quality checkpoints, continuous improvement practices, and fostering a mindset of excellence can significantly enhance project outcomes.
Techniques like Six Sigma, Total Quality Management (TQM), or Lean methodologies can be integrated into project processes to drive quality improvements and mitigate risks.
17. Stakeholder management
Stakeholder management is a crucial skill for project managers, circling the ability to identify, understand, prioritize, and effectively engage with individuals or groups impacted by or interested in the project’s outcome.
Managing stakeholders involves more than effective communication; it’s about building relationships, understanding their needs, and negotiating yours. Implementing robust stakeholder analysis techniques, such as power-interest grids or stakeholder mapping, aids in identifying key influencers and tailoring communication strategies accordingly.
18. Change management
Change is inevitable, and effective change management involves embracing it as an opportunity rather than a disruption.
It’s not just about managing change but also about leading people through it, ensuring a smooth adaptation to new processes, systems, or strategies while minimizing resistance and maximizing acceptance.
Introducing change management frameworks like ADKAR (Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, Reinforcement) can facilitate smoother transitions.
Encouraging a culture that embraces innovation and adaptation while minimizing resistance through effective communication and involvement can mitigate the impact of change on project objectives.
Developing proficiency in change management as a skill requires a blend of emotional intelligence, strategic thinking, and effective communication, enabling individuals to lead and navigate transitions effectively in today’s rapidly evolving world.
19. Reporting and documentation
Reporting and documentation are administrative skills a project manager must acquire for informed decision-making and transparency. Leveraging project management software to automate reporting, ensuring real-time visibility into project health, and employing storytelling techniques in reports can effectively engage stakeholders and convey complex information.
Additionally, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive documentation for lessons learned and future reference can enhance organizational knowledge management.
20. Procurement and vendor management
Effective procurement isn’t just about selecting vendors; it’s about fostering partnerships and managing contracts. Implementing robust procurement strategies, including vendor evaluation criteria and contract management practices, can ensure successful collaboration.
Emphasizing continuous performance evaluation, renegotiation when necessary, and aligning vendor goals with project objectives can mitigate risks associated with external dependencies.
21. Performance measurement and evaluation
Metrics and KPIs aren’t just numbers but indicators of project health and success. Establishing relevant performance indicators aligned with project objectives, like earned value management (EVM) or balanced scorecard metrics, helps measure progress accurately. Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement through regular evaluations, retrospective meetings, and adapting based on performance insights can drive project success.
Project management technical skills
Technical skills generally refer to specific abilities or knowledge required for a particular field or domain.
In project management, technical skills encompass proficiency in using tools, techniques, and methodologies specific to the discipline.
22. Project management approaches & methodologies
Project managers need to have good knowledge of diverse methodologies like Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, Kanban, Lean, or Six Sigma. Proficiency in these tools and techniques helps them adjust plans to fit what each project needs, roll with changes that pop up, and enhance the team’s productivity across the project’s lifecycle.
Becoming a pro at these styles means diving into learning, getting hands-on experience, and truly understanding how they work in practice.
If you are keen on leveling up your skills, you can check out these project management certifications. These programs aren’t just about theory—they give you the lowdown on how to use these styles in real projects.
23. Project portfolio management (PPM)
Project portfolio management (PPM) is a strategic approach that involves managing a collection of projects, programs, and other activities to achieve an organization’s strategic objectives.
Mastering PPM as a skill involves a deep understanding of how to align multiple projects within the organization for the best results. This involves knowing how to allocate human resources, funds, and technology across various projects.
To be more specific, it involves optimizing resource management to ensure every project meets its needs without overstretching its capacities.
24. Industry and domain-specific skills
To secure a role as a project manager for a particular project, possessing industry-specific knowledge is one of the primary requirements. It directly influences hiring decisions as it ensures a candidate’s capability to navigate the unique requirements of the project domain.
For instance, in technical projects, familiarity with engineering tools is a prerequisite, while healthcare project managers require knowledge of healthcare systems, and construction project managers benefit from specialized construction management software.
This specialized knowledge serves as a key differentiator and a crucial factor in being considered for project management roles within specific industries.
25. Project management software proficiency
Project management software like ProofHub is an indispensable solution to keep up with the pace of today’s dynamic environment.
A study by PWC has shown that 77% of successful projects are attributed to the effective utilization of project management tools.
Though many organizations provide the required training to handle workflows efficiently within these software platforms, having prior knowledge can go a long way.
With these tools, you get real-time updates on how the project is moving along. They show you where you are in the project timeline, what’s been done, and what’s coming up next. This way, you can spot any hiccups early and fix them before they become big problems.
26. Risk assessment tools
Project managers should be proficient in utilizing risk management frameworks like Monte Carlo analysis, SWOT analysis, etc., as they enable effective assessment, quantification, and mitigation of project risks. These tools help by giving a clear picture of all the things that could go wrong in a project. They also put numbers to these risks, which makes it easier to prioritize and decide where to focus resources.
Plus, having a dedicated platform to manage risks makes the whole process smoother, from spotting risks to dealing with them. It lets teams fix problems before they become big headaches, making projects more likely to succeed.
27. Financial and accounting software
Mastery of financial management tools like Excel, QuickBooks, or specialized project accounting software is essential to support your resource management skills.
These software solutions help with precise budgeting, meticulous cost estimations, and the creation of detailed financial reports. With these tools, project managers effectively manage the financial aspect of a project, ensuring the project reaches its closure stage within predefined monetary boundaries.
28. Data analysis and reporting tools
Analysis and reporting tools allow project managers to generate comprehensive project reports, analyze trends, and present data insights effectively to stakeholders, aiding informed decision-making. These tools act as the kaleidoscopic lenses through which project managers perceive the intricate patterns within their projects.
Most project management tools come with inbuilt reporting and analysis features to help project managers get a bird-eye view of their projects. They provide a detailed overview of where things stand, how they are going, and where the improvement can be made.
Unlock the power of data with ProofHub’s reporting feature! Gain insights, drive action, and make informed decisions.
Traits of successful project managers
Being a successful project manager takes more than just proficiency in the aforementioned skills. It’s an ongoing process of forging a character. Here are some of the characteristic traits organizations look for in a project manager.

- Emotional intelligence: As discussed earlier, successful managers are often emotionally intelligent and able to understand and manage their own emotions while also being attuned to the emotions of others. This helps in building positive relationships and navigating interpersonal dynamics.
- Flexibility: Managers are often faced with changing circumstances, and those who can navigate uncertainty tend to be more successful. They are open to new ideas, flexible in their approach, and able to adjust their strategies as needed.
- Resilience: The ability to bounce back from setbacks and maintain a positive attitude in the face of challenges is a must-have trait for successful managers. Not everything always goes as planned, especially in complex projects. To effectively lead teams through difficult times and setbacks, managers must be mentally strong to overcome the setbacks. The following quote perfectly reflects the importance of resilience.
“Sometimes life is going to hit you with a brick, don’t lose faith.”
—Steve Jobs
- Integrity: Trust is a cornerstone of effective leadership. Managers with integrity are honest, ethical, and consistent in their decision-making. This builds trust among team members and fosters a positive work environment.
- Strategic thinking: Successful project management goes hand in hand with strategic thinking. Adept project managers not only harbor a clear vision but also excel in formulating and executing strategic plans. This ability to think strategically becomes the linchpin, providing direction for much-needed alignment of team dynamics with company goals.
- Empathy: Empathetic managers understand the perspectives and feelings of their team members. This enables them to connect on a human level and have realistic expectations from the team members, fostering a collaborative work environment.
- Confidence: Confidence in one’s abilities and decisions is important for effective leadership. It instills trust in the team and helps the manager navigate challenges with a sense of assurance.
- Self-awareness: Successful managers are self-aware, understanding their strengths and weaknesses. This self-awareness allows them to leverage their strengths and seek support or development in areas where they may be less proficient.
Managers often face tough decisions and situations that require courage. Whether it’s addressing conflicts, making difficult choices, or taking calculated risks, successful managers exhibit courage in their leadership.
Maintaining an optimistic outlook, even in challenging situations, can be infectious. Positive managers can inspire and motivate their teams, creating a more productive and resilient work environment.
How to use your project management skills?
Understanding project management skills, in theory, provides a solid foundation, yet their true essence lies in the practical application within real-world projects.
Knowing about them is one aspect, but utilizing them effectively amid a project’s complexity and dynamism is where a project manager shines above the crowd.
For instance, a project manager adeptly employs their communication skills to establish a shared vision among team members and stakeholders.
However, that’s not all it entails to be an effective communicator. This skill also enables a project manager to steer the nuances of interpersonal dynamics, ensuring that diverse perspectives converge towards a unified goal.
In practice, this involves conducting productive meetings, actively listening to concerns, and articulating objectives in a manner that aligns everyone’s efforts.
Moreover, the strategic thinking of a project manager comes into play when they are required to alter their meticulously planned project roadmap to incorporate the change. This is where flexibility and adaptability become crucial.
A project manager’s ability to pivot seamlessly in response to unexpected challenges or changes in scope distinguishes exceptional project management. It requires calibration strategies, reassigning resources, and maintaining a steady hand to keep the project on course.
In a nutshell, proficiency in one skill over the other does not guarantee your success as a project manager. Whether you are a master of one skill or not, you have to be the jack of all trades.
The hallmark of exceptional project management lies not just in possessing these skills but in knowing where to use what is within the dynamic landscape of real-world projects.
Boost your project management skills with ProofHub
Success in any field often comes down to having the right tools to help you shine. When it comes to project management, getting it right to the “t” requires a lot of juggling between the aforementioned skills. Mastering these skills and truly making the most of them requires quality project management software that fits the bill.
This is where ProofHub comes in — a comprehensive project management and team collaboration software. It is not just your run-of-the-mill software loaded with overly complex features that might clutter the interface. Instead, it’s simple (like its pricing), customizable, and effective. Also, it’s not just about what it does, but how it helps you ace your game in project management.
Take task management, for instance. ProofHub is not just about ticking boxes. It provides you a task window with custom fields to set up tasks the way you need and communicate every aspect related to that task, making sure nothing slips through the cracks. Also, you get four different views to monitor the tasks.
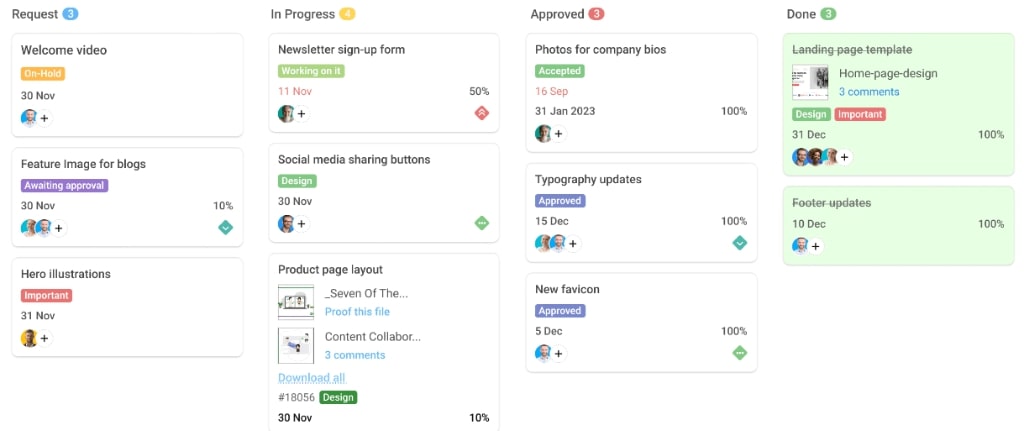
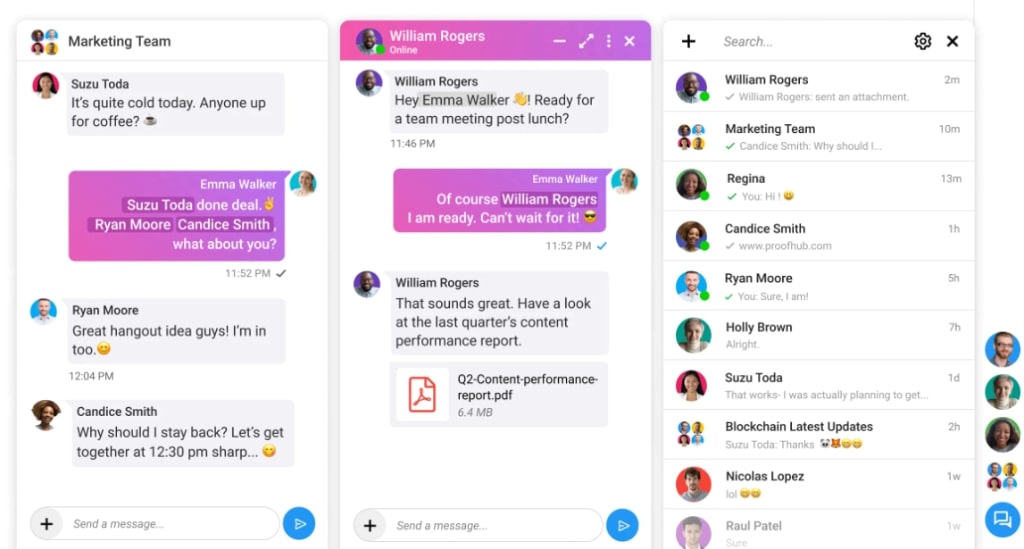
As I have mentioned in times before, smooth communication and collaboration are non-negotiable in effective project management.
ProofHub offers features like in-built chat, file sharing, real-time updates, and discussion boards, making sure all the information is centralized and available for quick access. Then there’s reporting and analytics.
Additionally, with robust reporting tools, you’re not just seeing what’s happening; you’re gaining insights.
All these features save you a lot of time and effort that you can utilize to enhance your project management skills. As a project manager, your work is to manage work. ProofHub helps you make sure it is getting done right, on time, and with the required quality.
Upskill your project management skills with a robust, customizable, and tailored suite of tools that empower your success!

